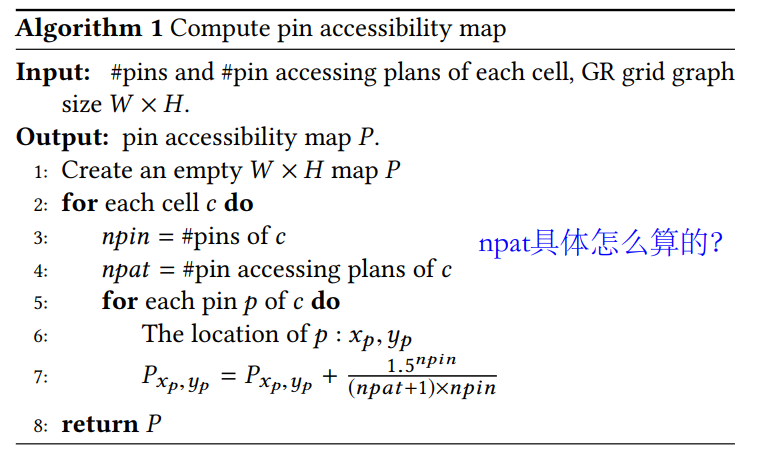
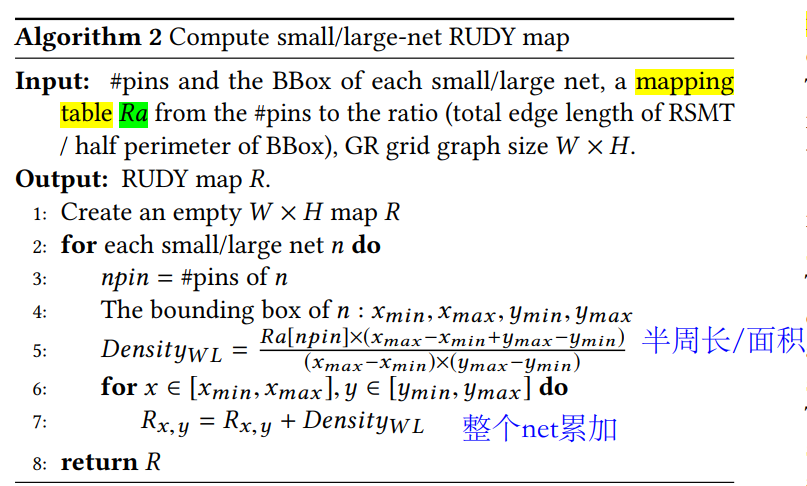
研究背景 #
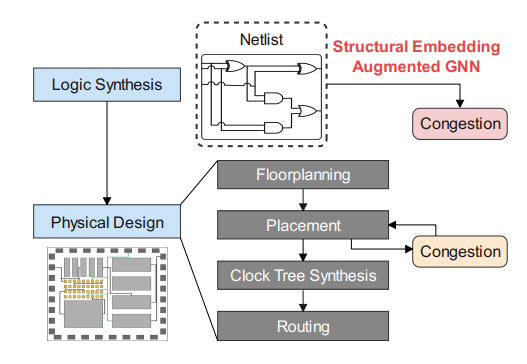
**典型的芯片设计流程是先做前端、后端设计,再去验证性能、功耗和面积。**但由于流程太长,在前端设计的时候,无法保证后端设计的效果,所以很多时候需要进行跨环节建模,在早期设计环节预测后续环节的求解质量,这当中就很适合AI算法来进行辅助。
除了建模之外,另外一个关键问题是优化。EDA中经常要求解各种各样的组合优化问题。这些问题往往是 NP难题,比如经典的旅行商问题。传统上,我们会通过一些启发探索的方法来求解。但随着规模不断增大、设计约束越来越多,这种探索往往遇到效率瓶颈,所以我们需要通过机器学习技术进行辅助,寻找有效策略,提高效率。

难点 #
- 大图–>
- 数据集–>
- 泛化能力–>
- 非DAG?
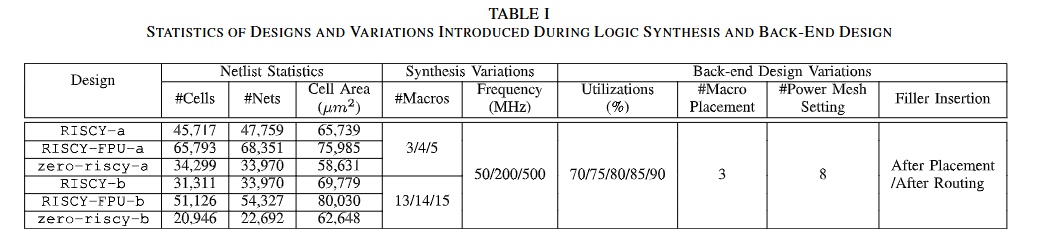
- route: 3D,45°,30°
- 先进的工艺:7nm
- 很多Placer and Router还是有很多人工定义的超参数?(不general)
- 现在真的还有必要把Router分成Global 和Detail 吗?
- GR: total maze routing
- GR: Consider timing and power consumption
研究方向 #
Cross-Stage Prediction #
routing congestion prediction #
background #
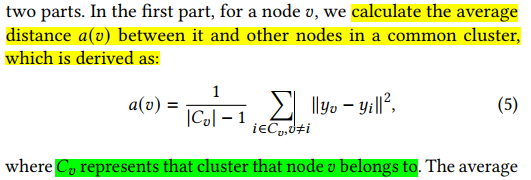
Routing congestion can overwhelm routing resources and lead to low cell utilization and routing detours
congestion is not known accurately until late in the design cycle, after placement and routing.
Many modern placement and synthesis tools leverage congestion estimation in their cost analysis in order to minimize the effects of congestion in the final physical design

