简介 #
GR & DR #
Routing is a critical yet complex phase in the implementation process of integrated circuits (ICs), often necessitating considerable time and effort. Given its complexity, the routing process is typically divided into two stages: global routing and detailed routing. Global routing, the initial stage, establishes coarse-grained wire paths for signal nets, thereby providing valuable guidance for the subsequent detailed routing stage, enhancing its efficiency. Detailed routing, on the other hand, focuses on identifying valid physical paths, primarily within the routing guides set by global routing, while taking into account design rule constraints
Routing is usually divided into global routing (GR) and detailed routing (DR) –cite–> C. J. Alpert, D. P. Mehta, and S. S. Sapatnekar, Handbook of Algorithms for Physical Design Automation. CRC press, 2008.
Routing is usually divided into global routing (GR) and detailed routing (DR) [2]. Global routing serves as a fast routing planning to generate guidance for detailed routing to reduce the search space of each net. Detailed routing then takes the guidance as input and finishes the physical wiring to connect pins in each net. Global routing is also used for routability estimation at early design stages like placement [3–9]. With growing design scales and complexity, it becomes increasingly challenging for global routing to resolve routing overflow within a short time. Therefore, the quality and efficiency of global routing is critical to design closure, as it impacts both its proceeding and succeeding design stages.
background #



输入 #

输出 #

优化指标 #

约束 #
- 线网连接正确性
- 布线障碍
- 版图设计规则 :金属线的最小宽度(min-width);金属线间及金属线与布线障碍间的最小线间距(min-spacing);一条金属线的最小面积(min-area),当金属线的宽度固定为最小宽度时 ,最小面积约束也被称作最小长度约束
Global Router #
概念 #

甚至不需要考虑大部分几何级问题 ,其布线模型的建模较为简单 ,即使在具有数以万计的区域的芯片版图上布线,也只产生较低的时间开销

routes every net with only two pins under design constraints turns out to be an NP-complete problem –cite–> M. Kramer and J. Van Leeuwen. The complexity of wirerouting and finding minimum area layouts for arbitrary vlsi circuits. Adv. Comput. Res, 2:129–146, 1984
term #
net order: 串行
OF: over flow
conjointly: 并行
guide: 在GR中就是布线通路,GR最终的输出结果
preferred routing direction : 比如第一层水平优先,第二层垂直优先
challenge #
advance GR are GPU-Accelerate-based now,main challenge are:
- GPU memory is limited
- This requires memory-efficient solutions that can minimize CPU-GPU communication while maximizing GPU utilization
- large designs have more nets with bigger routing graphs, providing many new parallelization opportunities that are not yet explored
技术方向 #
DP base-layer assignment
- CUGR, InstantGR
- start use GPU accelarate
RL-based
- slow
- 理论上DRV会很小
generative model
- such as: CNN-based, PRNet, Hub Router
- Actually, global routing is a combinatorial problem and can be formulated as a 0-1 integer linear programming (0-1 ILP) problem
- it is still NP-complete
另一种分类:来自 HeLEM-GR
grid models
2D
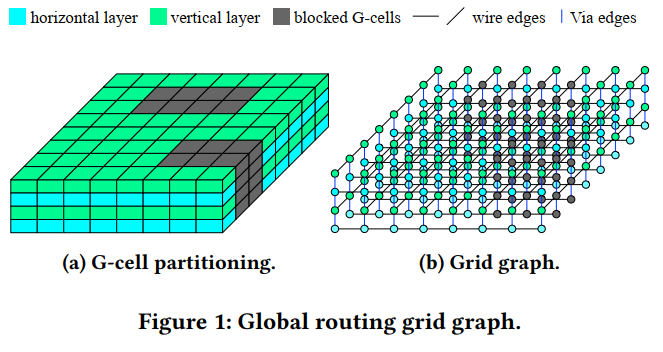
Many routers such as FastRoute 4.0 [10], BoxRouter 2.0 [11], NCTU-GR 2.0 [12], and SPRoute 2.0 [13] are based on 2D grids (a.k.a 2D routers), which perform layer assignment after routing all nets on the 2D space
3D
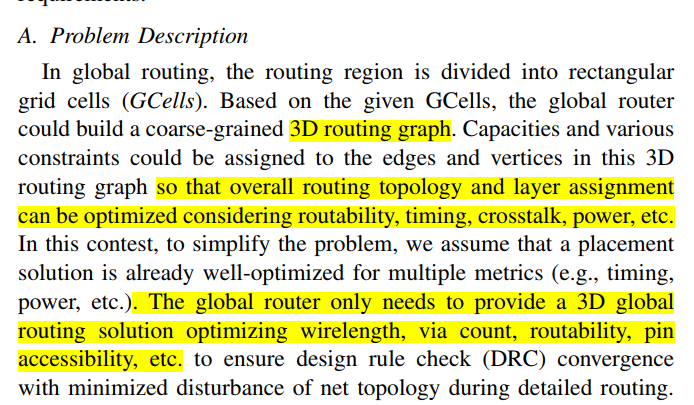
Other routers such as FGR [14] and CUGR [15] try to directly route on 3D grids to simultaneously determine the routing paths and layers for each net
hybrid
- generates initial routing results on 2D grids and then refines it on 3D grids.
- TritonRoute-WXL
routing kernels
- Lee’s algorithm [17] is the basic maze routing kernel in many routers, but it is very time-consuming.
routing schemes
问题建模 #
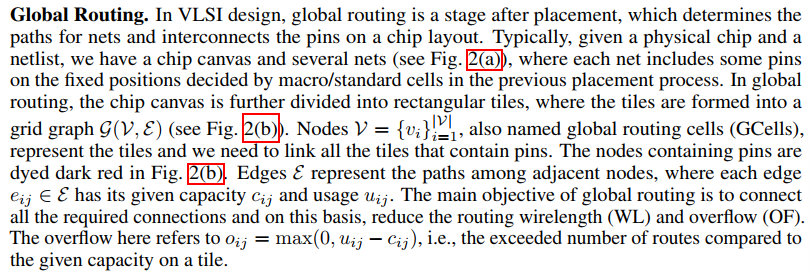
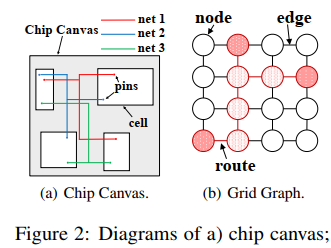
3d method:
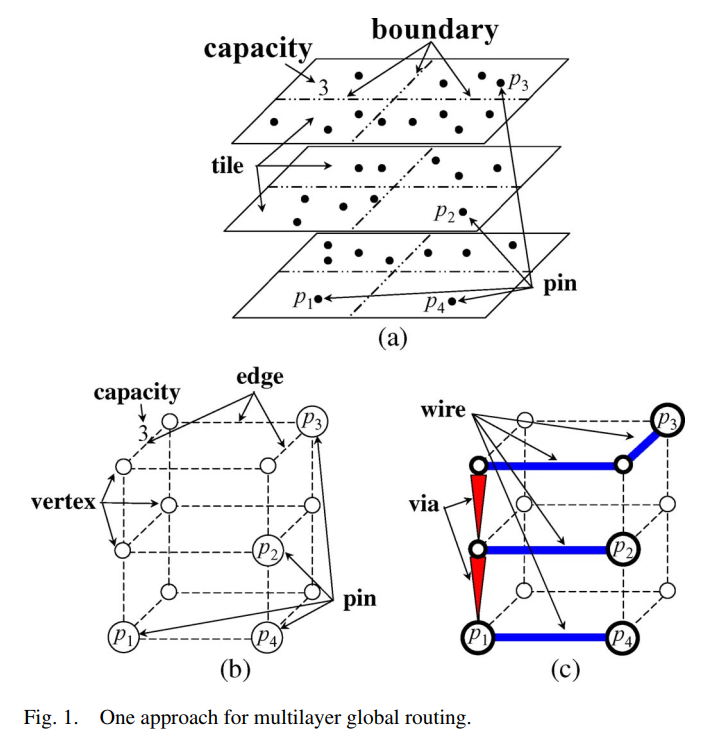
2D method:
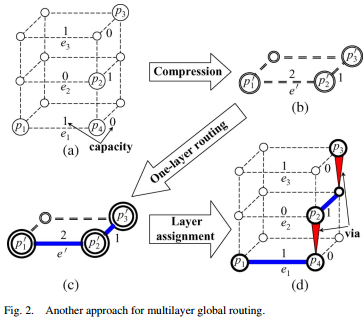