It is known that the total net length can be a good proxy for congestion
A simple approximation for congestion prediction is to use the size of the local neighborhood
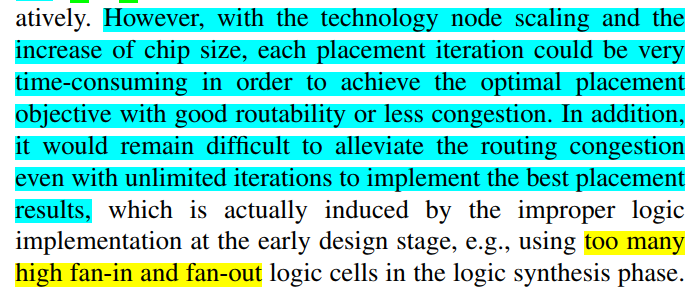
和fan-in, fan-out强相关
Precise congestion prediction from a placement solution plays a crucial role in circuit placement
Multiple previous works have attempted to predict detailed routing congestion in the placement step in an effort to optimize routability of the placement solution: RUDY, POLAR 2.0. All these techniques are implemented in the placement step and need the position information of cells .
To avoid the high computation cost of placement, it is more useful to be able to predict congestion in the logic synthesis phase.
congestion prediction problem can be frame as node regression problem
with the growth of circuit scale and complexity, time consumption tends to be unacceptable when utilizing a global router in the placement cycle to obtain the congestion map.
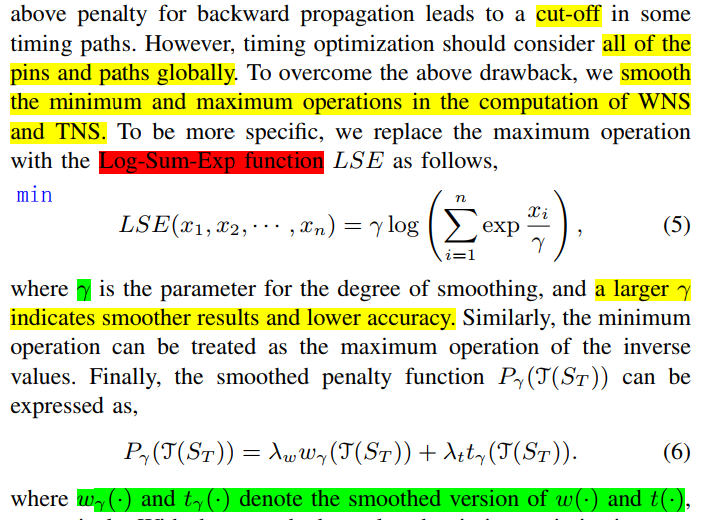
Current machine learning models commonly follow a two-phase workflow. First, based on domain knowledge, human experts generate various local features on the circuit using predefined functions on netlist. Then, based on the generated features, a specific model, e.g. convolution neural network (CNN) model is designed to predict either the routing demand map or the congestion map
the emergence of Graph Neural Network (GNN) triggered applications of undirected homogeneous graphs models on routing congestion prediction, since a VLSI circuit can be naturally represented by a graph
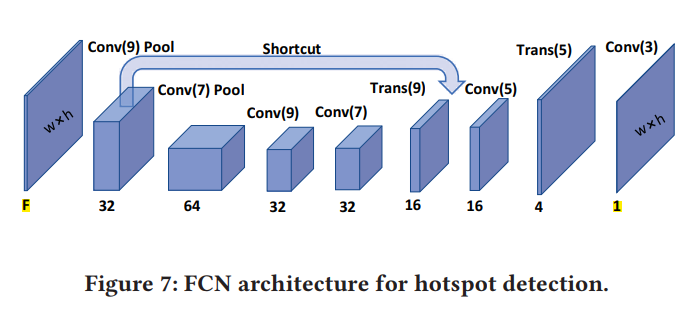
RouteNet-DRC Hotspot Prediction-ICCAD-2018-CNN #
background:
Every chip design project must complete routing without design rule violation before tapeout. However, this basic requirement is often difficult to be satisfied especially when routability is not adequately considered in early design stages.
In light of this fact, routability prediction has received serious attention in both academic research and industrial tool development. Moreover, routability is widely recognized as a main objective for cell placement
CNN and Transfer Learning
- CNN learns more abstract patterns from images
- Our RouteNet transfers such state-of-the-art ability in image pattern recognition to circuits for capturing the patterns about routability. RouteNet predicts routability based on a pretrained ResNet architecture
- Fully Convolutional Network (FCN): outputs an image with size equal to or smaller than input. many FCNs have both deep and shallow paths in one network.
RUDY(Rectangular Uniform wire DensitY)
- 它被用作我们RouteNet的输入特征,因为它与路由拥塞部分相关,获取速度快,可以直接表示为与RouteNet相吻合的图像
challenge of macros
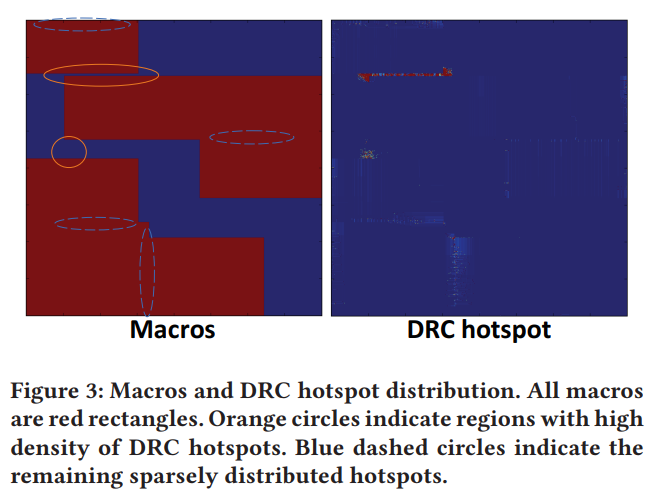
- The orange circles in Figure 3 indicate a strong tendency for hotspots to aggregate at the small gap between neighboring macros
- Blue dashed circles indicate the remaining sparsely distributed hotspots
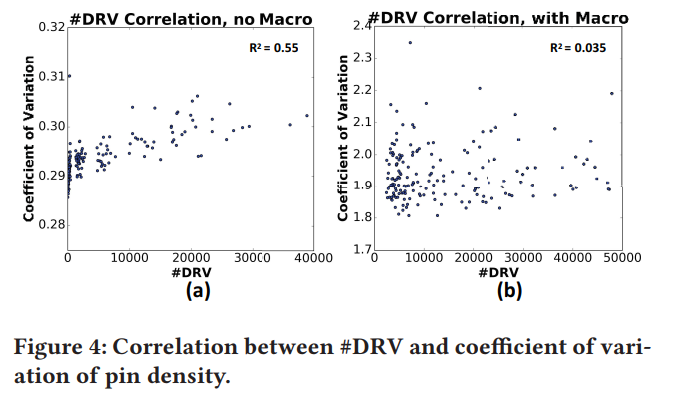
- 有macro,线性程度低
task:
- predict overall routability (DRC count), 分类任务,预测总的#DRV
- predict
DRC hotspotlocations.DRC hotspots mean the specific locations with high density of DRVs. like an end-to-end object detection task, which is more difficult to solve. GCell内#DRV超过设定值则为DRC hotspot
contribution:
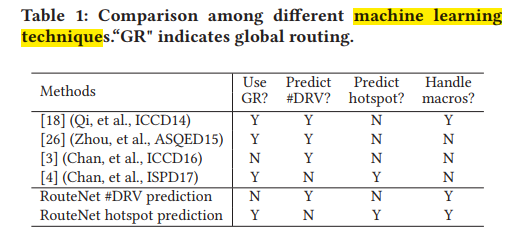
- mixed-size macros
- first systematic study on CNN-based routability prediction
- high accuracy and high speed
flow:
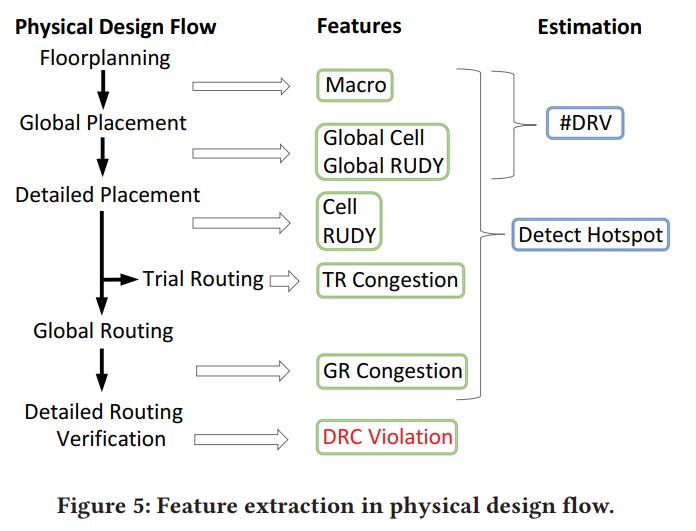
model
#DRV prediction
ResNet18-based
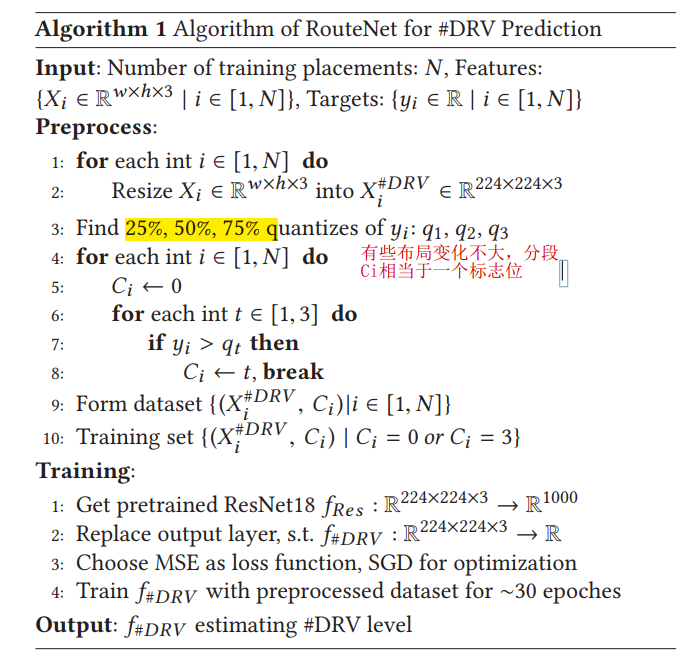
preprocess

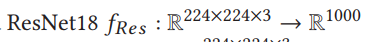
ResNet是一个固定输入(224*224)的模型,为了使用知识迁移,将输入
 。具体怎么插?
。具体怎么插?
hotspot prediction
data:
dataset:
ISPD 2015 benchmarks
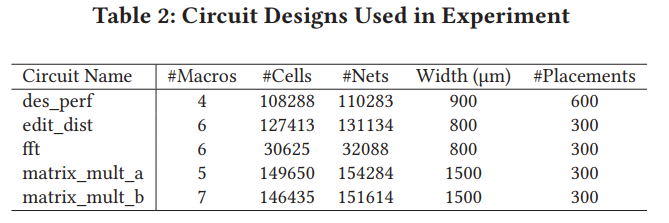
different placement made by “obstacle-aware macro placement" algorithm [5].
each floorplan is placed and routed by Cadence Encounter v14.20 [2]
experiment:
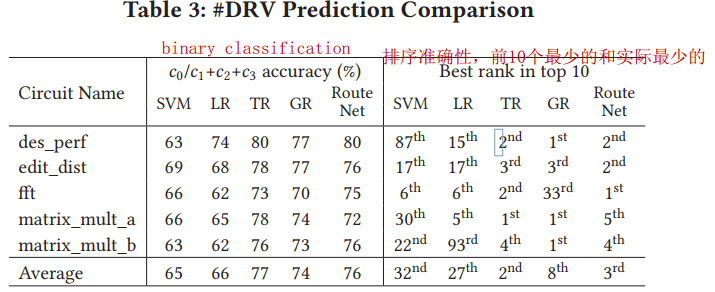
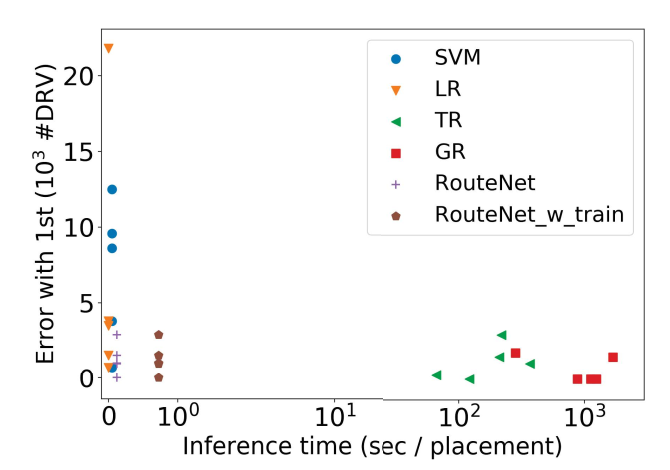
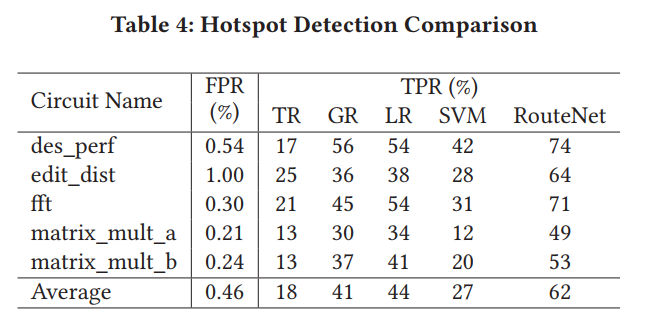
we compare the TPR of all methods under the same FPR (error under 1%)
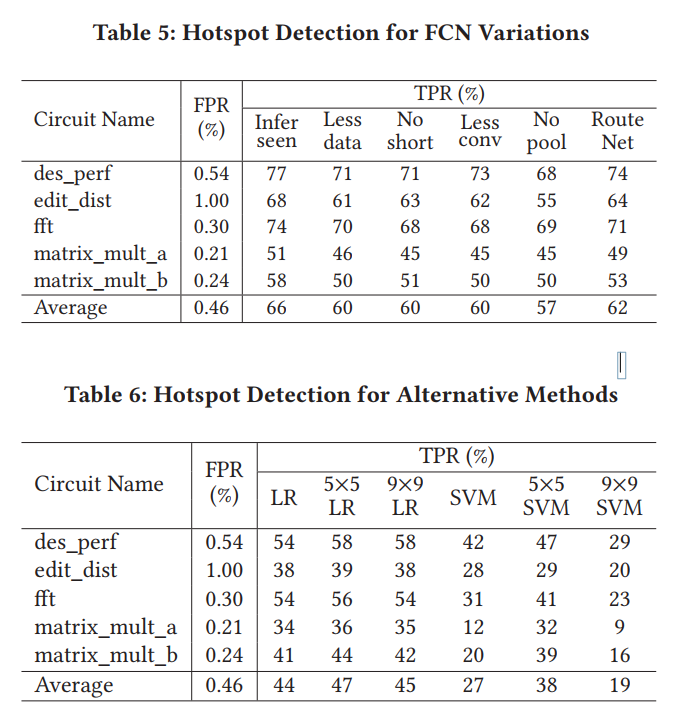
CongestionNet-predict congestion hotspots-IFIP-2019-GNN(GAT)-nvidia #
a graph-based deep learning method for predicting routing congestion hotspots from a netlist before placement. Predict the detail routed lower metal layer congestion values

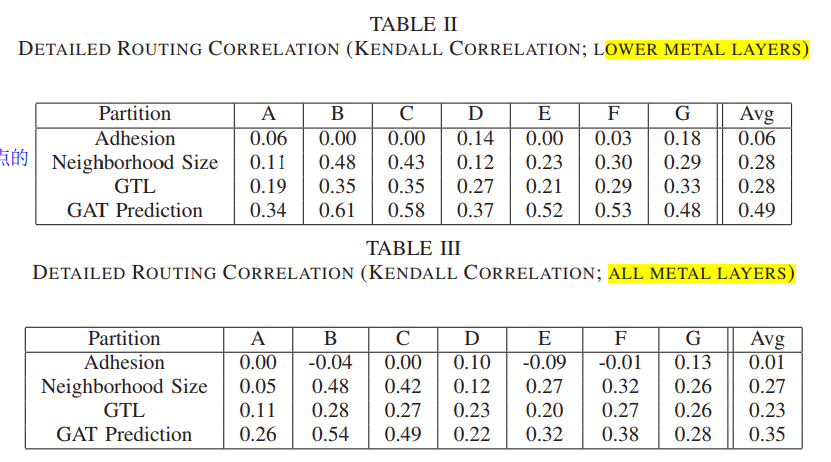
why low layer? 因为较低金属层上的拥塞主要是由局部逻辑结构驱动的,而不是由无关逻辑簇之间的较长互连驱动的,后者往往在较高金属层上运行. predicting lower metal layer congestion is not only more important for the underlying task of identifying congested logic structures, but also simplifies the task for our graph based network
contribution:
- 阶段早,只使用网表
- 由于该模型仅基于网表的逻辑结构而不是任何特定的单元布局进行预测,因此它消除了基于布局的方法中存在的次优布局的伪影

- can be done without any physical information
- GNN, 快
- the first work exploring the use of graph based deep learning for physical design problems
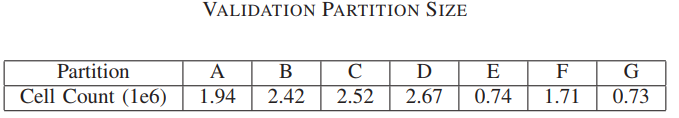
数据:

roughly 5000 distinct cell types
we project our per cell predictions back onto their respective 2D grid (using the final ground truth physical placement) and average all cells within each grid cell to come up with a predicted value that can be compared to the original ground truth grid value.
模型参数:
an 8 layer Graph Attention Network (GAT) with size 16 intermediate (or hidden) state
无向图, each node corresponds to a cell
节点特征: length 50 for each cell type and each cell’s logic description as well as the pin count and cell size of that cell
实验:
report correlation values using the Kendall ranking coefficient
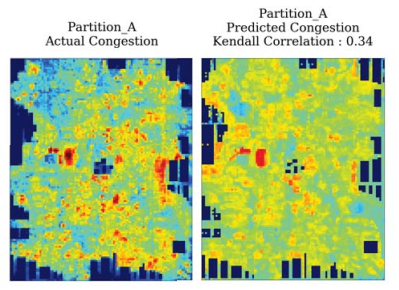
实际效果可视化
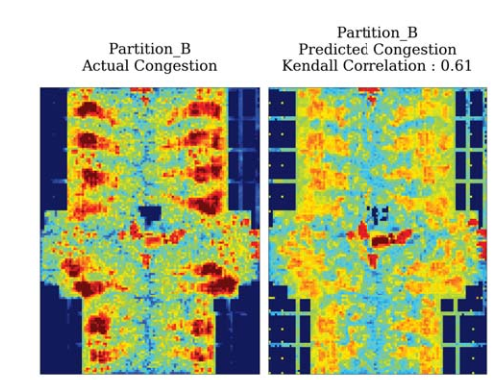
对比实验
消融实验
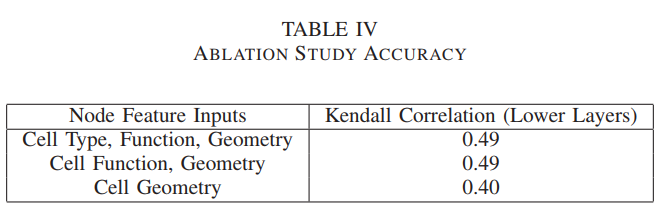
cell type or function is an essential part of our predictions.
cell type 不是没起作用吗
缺点:
- model needs to be retrained for every new process technology, since the embeddings are over cell types specific to a process technology.
- it occasionally over predicts congestion in areas of low to moderate congestion, such as in most failing parts of Partition A
- due to the graph based nature of the model, it sometimes makes overly soft decision boundaries

- the CongestionNet uses informative cell attributes (cell size and pin count) alone as the input to the GAT and does not use any embedding encoding the netlist structure
可改进的点:

-Congestion prediction + embedding + matrix factorization + partition-arXiv-2021-GNN(Sage)- #
background
- predicting cell congestion due to improper logic combination can reduce the burden of subsequent physical implementations.
- previous work: require informative cell features
- Although the global routing result provides a good estimation of routing congestion [6], [19], an awareness of high congestion areas at an early design stage is of great importance to provide fast feedback and shorten design cycles
- Multiple works have attempted to predict detailed routing congestion in the placement step in an effort to optimize routability of the placement solution
task
during the logic synthesis stage

到底是什么时候的congestion数据? Routing后的真实值还是预测plcament后的congestion RUDY预测值? 应该是Global Routing后的:强调了congestion value = wiring demand/routing capacity
contrbution
data
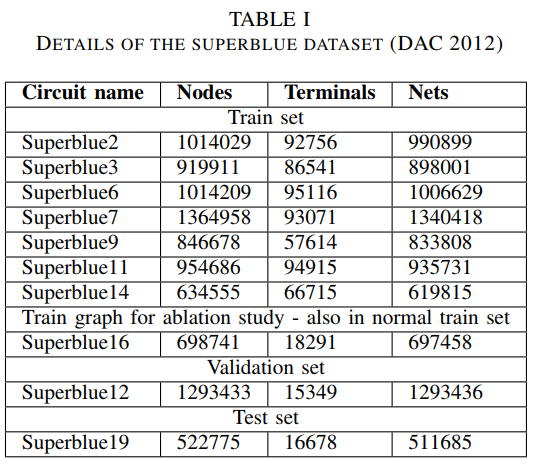
DAC2012 contest benchmark
http://archive.sigda.org/dac2012/contest/dac2012_contest.html
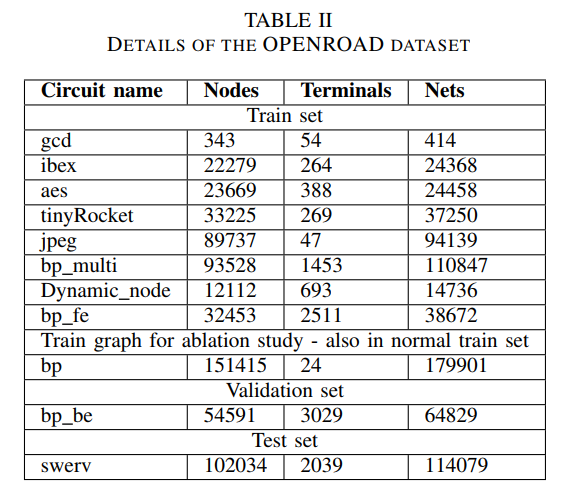
OpenROAD dataset
place via DREAMPLACE