gcell 定义在.def 文件中



输入
输出
约束
优化指标
全局布线要在给定布线资源的情况下 ,优化线长、通孔数及关键线网时延等目标函数
线长、通孔数、溢出数量、运行时间
FasterRoute4.1 in OpenROAD #
结构 #
fastroute #
FastRouteCore #
vector<FrNet*> nets_;vector<StTree> sttrees_; // the Steiner treesrun()gen_brk_RSMT()- for (const int& netID : net_ids_)
rsmt= stt_builder_->makeSteinerTree(…)- Tree
tree= pdr::primDijkstra(x, y, drvr_index, alpha, logger_); - flute_->
flutes(x, y, s, accuracy)
- Tree
steinerTreeVisualization
getOverflow2Dmaze()getOverflow2DmazefluteNormal(rsmt)layerAssignment()StTreeVisualization()//2d or 3d
getOverflow2DrouteLAllconvertToMazeroute- // debug mode Rectilinear Steiner Tree before overflow iterations
SteinerTreeBuilder #
FrNet #
odb::dbNet* db_net_;vector<int> pin_x_;vector<int> pin_y_;vector<int> pin_l_;//layerfloat slack_;std::unique_ptr<std::vector<int>> edge_cost_per_layer_;void addPin(int x, int y, int layer)
StTree #
vector<TreeNode> nodes// The nodes (pin and Steiner nodes) in the tree.vector<TreeEdge> edges
TreeNode #
int16_t x, y; // position in the grid graph- int
nbr[3]; // three neighbors - int
edge[3]; // three adjacent edges
TreeEdge #
stt #
Flute #
initLUT()- 主要是读取.dat文件
flute()flutes()flutes_RDPflutes_ALLD
SteinerTreeBuilder #
unique_ptr<flt::Flute> flute_
Tree #
int deg; // degreeStTreeint length; // total wirelengthvector<Branch> branch; // array of tree branchesvoid printTree(utl::Logger* logger)const;int branchCount()const { return branch.size(); }
Branch #
int x, y; // starting point of the branchint n; // index of neighbor
odb #
dbNet
pdr #
- Tree
primDijkstra(const vector& x,const vector & y, const int driver_index, const float alpha, Logger* logger) - ListGraph
graph get_nearest_neighborsbuildSpanningTreesteinerizemakeTreemakeTreeRecursive
- ListGraph
lemon #
ListGraph #
CUGR #
cuhk-eda/cu-gr: CUGR, VLSI Global Routing Tool Developed by CUHK
install #
#还是在docker跑把,服务器上的boost版本总是搞不好。。。
apt update
apt install git
apt install vim
apt install build-essential
apt install -y build-essential gcc g++
apt install cmake
apt install -y libboost-all-dev
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
#yes, opt/miniconda3, yes
source ~/.bashrc
git clone https://github.com/cuhk-eda/cu-gr
cd cu-gr
scripts/build.py -o release
报错:
CMake Error at /usr/local/lib/cmake/Boost-1.80.0/BoostConfig.cmake:141 (find_package): Could not find a configuration file for package “boost_filesystem” that exactly matches requested version “1.80.0”.
The following configuration files were considered but not accepted:
/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake/boost_filesystem-1.74.0/boost_filesystem-config.cmake, version: 1.74.0 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/cmake/boost_filesystem-1.74.0/boost_filesystem-config.cmake, version: 1.74.0
Call Stack (most recent call first): /usr/local/lib/cmake/Boost-1.80.0/BoostConfig.cmake:262 (boost_find_component) /usr/local/share/cmake-3.24/Modules/FindBoost.cmake:594 (find_package) CMakeLists.txt:39 (find_package)
fix:
可以使用以下命令来查看系统上安装的 Boost 版本:
dpkg-query -s libboost-all-dev | grep Version # 对于 Debian/Ubuntu 系统
#如果您已经安装了 Boost 1.74.0,则需要升级到 Boost 1.80.0 版本。
tar -xvf boost_1_80_0.tar.bz2
cd boost_1_80_0
./bootstrap.sh
./b2
sudo ./b2 install
cmake -DBOOST_ROOT =/usr/local/
报错:
CMake Error: Invalid value used with –target Usage: cmake –build
[options] [– [native-options]] cmake –build –preset [options] [– [native-options]] Options: = Project binary directory to be built. --preset , --preset= = Specify a build preset. --list-presets = List available build presets. --parallel [ ], -j [ ] = Build in parallel using the given number of jobs. If is omitted the native build tool's default number is used. The CMAKE_BUILD_PARALLEL_LEVEL environment variable specifies a default parallel level when this option is not given. --target ..., -t ... = Build instead of default targets. --config = For multi-configuration tools, choose . --clean-first = Build target 'clean' first, then build. (To clean only, use --target 'clean'.) --resolve-package-references={on|only|off} = Restore/resolve package references during build. --verbose, -v = Enable verbose output - if supported - including the build commands to be executed. -- = Pass remaining options to the native tool. cmake --build build --target -- -j 6
fix:
scripts/build.py -o release -t iccad19gr#cu-gr, github 写的有问题
scripts/build.py -o release -t route#cu-gr2
run #
按照他说的,不过要自己把iccad19的benchmark放到toys/iccad2019c/下
FastRoute #
install #
#in a new ubuntu:22.04 container
apt install build-essential
apt install gcc
apt install libboost-all-dev
apt install cmake
apt install tcl-dev
apt install swig
apt install git
apt install bison
apt install flex
git clone --recursive https://github.com/The-OpenROAD-Project/FastRoute4-lefdef
cd FastRoute/
cmake .
make PARALLEL=nthreads
debug #
/root/FastRoute-master/third_party/OpenDB/include/opendb/ZInterface.h:38:10: fatal error: tcl.h: No such file or directory 38 | #include <tcl.h> | ^~~~~~~ compilation terminated.
#cmake 中加上以下两句
include_directories(/usr/include/tcl8.6)
link_directories(/usr/lib)
CUGR 2.0 #
InstantGR #
model #
database #
- layer
- db::net
database_cuda #
- cudb::net
flute.hpp #
- readLUT
robin_hood.h #
- 一个高性能的哈希表实现库
- 开源
- 这个库在高性能计算场景(如本项目的集成电路布线)中特别有用,因为它能提供更快的查找和插入操作,同时保持较低的内存占用。
- 主要优势:
- 比标准库的 std::unordered_map 性能更好
- 内存使用更高效
- 缓存友好的设计
- 开放寻址法解决冲突
- 支持异构查找
flow #
开启时钟
program_start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();read input files
read()- 输入:
cap_file_name[]: 容量文件的路径
net_file_name[]: 网络文件的路径
- 输出:
代码将读取的数据存储在类的成员变量中:
layers[]: 存储每层的信息
capacity[][][]: 3D数组存储容量信息
nets: 存储所有网络信息
其他相关的网格和坐标映射信息
readLUT("POWV9.dat", "POST9.dat")build_cuda_database()cuda相关变量初始化先处理单pin的net(有一些两个pin重叠,二维变成单个pin)
设置两个核函数cuda共享内存大小
cudaFuncSetAttribute具体有什么用?
对非单Pin的net(
nets2route)进行FLUTE建立MSRTFLUTE:
- net.
construct_rsmt()- my_flute(unordered_set
&pos)` - flute::
flute(cnt, x.data(), y.data(), 3);
- flute::
- my_flute(unordered_set
最后处理得到水平和垂直segments
- net.
sort, 对非单Pin的net(nets2route)进行根据hpwl从小到大排序generate_batches_rsmt(nets2route)sort, 对每个batch根据net数量从小到大排序 //这个有什么用?
可以问问
根据
sort后的batches,重新对每个net依次排列到nets2routeDFS获取DAG图:
Routing DAG,得到一个segment排序
对每一个batch, 开启L_shape
Lshape_route_cuda<<<BLOCK_NUM(batches[i].size()), THREAD_NUM>>> (batches[i].size(), batch_cnt_sum[i], node_cnt_sum, nodes, par_nodes, dist, from, layer_range, global_timestamp);
install #
compile directly
debug #
contest #
ISPD 07 #
ISPD 08 #
ICCAD 19 Contest Problem C: GR use Real world design and evaluate by DRouter #
也给了后端详细布线器DrCu,和用于评估结果的脚本
用的 ISPD2018/19 的数据