Macros and terminals are removed from the graph
Nets with degree more than 10 are excluded from the final graph as they introduce cliques too large to work with efficiently.
node features (pin number, cell size) , This follows the flow of CongestionNet
flow:
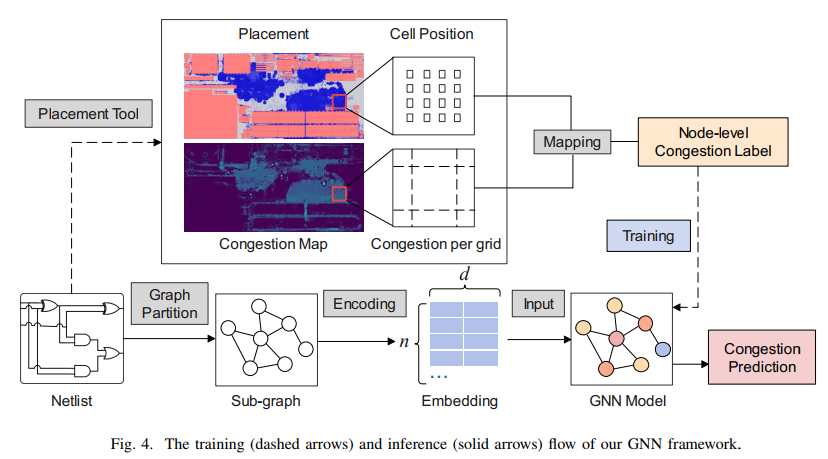
congestion value for each grid cell computed as the wiring demand divided by the routing capacity , The output along the z-axis is reduced by a max function,
Our focus is on predicting congestion due to local logic structure, which manifests itself on lower metal layers. Therefore, we use congestion labels from the lower half of the metal layers to train and evaluate the model
推理的时候取所有cell的预测平均值
principle
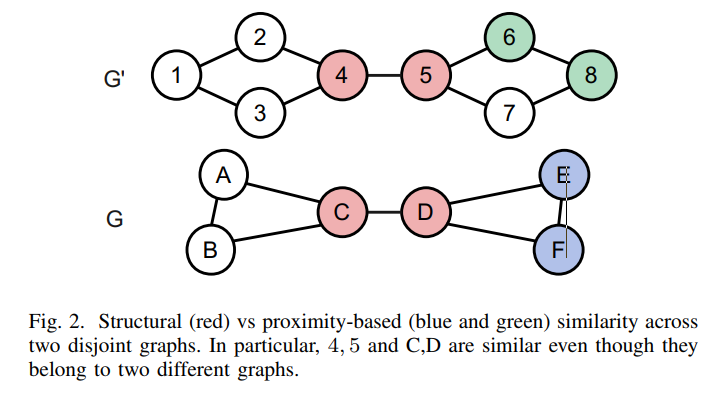
提出相连越近的节点相似度越高,
提出structural node similarity
Sub-graph partition ? METIS? ClusterGCN?
Matrix Factorization ?
model
The key difference between this approach and CongestionNet lies in embedding pipeline
graph is undirected complete circuit is too large for direct matrix factorization and must be partitioned into clusters, use METIS partitioning tool in ClusterGCN
Sub-graph partition: clusters of ≈ 5000 nodes each
Matrix Factorization ?
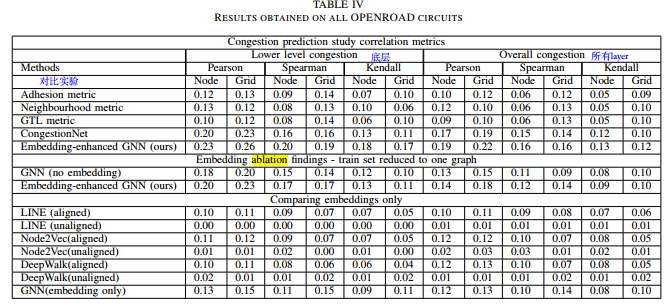
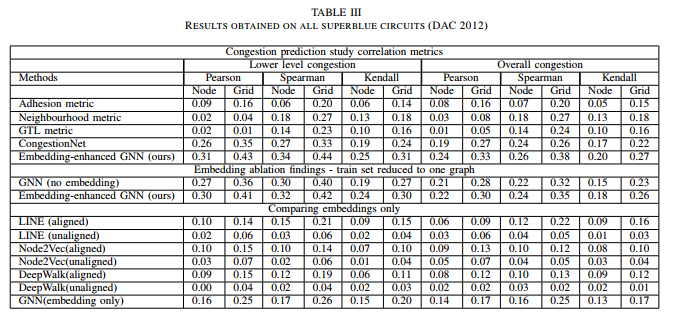
experiment
three metrics of correlation to measure performance: Pearson, Spearman, Kendall
Before evaluation, both the prediction and the label have some (very low) noise added to them.
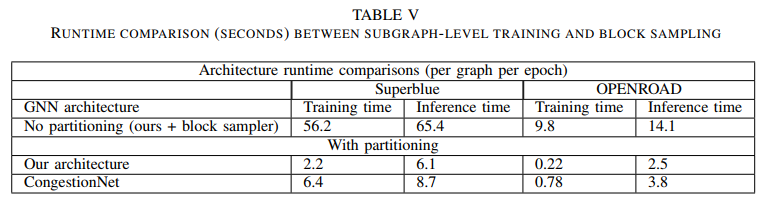
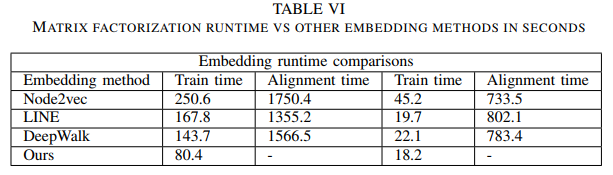
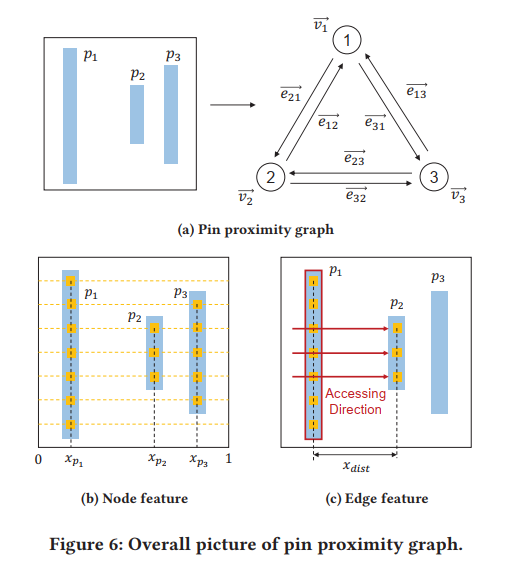
PGNN-DRVs prediction+Pin Proximity Graph-ICCAD-2022-GNN+UNet(CNN)-Korea #
background
(1) pin accessibility and (2) routing congestion are two major causes of DRVs (design rule violations)
Particularly, the complex design rules put so much burden on physical design, demanding lots of iterations on the time-consuming process of cell placement and net routing to clean up all DRVs (design rule violations) before tapping out . Thus, at the placement stage, if we were able to identify, with high confidence, DRC (design rule check) hotspots that would be likely to occur at the routing stage, we can pay more attention
shortcoming of image based:
local pin accessibility cannot be accurately modeled by pin pattern image alone
using high-resolution pin pattern images incur significant additional run-time as well as memory overhead to the prediction models
to optimize the placement before routing.
task
a novel ML based DRC hotspot prediction technique,
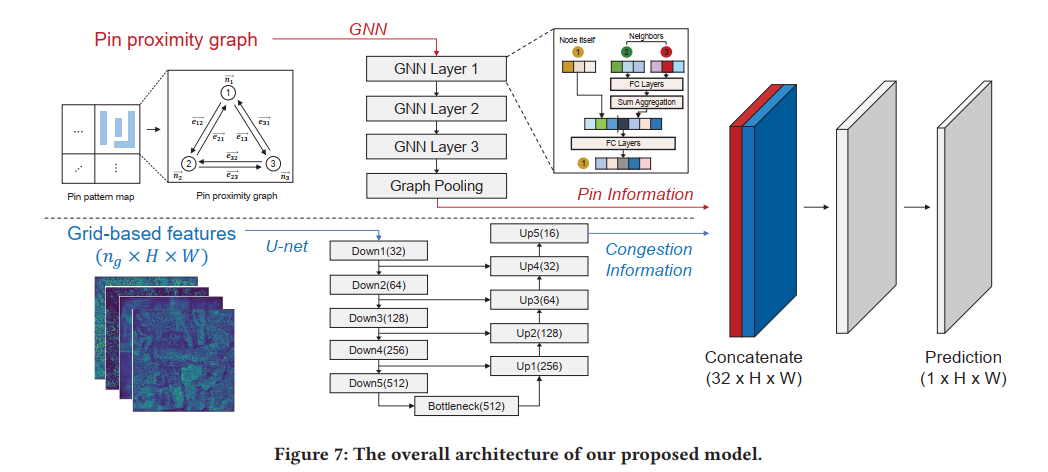
- GNN is used to embed pin accessibility information, U-net is used to extract routing congestion information from grid-based features
- placement 分割为grid, 长宽=G-Cell
- DRVs are extracted as the ground-truth after detailed routing
contribution
- GNN model, base pin proximity graph
model
PGNN can adopt pin proximity graph as well as grid-based feature map as input feature
Pin Proximity Graph :
- 无向图, 同构图

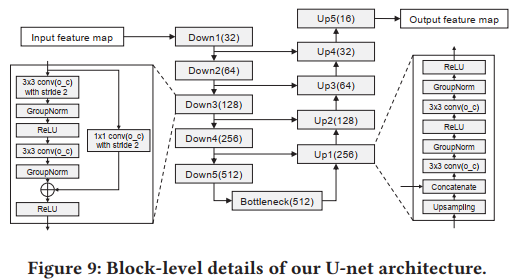
U-Net:
featrue:

整体模型:
数据集:
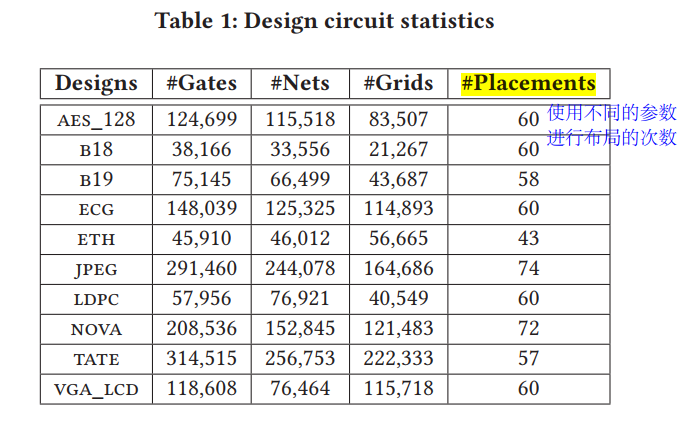
以后也可以这么做, 同一个benchmark不同的config参数就有不同的数据
experiment
Nangate 15nm library
9 groups are used for training and the remaining 1 group for test. K折验证

positive 和 negative是什么意思?
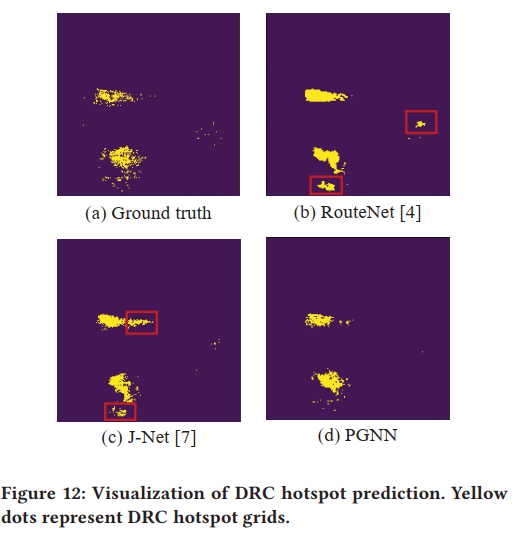
可视化:
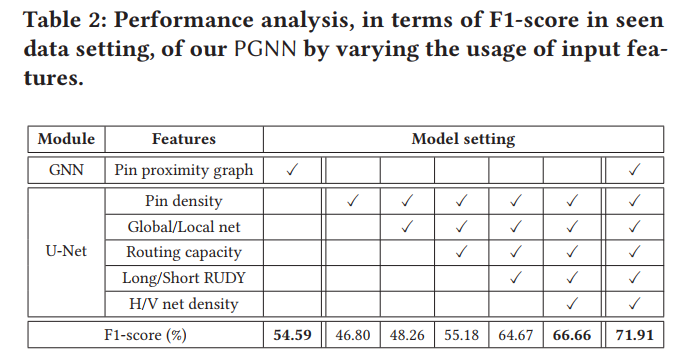
消融实验:
以后也可以这样用特征消融?
对比实验(F1-score):
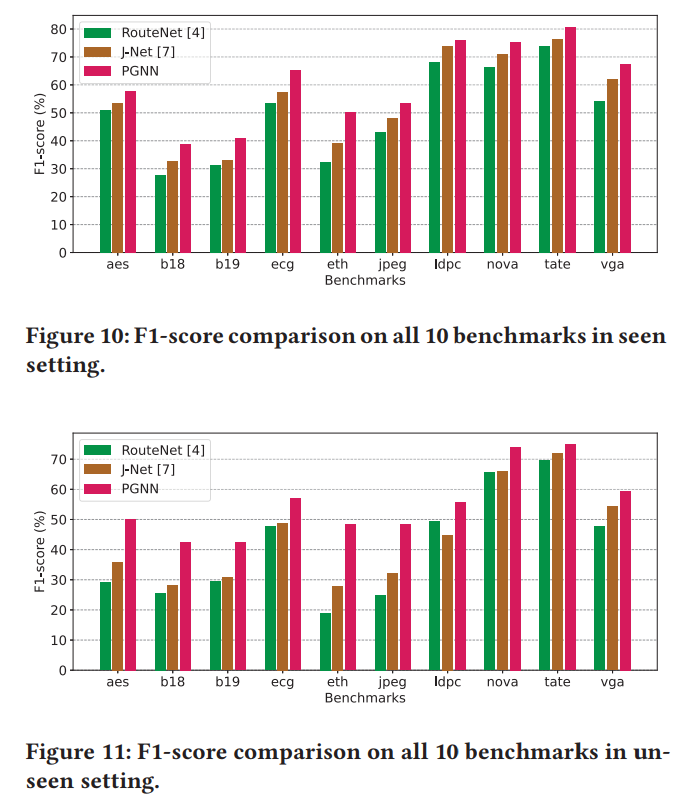
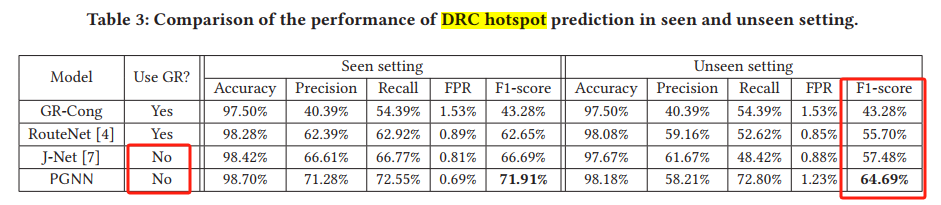
注意不需要GR!
GR-Cong is obtained from ICC2 after global routing stage, and grids with high routing congestion are classified as DRC hotspot. 商用
RouteNet和J-Net都是相关的学术工作
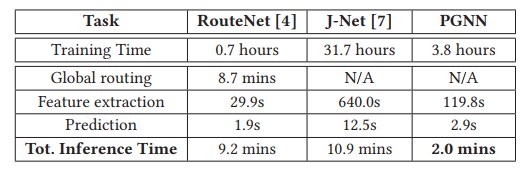
时间对比:
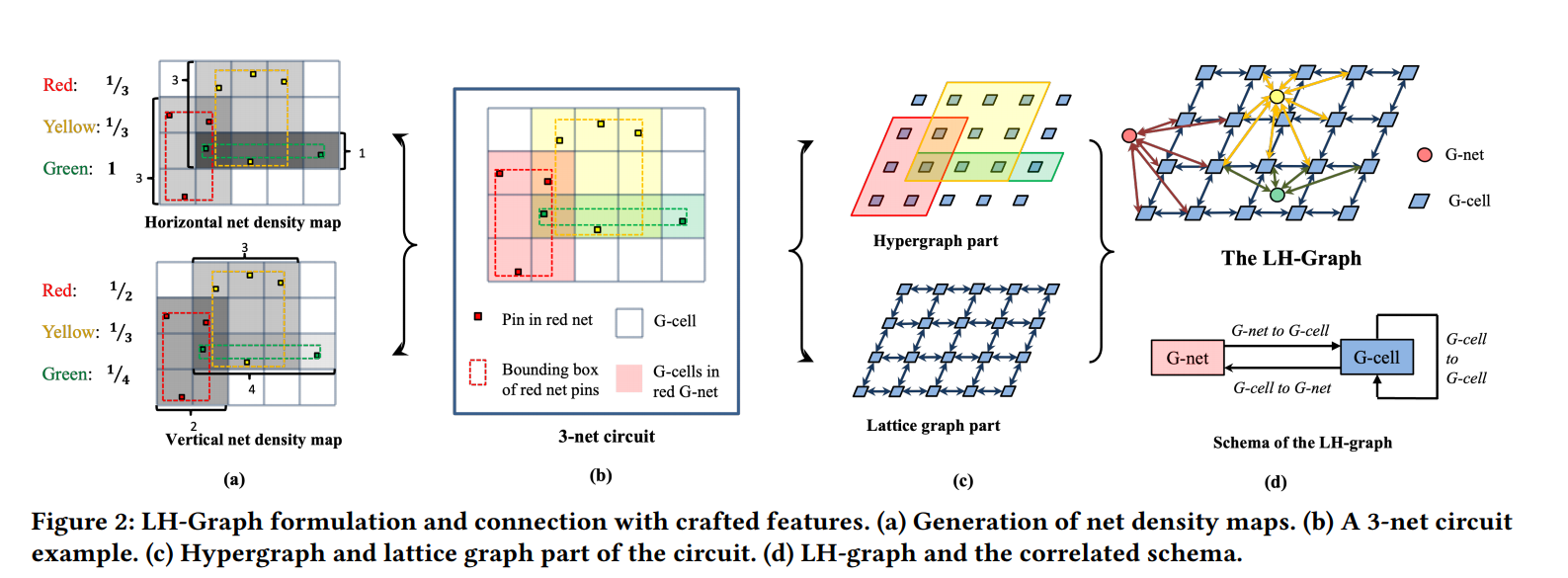
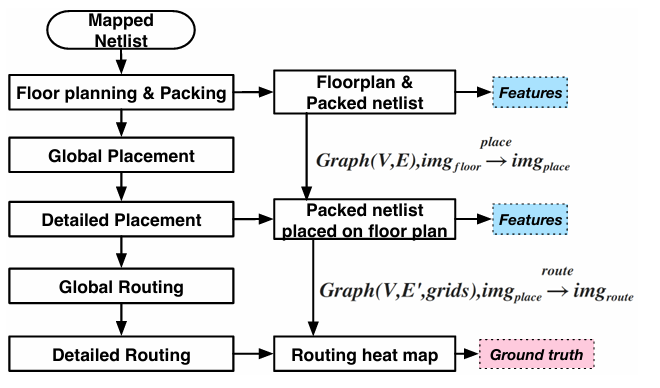
LHNN-CongestionPrediction-DAC-2022-GNN-CUHK+Huawei+YiboLin #
background
- 图的节点的设置很新颖
- with the growth of circuit scale and complexity, time consumption tends to be unacceptable when utilizing a global router in the placement cycle to obtain the congestion map.
- due to the need for the “shift-left” in circuit design, researchers begin to seek alternative solutions in machine learning [4] [5] to achieve accurate and fast congestion map prediction
task
- two related tasks, routing demand regression and congestion classification
data
regard each G-cell as a node and add an edge between two nodes if the respective two G-cells are adjacent.
hypergraphs and heterogeneous graph , 两种节点:G-cell和G-net

feature:

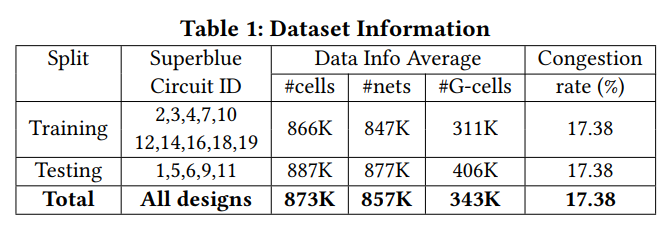
ISPD 2011 [16] and DAC 2012 [17] contest benchmarks ,
model
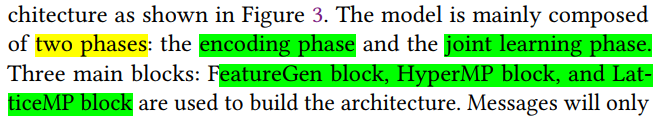

他这里说congestion map是一个二值化(0/1?)的数据集, 所以是分类任务, 但是为了利用数据,同时防止routing demand的信息丢失, 还设置了一个预测routing demand的任务?
experiment
15benchmarks: 10 for training and 5 for testing
run DREAMPlace [18] on each of the designs to generate placement solutions
NCTU-GR 2.0 [2] to attain horizontal/vertical routing demand maps , and set the congestion maps as a binary indicator according to whether the horizontal/vertical routing demand of the G-cell exceeds the circuit’s capacity

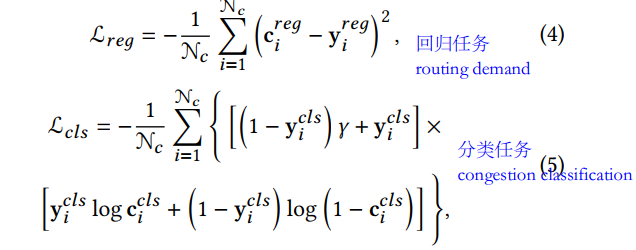
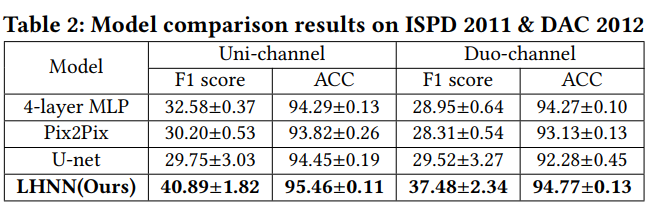
对比实验:

可视化:
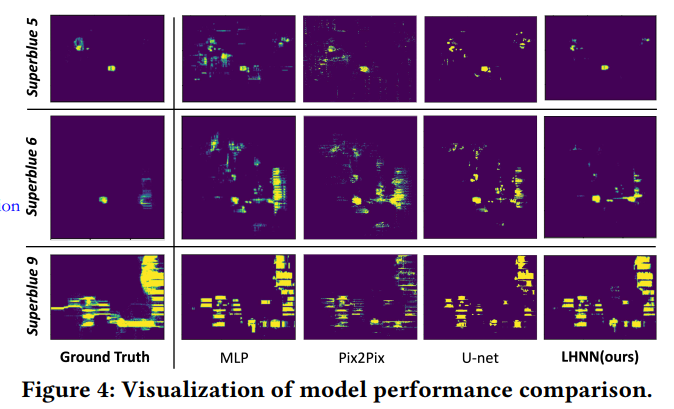
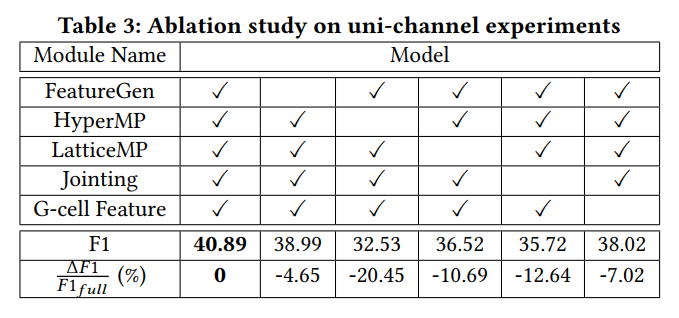
消融实验:
-NN Robustness improve-arXiv-2024- -UC- #
background:
- 最近的工作已经证明神经网络通常是容易受到精心选择的输入小扰动的影响
- Our definition of imperceptibility is characterized by a guarantee that a perturbation to a layout will not alter its global routing
- recent work [10, 18] has demonstrated that image classifiers can be fooled by small, carefully chosen perturbations of their input