输入:
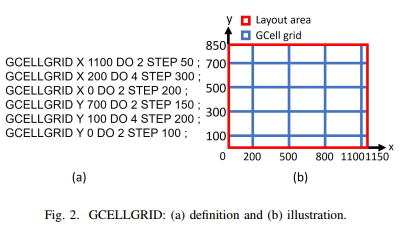
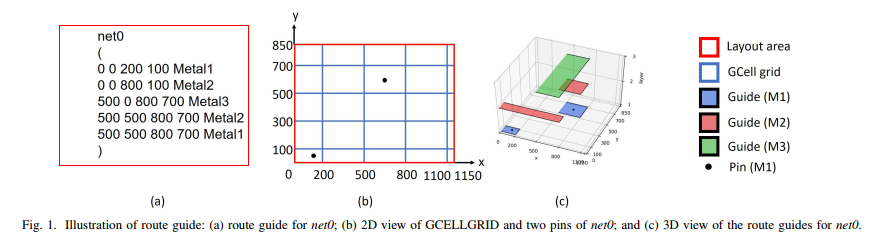
输出:
ispd24的比赛是要via的

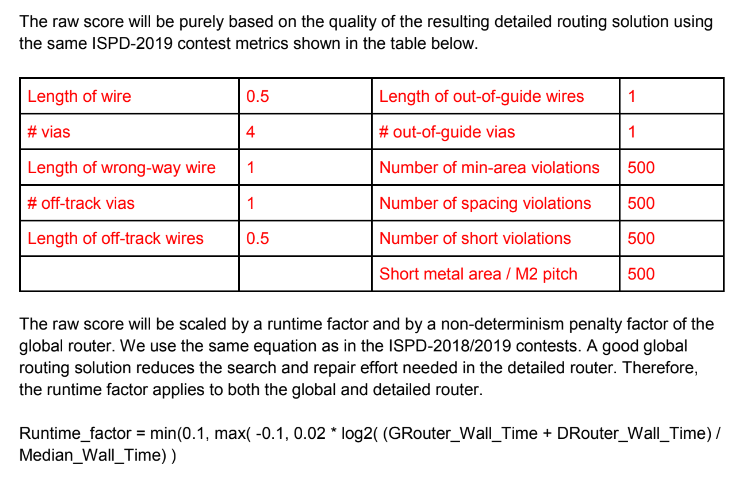
evaluate:
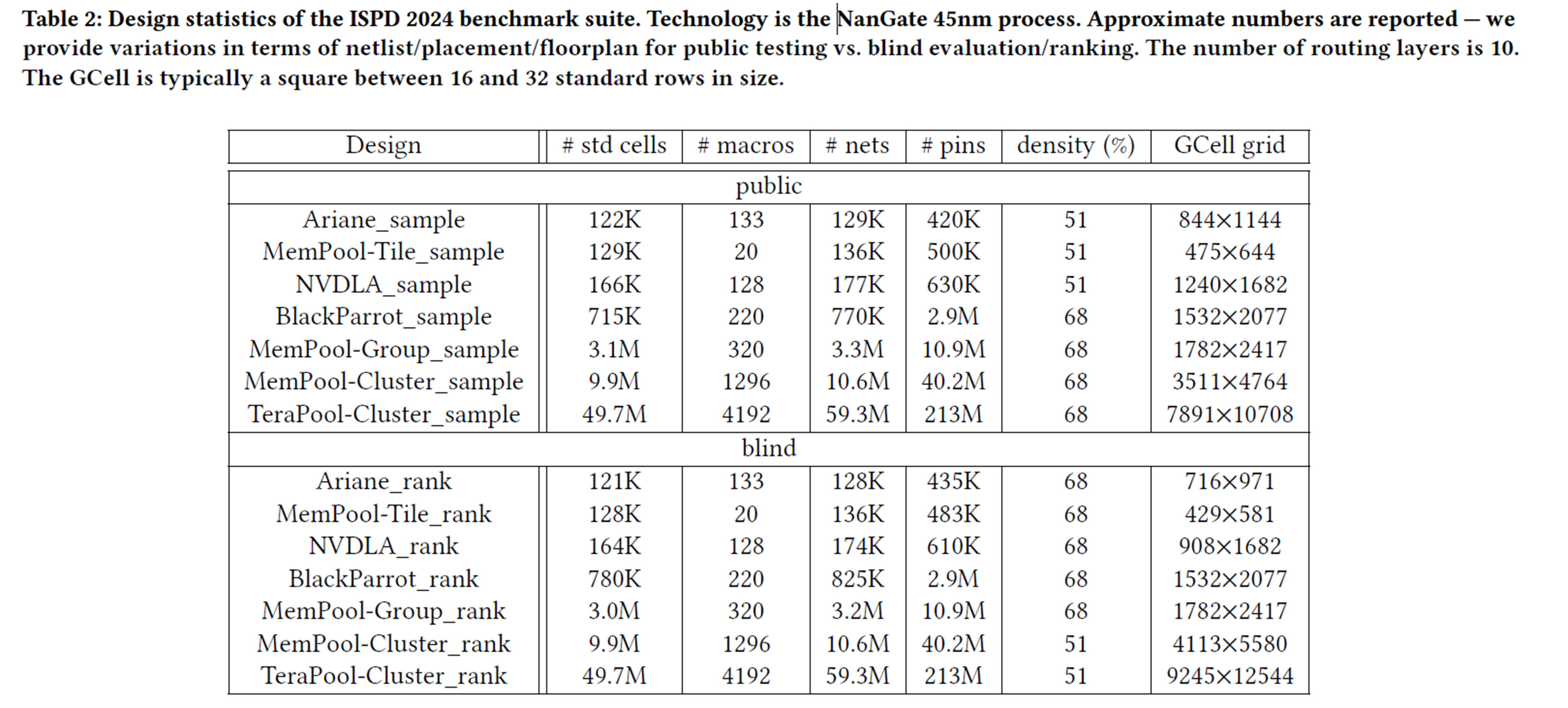
ISPD’24 Contest: GPU/ML-Enhanced Large Scale Global Routing Contest #
background:
data
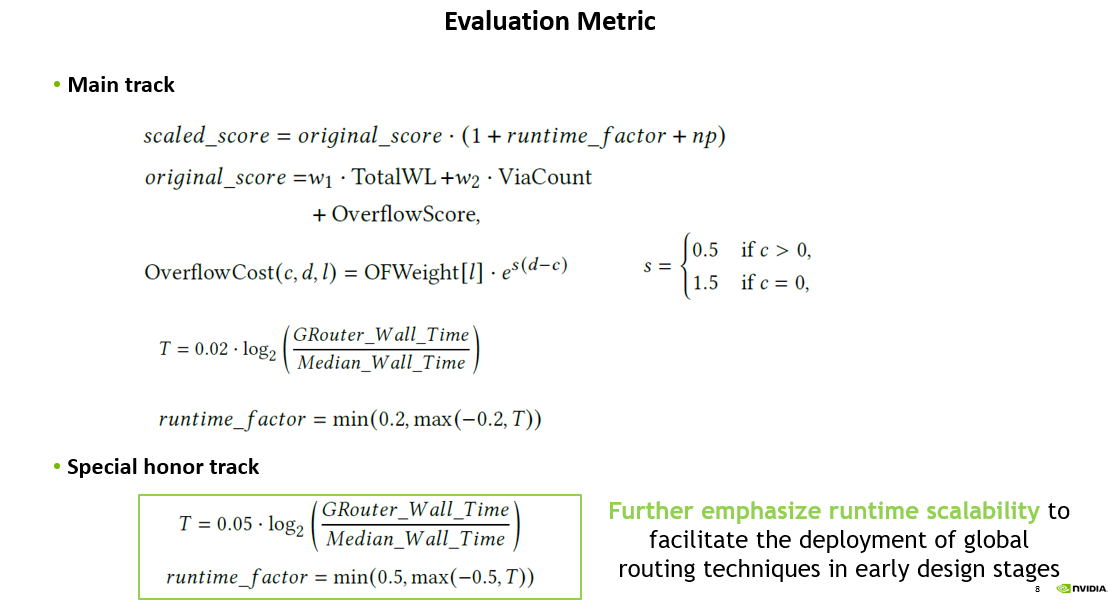
evaluate:
和 ICCAD19 很像
scale 越大权重越大
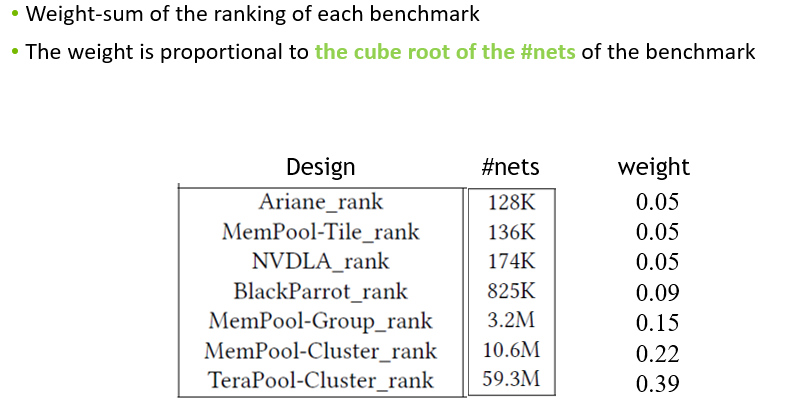
限制:
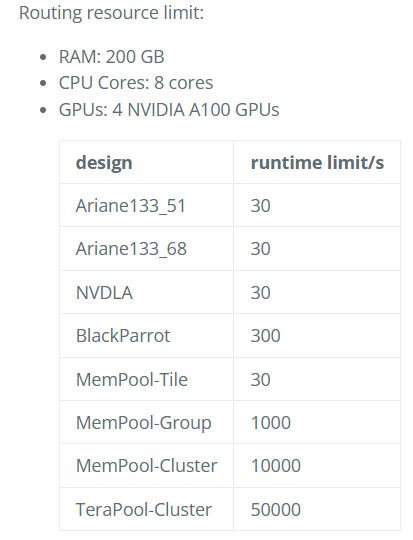
最好结果:
越小越好
| design | WL cost | via cost | overflow cost | raw score | runtime /s | median runtime /s | scaled score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane133_51 | 9335109 | 3060400 | 10369862 | 22765372 | 4 | 11 | 22100882 |
| Ariane133_68 | 9443754 | 2981836 | 7825647 | 20251238 | 8 | 12 | 20014313 |
| BlackParrot | 58347098 | 19740536 | 35450029 | 113537664 | 27 | 70.5 | 110393434 |
| Nvdla | 21345766 | 4630872 | 23933347 | 49909986 | 4 | 20 | 47592238 |
| MemPool-Tile | 8407884 | 3425828 | 3569040 | 15402753 | 3 | 10 | 14867672 |
| MemPool-Group | 262817992 | 76146200 | 70345580 | 409309772 | 81 | 375 | 391210938 |
| MemPool-Cluster | 1094650057 | 268335040 | 300359611 | 1663344708 | 478 | 2048 | 1593513066 |
| Tera-Cluster | 12190406272 | 1542639724 | 6705414754 | 20438460750 | 4310 | 4584 | 20402113329 |
issue:
ISPD25 Contest: Performance-Driven Large Scale Global Routing #
Background #
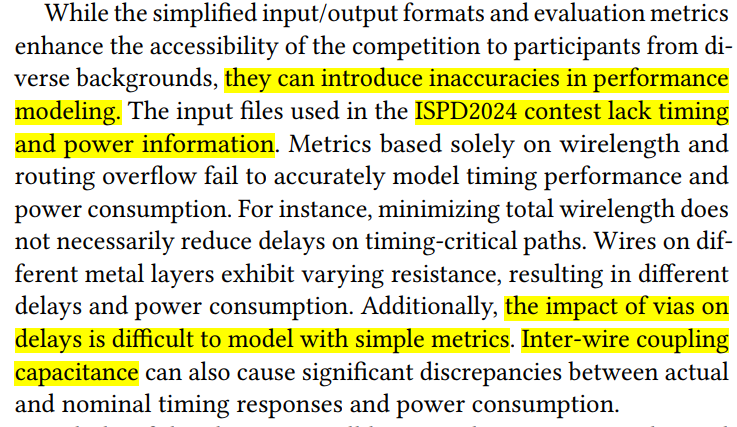
ISPD2024 竞赛虽然简化的输入/输出格式和评估指标提高了来自不同背景的参与者对比赛的可访问性,但它们可能会在性能建模中引入不准确性。ISPD2024 竞赛中使用的输入文件 缺少时序和功率信息。仅基于带宽和路由溢出的指标不能准确地模拟定时性能和功耗。例如,最小化总长度并不一定会减少时间关键路径上的延迟。Wires on different metal layers exhibit varying resistance, resulting in different delays and power consumption. Additionally, the impact of vias on delays is difficult to model with simple metrics. Inter-wire coupling capacitance can also cause significant discrepancies between actual and nominal timing responses and power consumption
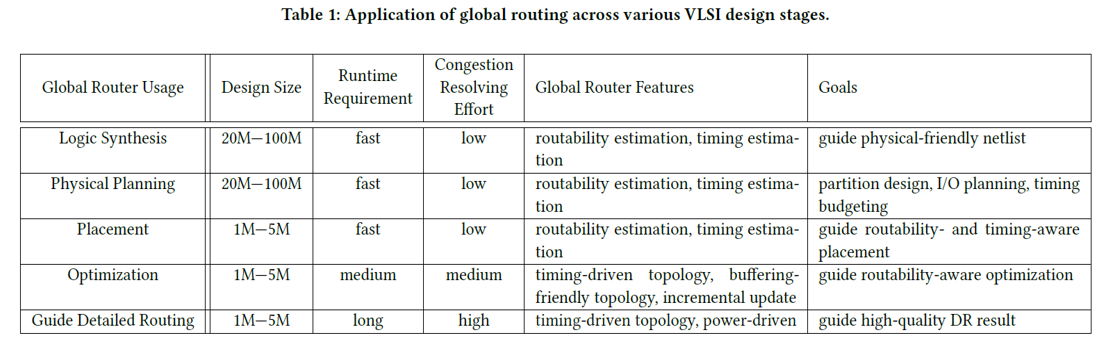
Problem Formulation #
In global routing, a 3D routing space is defined using global routing cells (GCells), created by a regular grid of horizontal and vertical lines. This configuration results in the formation of a grid graph where each GCell is treated as a vertex and edges connect adjacent GCells within the same layer (GCell edges) or between GCells in neighboring layers (via edges). The global router needs to establish a concrete path for each net within the grid graph and optimize the routability, timing and power.
For each testcase, the global router starts with a placed design, and generates a global routing solution. The global routing solution is evaluated by OpenROAD, which reports timing, power, and routing congestion. Additionally, the runtime and memory efficiency of the global router are critical factors.
文件 #


输入
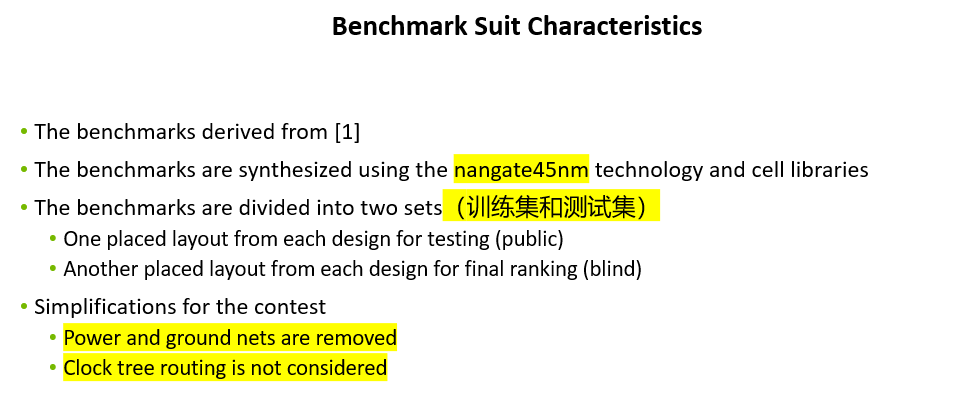
For each testcase, two sets of input files are provided: industry-standard files and simplified files.
The industry-standard files include DEF, LEF, LIB, and SDC files. The DEF file contains definitions for CORE, ROW, TRACKS, and GCELLGRID, along with placed COMPONENTS and unrouted NETS. Similar to the
ICCAD2019 global routing contest, GCells are specified using the definition from the DEF GCELLGRID section. The LEF file includes MACRO definitions and technology information. The LIB files offer timing and power data for library cells, while the SDC files provide timing constraints. These files serve as the raw input, allowing contestants to perform the most accurate routing resource and performance modeling.
For each circuit, we also provide a set of simplified input files, which include a routing resource file (with a .cap extension) and a net information file (with a .net extension). The routing resource file follows the same format as used in the ISPD2024 contest, while the net information file is an extended version of the one used in ISPD2024. The routing resource file offers a detailed representation of the GCell grid graph and its available routing resources. The net information file provides the access points for all the pins within each net, along with the pin names and pre-routing stage slack estimates. These slack estimates provide a rough timing view of the circuit and enable contestants to perform net-based timing optimization. The simplified input files enable contestants to quickly engage with the contest and facilitate framing global routing challenges as mathematical optimization problems.
输出
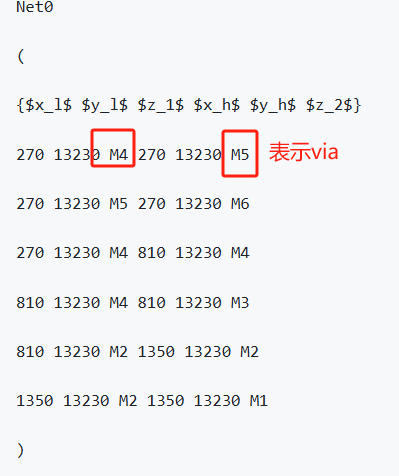
镜像使用:
docker run -it ispd25:latest /bin/bash #启动
Detail Router #
概念 #




问题建模 #
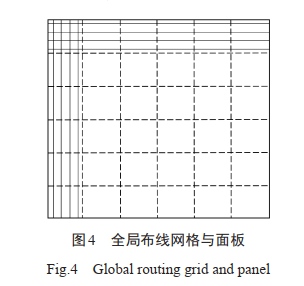
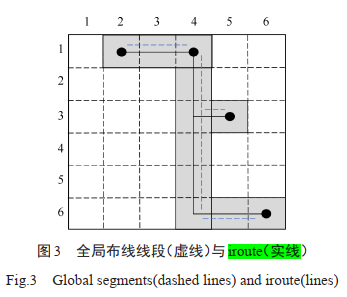
Contest #
ISPD-2018 #

ISPD-2019 #

算法 #
最小树算法 #

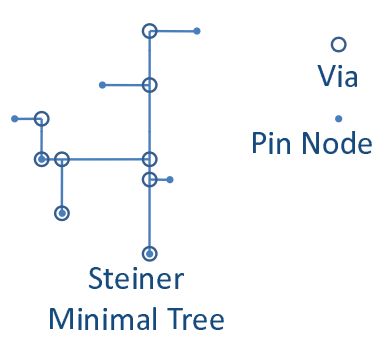
- 矩 形 最 小 斯 坦 纳 树(rectilinear steiner minimal tree,RSMT)
一般会先基于 Pin 生成最小树,分解最小树为 2-Pin(两端口) wire 然后再进行后续处理
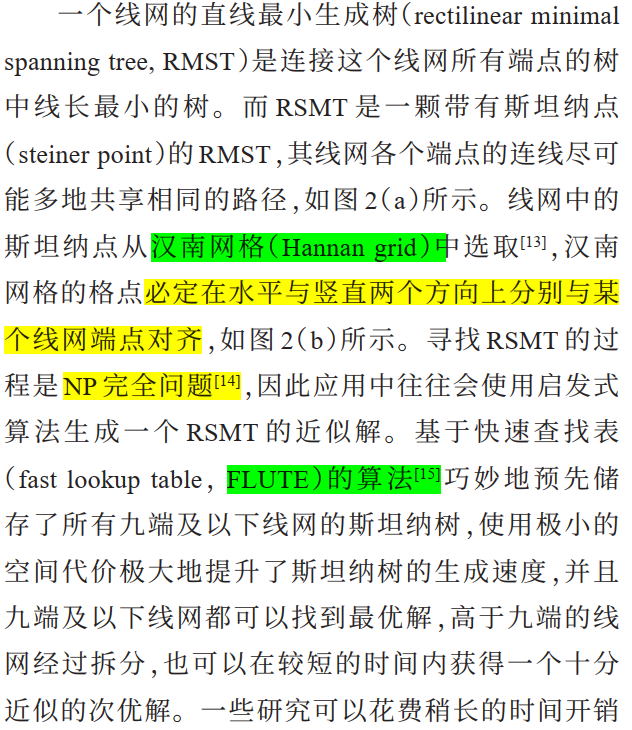


RSMT 和 RMST 的区别
在图论和计算几何中,RSMT(Rectilinear Steiner Minimum Tree)和 RMST(Rectilinear Minimum Spanning Tree)是两种不同的树结构,主要用于解决不同类型的最小树问题。以下是它们之间的主要区别:
1. 定义 #
- RSMT(Rectilinear Steiner Minimum Tree)
- RSMT 是一种最小生成树,允许在树中添加额外的点(称为 Steiner 点),以减少连接给定终端(节点)所需的总边长。RSMT 的目标是最小化连接所有终端的总路径长度,使用的是矩形距离(L1 距离或曼哈顿距离)。
- RMST(Rectilinear Minimum Spanning Tree)
- RMST 是一种最小生成树,连接给定的终端节点,但不允许添加额外的点。RMST 的目标是找到连接所有终端的最小边长树,同样使用矩形距离。
2. 额外点的使用 #
- RSMT 允许在树中添加额外的 Steiner 点,这些点可以帮助优化路径,减少总边长。
- RMST 仅使用给定的终端节点,不允许添加额外的点,因此可能会导致较长的连接路径。
3. 应用场景 #
- RSMT 通常用于更复杂的网络设计问题,例如 VLSI 设计和电路布局,其中需要优化连接以减少布线长度和提高效率。
- RMST 更常用于简单的网络连接问题,适用于需要在给定节点之间建立最小连接的场景。
4. 计算复杂性 #
- 计算 RSMT 通常比 RMST 更复杂,因为需要考虑如何有效地选择 Steiner 点以优化树的结构。
- RMST 的计算相对简单,因为只需连接给定的终端节点。
相关文献

FLUTE #
介绍 #
问题阐述
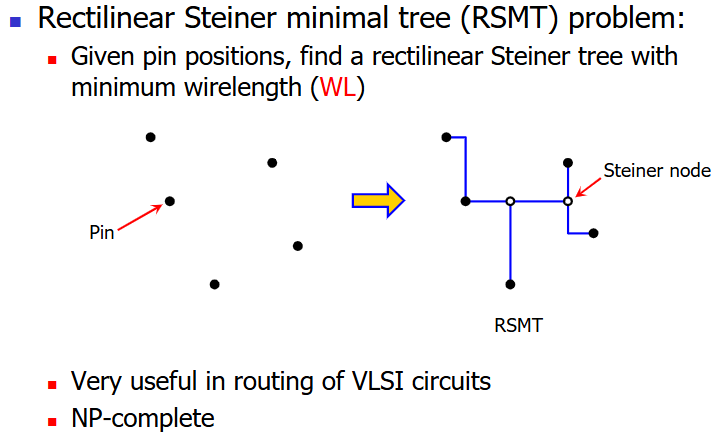
- 一个常见的steiner tree算法
- 9端最快,9端一样也是次优解
- 基于查找表
- 诞生与2004 ICCAD, ISPD 05 和 TCAD 07 有相关优化
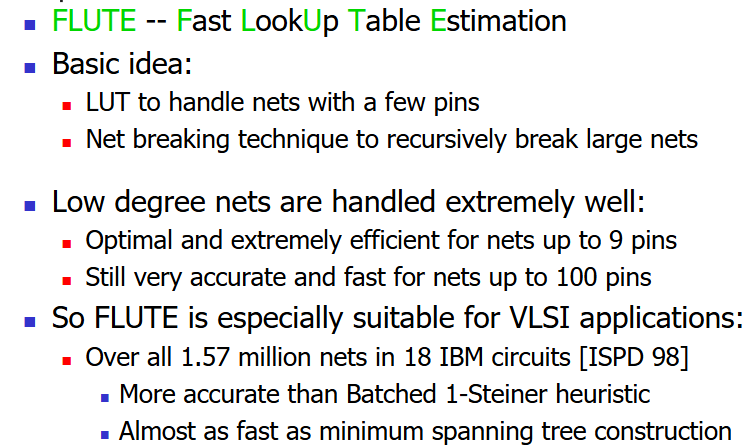
版本信息

基本定义 #
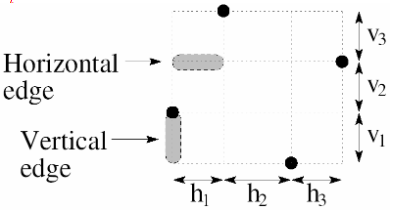
Degree
Degree of a net is the number of pins in it
Hanan grid
只考虑节点是4个方向
WL
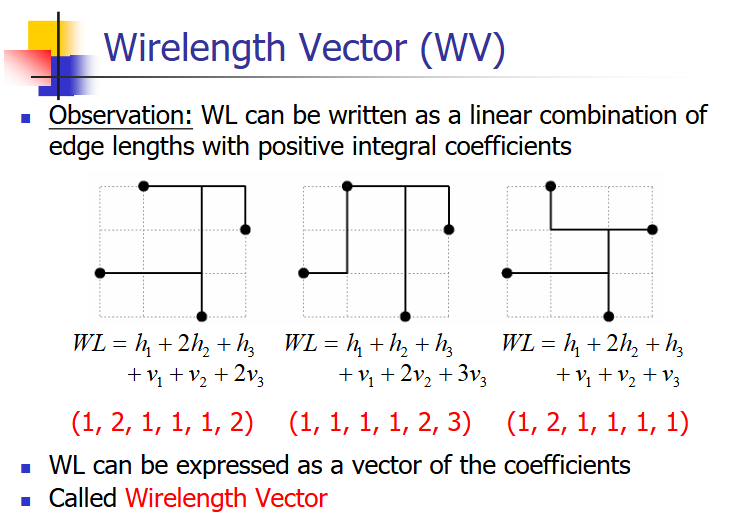
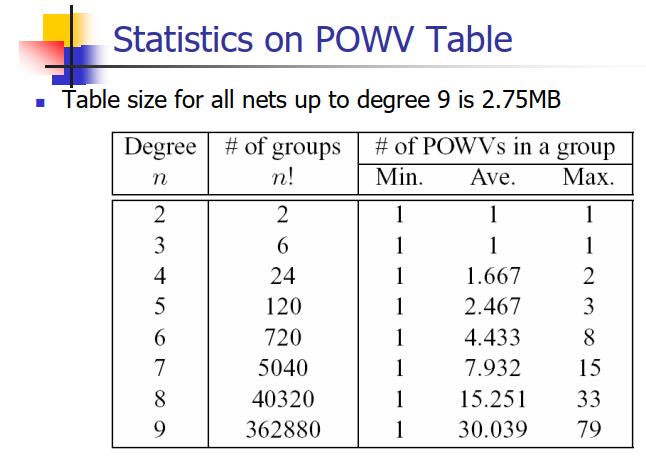
POWV

使用WV的好处

position sequence
y方向是1~4
position sequence从x=0开始数
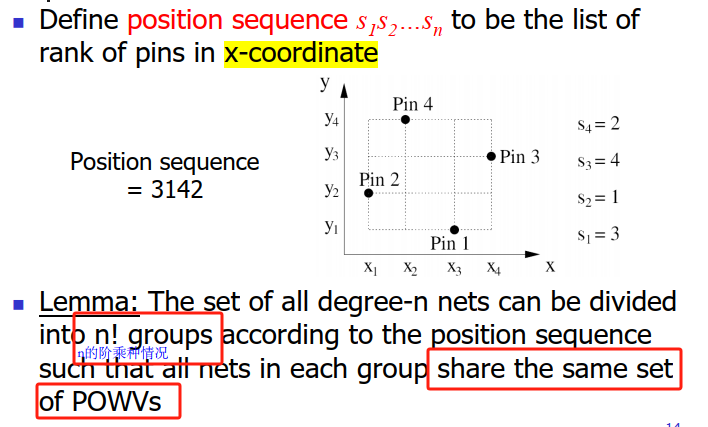
flow #
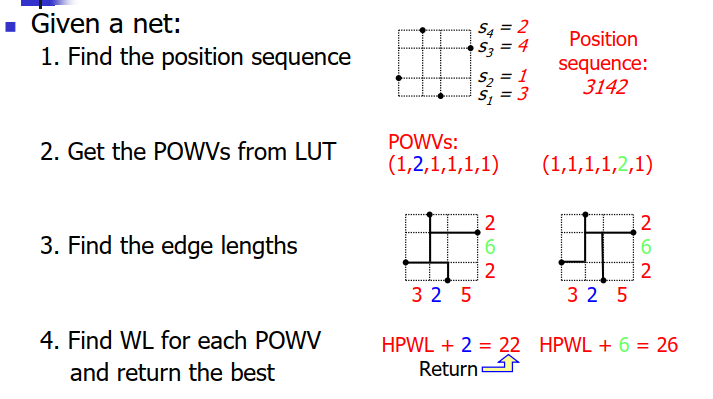
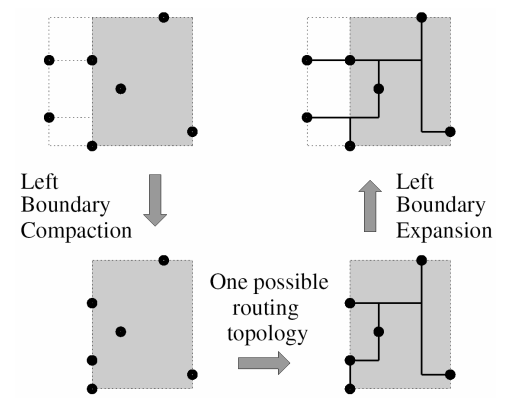
POWVs Generation : boundary compaction #


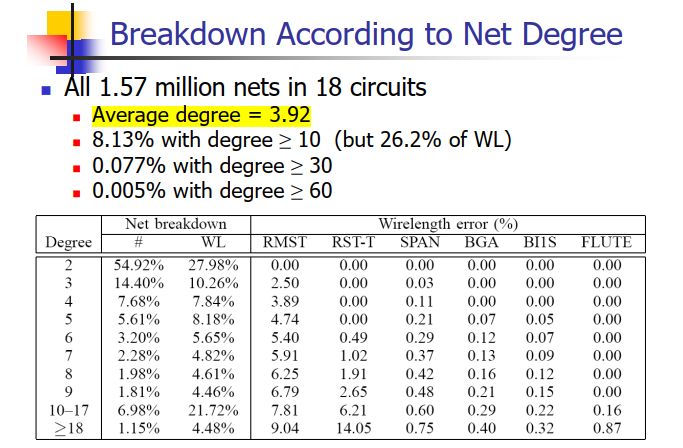
Net Breaking for High degree Net
For nets with degree > D, recursively break net until degree <= D

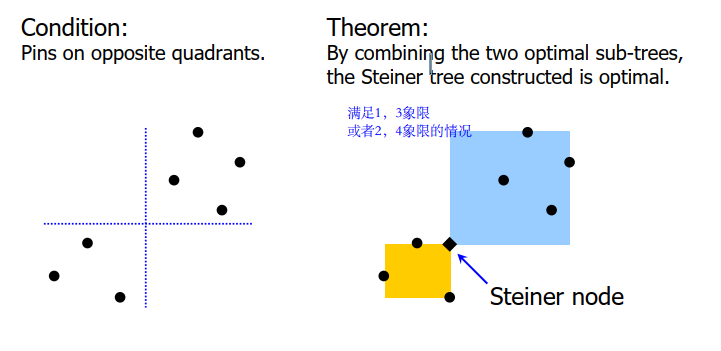
第一步
查看满足1,3象限 或者2,4象限的情况
还不能拆成9degree以下的话,使用Net Breaking Heuristic:
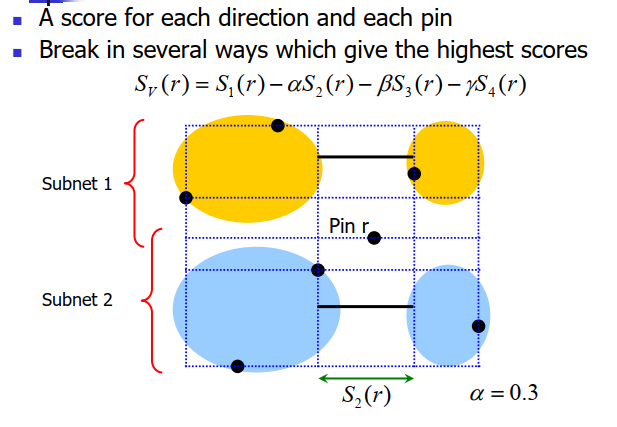
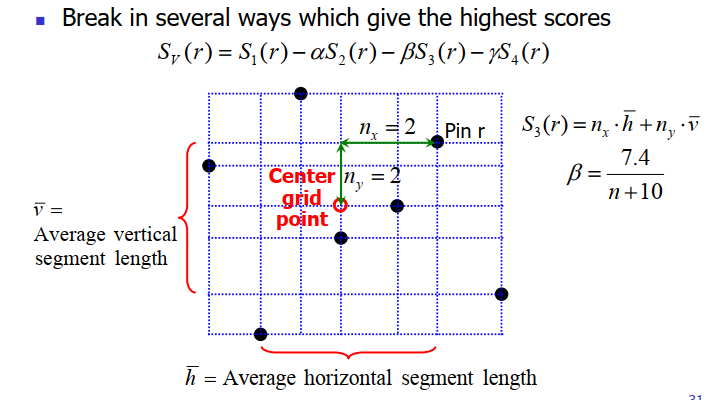
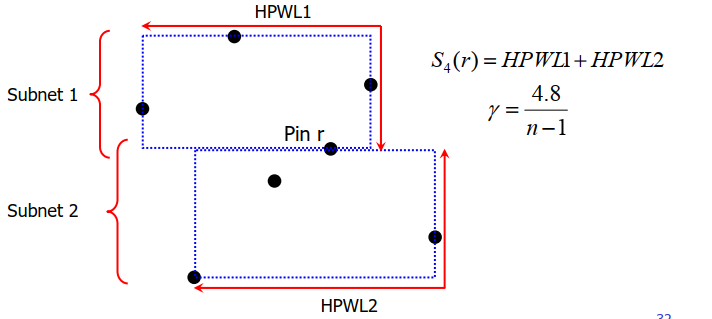
A score for each direction and each pin:
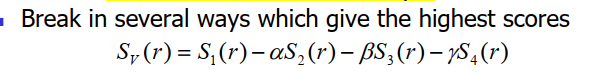
for Pin_r in Net:
S1:
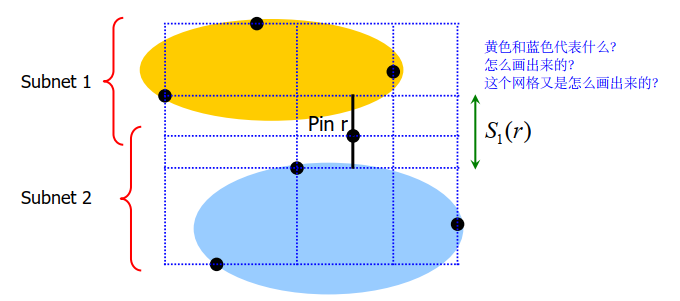
S2:
S3:
S4:
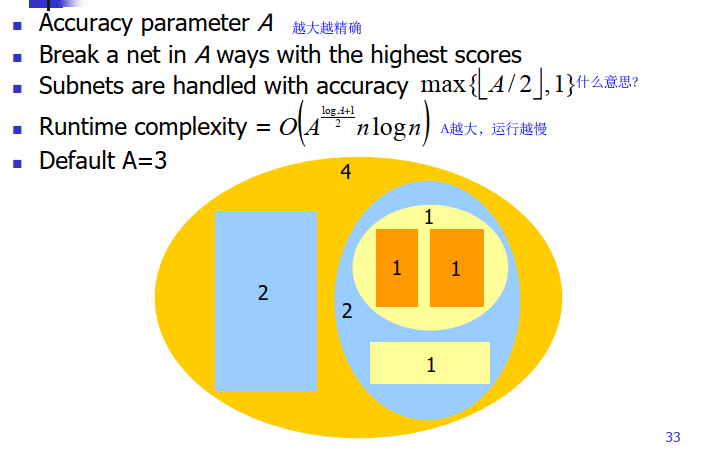
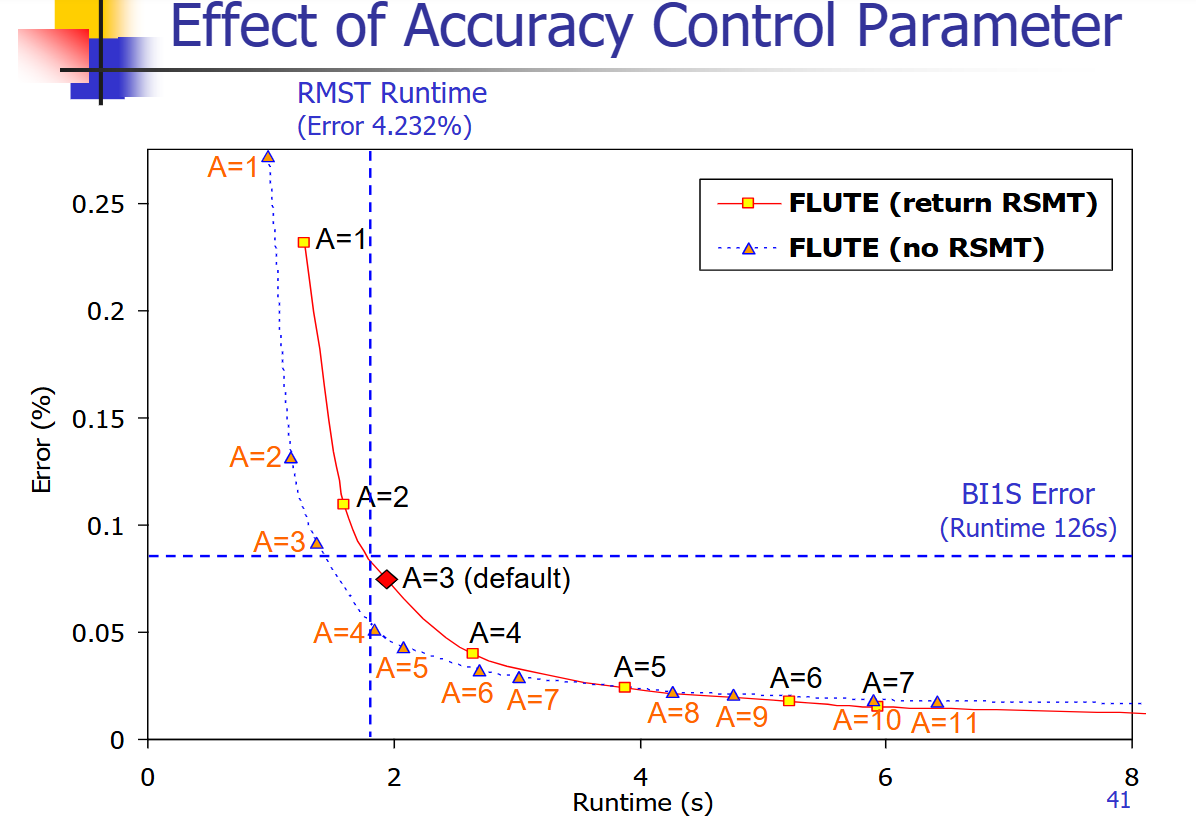
Accuracy Control Scheme #
文件介绍 #
flute.[ch]
查找表
- POWV9.dat – The lookup-table of optimal POWVs up to degree 9.
- POST9.dat – The lookup-table for optimal Steiner tree up to degree 9. (Note that it is formerly called PORT9.dat.)
TCAD 07 有相关优化(net breaking and merging techniques)
- flute_mst.c – The net breaking and merging techniques described in the VLSIDAT 08 paper.
- dist.[ch], dl.[ch], err.[ch], heap.[ch], mst2.[ch], neighbors.[ch], global.h – Utility functions used by flute_mst.c
evaluate
- flute-net.c – A program to evaluate the wirelength of a net. It takes input from stdin as a list of points.
- rand-pts.c – A program to generate a list of random points.
bookshelf
- flute-ckt.c – A program to find FLUTE and half-perimeter wirelength of a circuit in bookshelf format.
- memAlloc.[ch] – Functions for flute-ckt.c to allocate memory.
- ibm01/ibm01.* – ibm01 bookshelf files that can be read by flute-ckt.c
实验结果 #
模型 #
输入
结构
输出
参考 #
模式布线 #

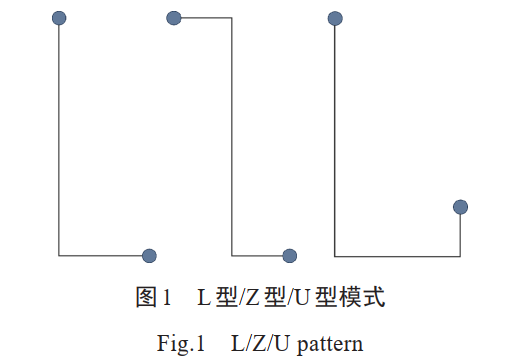

单调

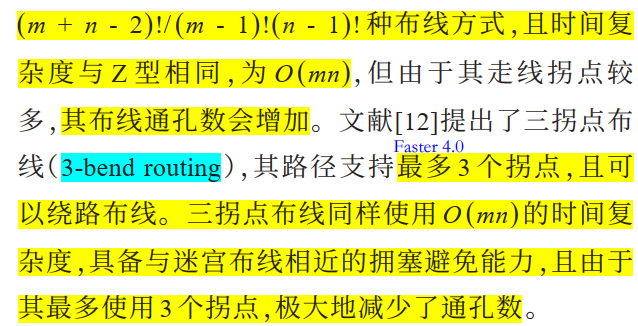
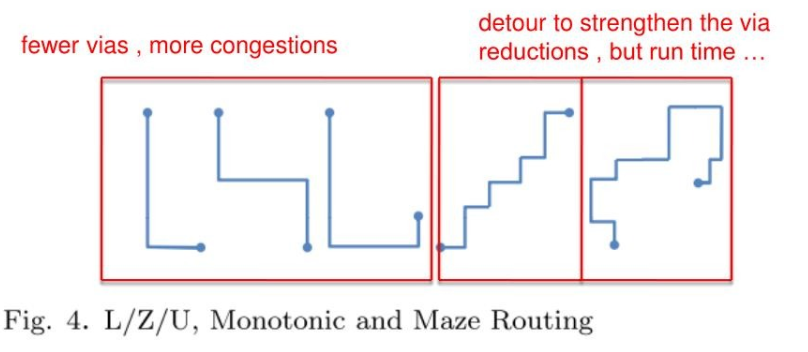
FastRoute 4.0 的 3-bend Routing
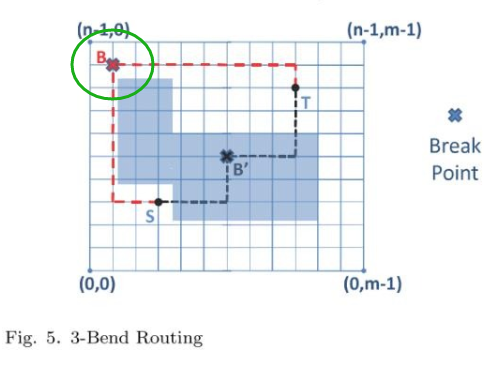
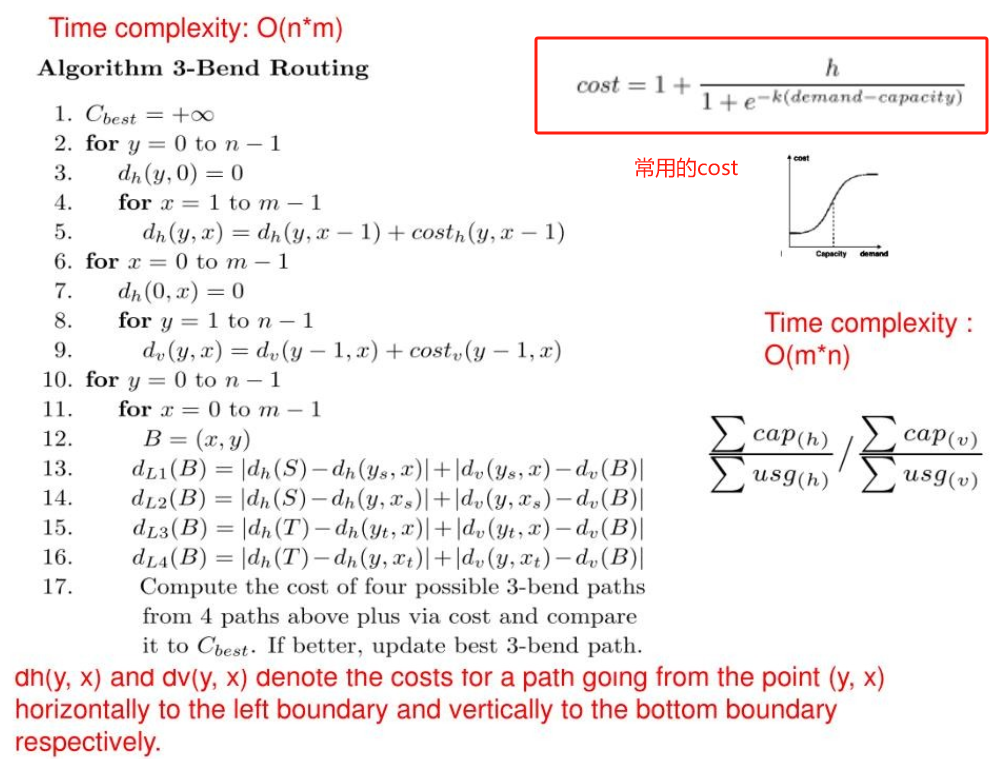
迷宫算法 #
概念 #

李氏算法 #
有点像 BFS
A*算法 #




往往是串行的,慢
往往需要多个 pin 的连线拆成一对一对,导致:

线搜索算法 #

Hetzel 算法
pattern + maze #

线序选择 #
对于串行布线算法, 布线顺序对最终布线质量的影响很大


以上几种启发式的线序选择策略往往不能完全避免溢出。拆线重布(rip-up and reroute) 策略在初次布线完成后 ,对发生溢出的拥塞区域的线网进行拆除 ,并迭代地 调整线序多次重新布线 ,直到溢出不再减少 ,或达到运行时间限制为止。
拆线重布 #
rip-up and reroute



层分配 #
并行布线算法 #
整数线性规划 #



线性规划 #

数据集 #
文件定义 #