task
- design two efficient methods for finding perturbations that demonstrate brittleness of recently proposed congestion predictors
- one potential approach to address the issues by modifying the training procedure to promote robustness
contribution
Painting on PIacement-predict the routing congestion-ACM-2019-GAN-
-DRC Hotspot Prediction-ISCAS-2021-CNN
-Routing Congestion Prediction-ASPDAC-2020-GAN
-predict #DRV, a macro placer-DATE-2019-CNN
Timing Prediction #
Pre-Routing Timing Prediction #
background #
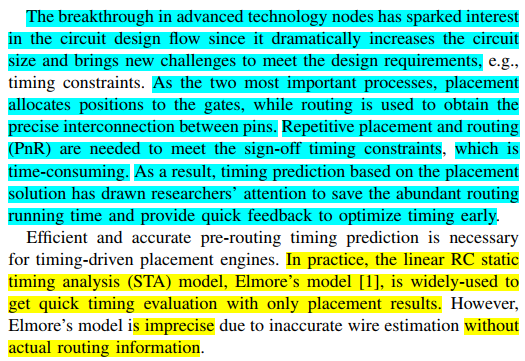
relate work #
TimingGCN-STA prediction-DAC-2022-GNN
- the first work!
- opensource
- still relies on local net/cell delay prediction as auxiliary tasks
- no optimization, not fit the real-world scenario where timing optimization is taken into account
PreRoutGNN-STA prediction-AAAI-2024-GNN
- opensource
[Multimodal Fusion-Restructure tolerant+CNN+Endpoint-wise Masking4Layout -DAC-2023-GNN+CNN-7nm RISCV](D:\MyNotes\EDA\Timing\Multimodal Fusion-Pre Route Timing Prediction-DAC-2023-GNN-7nm RISCV.pdf)
Restructure:预测终点的延时,但是Timing Opt会改变网表结构(end point不变)。对一个Pre-routing任务来说,输入的网表和最终的网表不一样
netlist restructuring causes a mismatch between local input features and ground-truth features in the restructured sub-regions
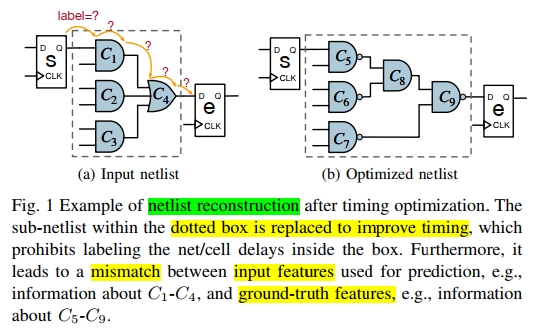
As a result, prior local-view models can only be trained on the unchanged regions in a semi-supervised manner.
In other words, the better the models fit on labeled (unreplaced) net/cell delays, the worse they fit on replaced regions and eventually on endpoint arrival time
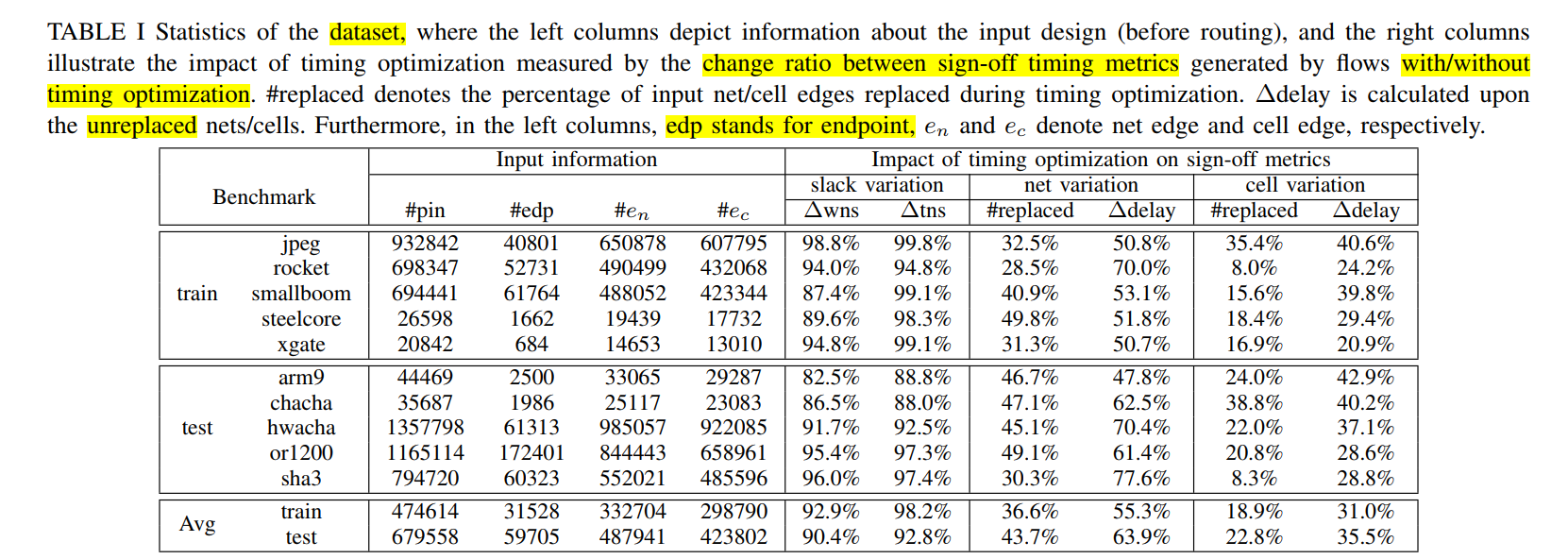
数据集:基本信息和Timing优化导致的网表变化
- average 40% nets and 21% cells are replaced during timing optimization
- timing optimization brings an average change of 59.6% to net delays and 33.3% to cell delays
为什么用layout信息:Since most timing optimization techniques include gate insertion or gate sizing, placement should reserve space for subsequent timing optimization. In other words, the timing optimizer’s efficacy is tied closely to global layout information. The layout information plays a dominant role in determining the timing optimizer’s impact since most optimization techniques need space to be applied
整体模型
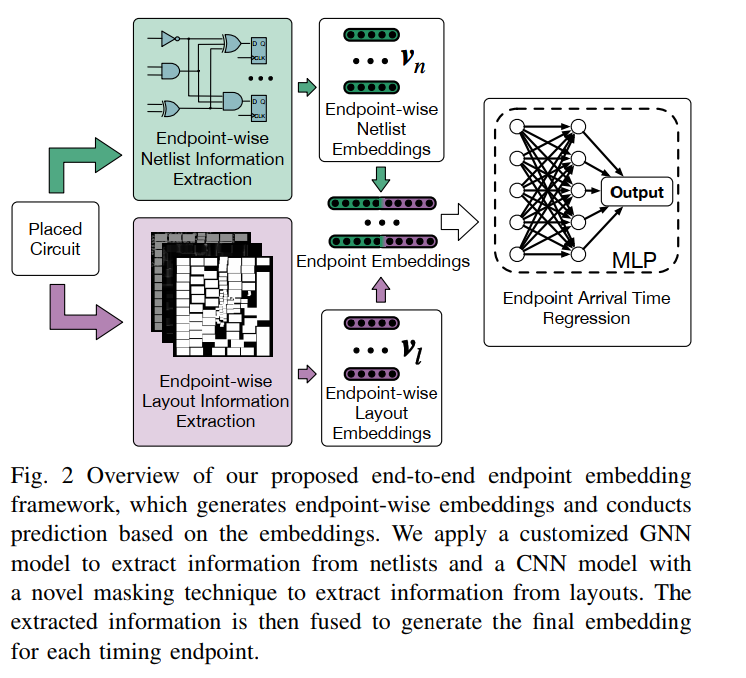
组成:GNN+CNN+Endpoint-wise Masking
- Netlist(GNN):
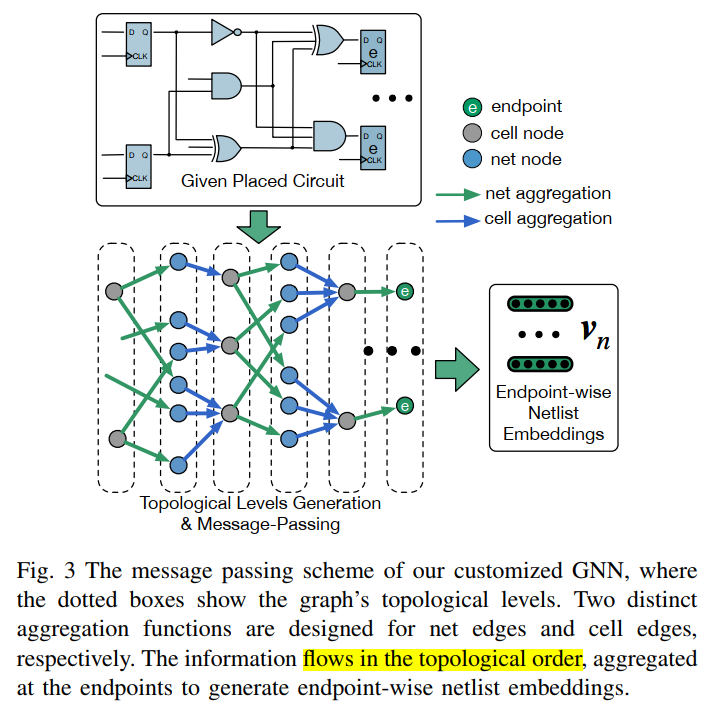
和 TimingGCN-STA prediction-DAC-2022-GNN很像(没发现不同)
Layout(CNN+Endpoint-wise Masking)
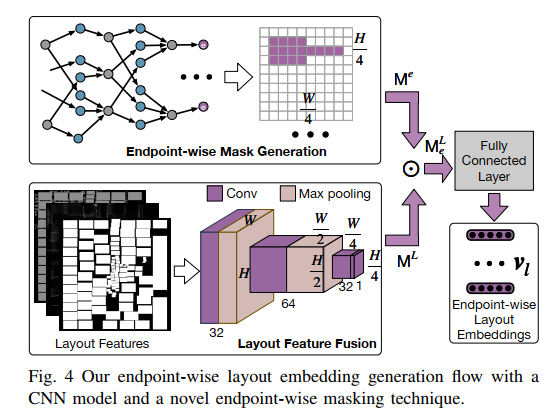

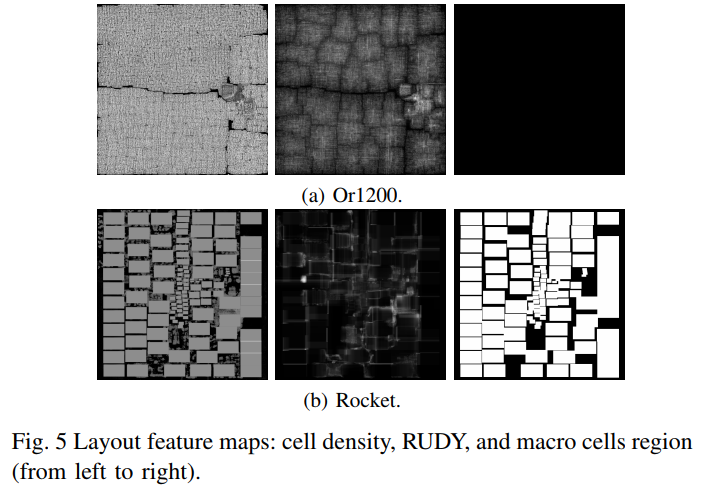
三个特征:cell density, rectangular uniform wire density (RUDY), and macro cells region
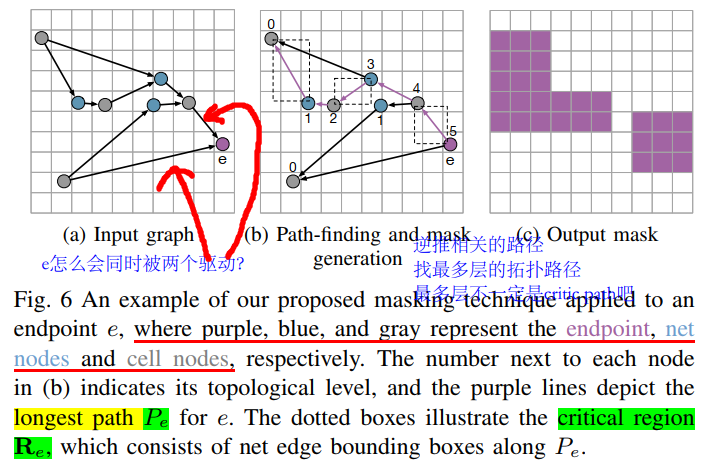
Endpoint-wise Masking
对比实验:

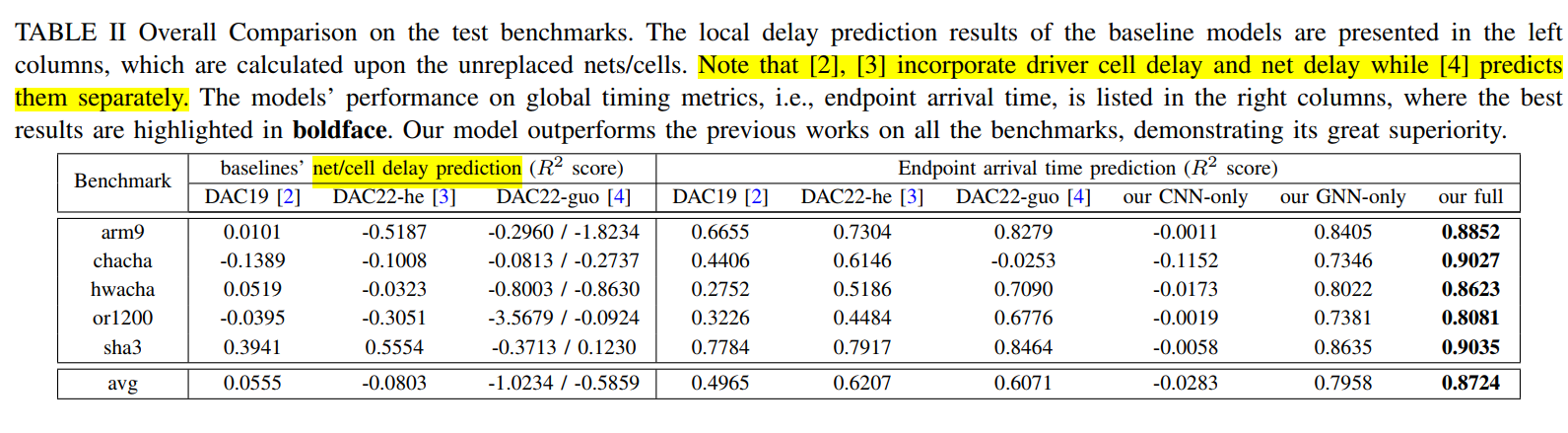
run time实验
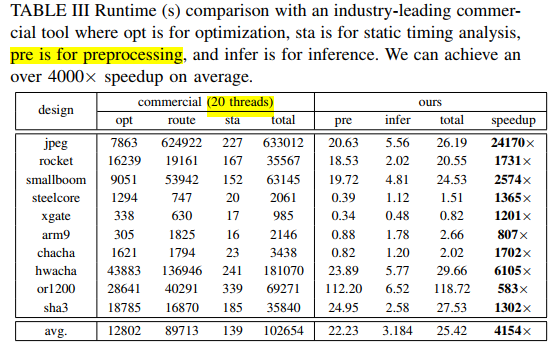
other #
Ahead RC network-STA prediction-DAC-2022-?
TSteiner-STA prediction and refinement&steiner point refinement-DAC-2023-GNN-Yibo Lin
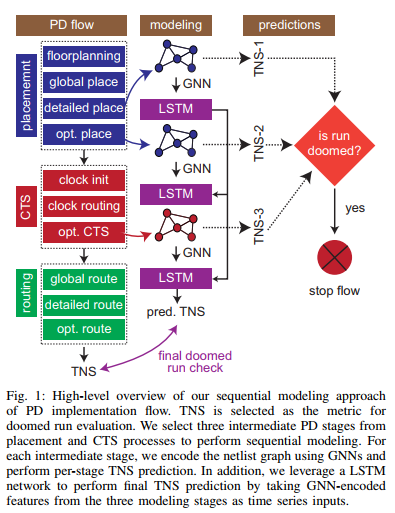
Doomed Run Prediction-TNS prediction-ACM-2021-GNN+RNN
not DL #
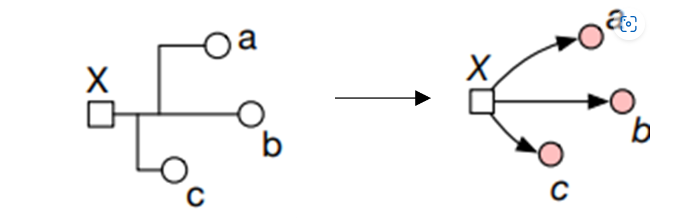
 The two-stage approaches [2], [3] first predict localnet/cell delays and then apply PERT traversals [5] to evaluate the global timing metrics, i.e., endpoint arrival time.
The two-stage approaches [2], [3] first predict localnet/cell delays and then apply PERT traversals [5] to evaluate the global timing metrics, i.e., endpoint arrival time.
Optimization #
Timing #
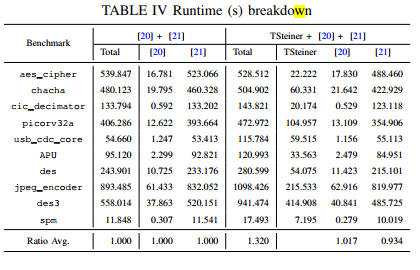
TSteiner - Steiner Points Opt-DAC-2023-GNN-CUHK
background
对于multi-pin net需要构建steiner tree来进行routing,故steiner tree中steiner points也会影响routing
FLUTE[ 3]是常用的生成steiner tree的算法。在生成steiner tree后,我们可以通过近一步优化steiner point来优化timing

the previous early-stage timing optimization works only focus on improving early timing metrics. 提出了诸如net加权和可微分时间目标等策略来优化时间, only focus on improving pre-routing timing metrics, which may have a considerable gap to signoff timing performance. 斯坦那点更加靠近布线阶段(和布线更加相关)
all the aforementioned works are not directly targeted at sign-off timing performance due to its high acquisition cost
任务:
In this paper, we focus on explicit sign-off timing optimization at the pre-routing stage to reduce the turnaround time
optimization framework is built to adjust Steiner point positions for better sign-off timing performance iteratively
The most popular Steiner minimum tree construction algorithms aim to minimize wirelength. Moreover, the Steiner point refinement is introduced to update the generated Steiner point positions for specific objectives, e.g., sign-off timing performance, while maintaining the two-pin net connections
启发:
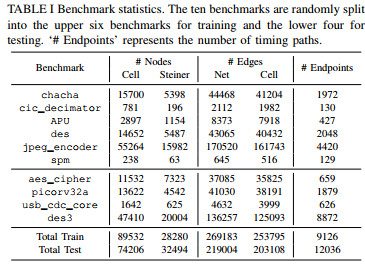
we surprisingly find that the signoff timing performance could be significantly affected even by a random disturbance on Steiner point positions, as shown in Fig. 2.
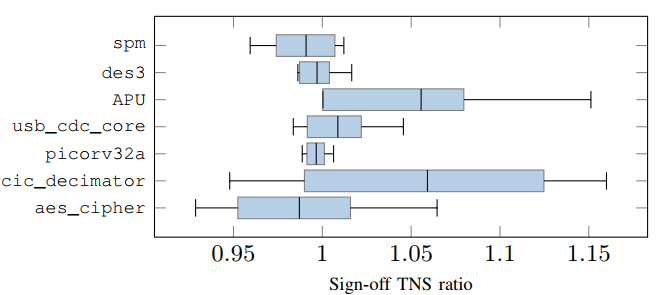
Nevertheless, the impact of random moving is considerately unstable, and its average performance is slight (with a ratio close to 1.0). 所以启发找到一个好的方法来更新斯坦纳点来降低TNS
在最广泛使用的技术节点中,与路径长度最相关的定时度量——净延迟,并不能解释大部分的整体定时性能. 这里用的初始化斯泰纳树的方法的优化目标都是路径长度最短
contribution:
- first earlystage timing optimization framework via Steiner point refinement
- GNN
- TSteiner framework is fully automated with an adaptive stepsize scheme and the auto-convergence scheme
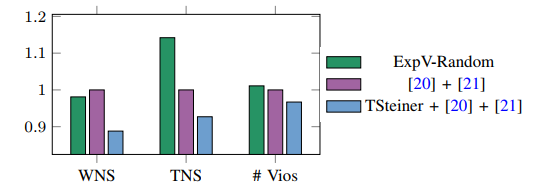
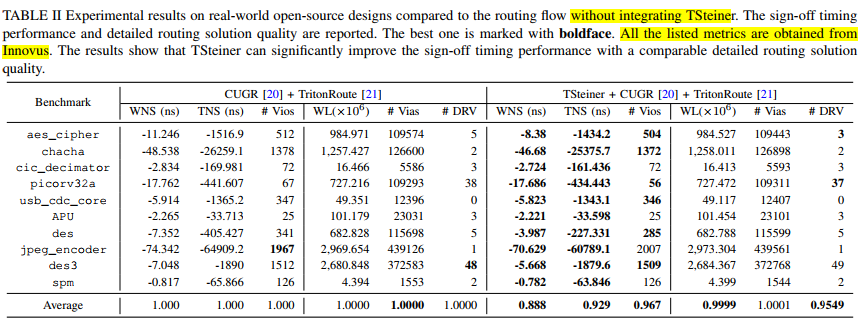
- improves 11.2% and 7.1% on average (up to 45.8% and 43.9%) for WNS and TNS
模型:
Steiner tree construction decomposes each multi-pin net into a set of two-pin nets via additional Steiner points before global routing to reduce the problem complexity
The proposed framework can be divided into two stages, sign-off timing gradient generation (Section III-A) and concurrent Steiner point refinement (Section III-B)

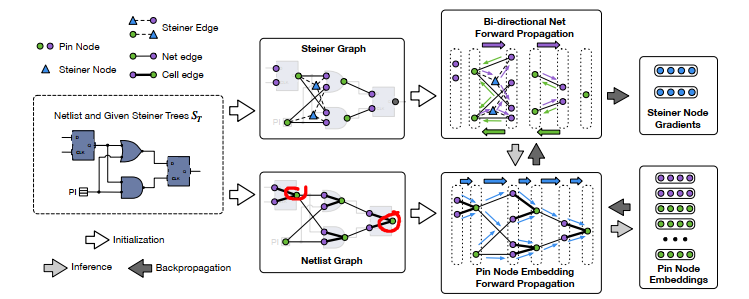
和TimingGCN相比就是多了Steiner 节点, 然后吧第一部分的的node embedding部分加上了steiner的部分
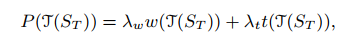
实际是:
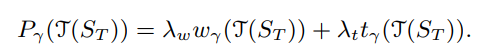
优化的指标, WNS和TNS的加权
根据优化指标对斯泰纳点坐标参数做梯度下降
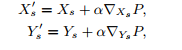
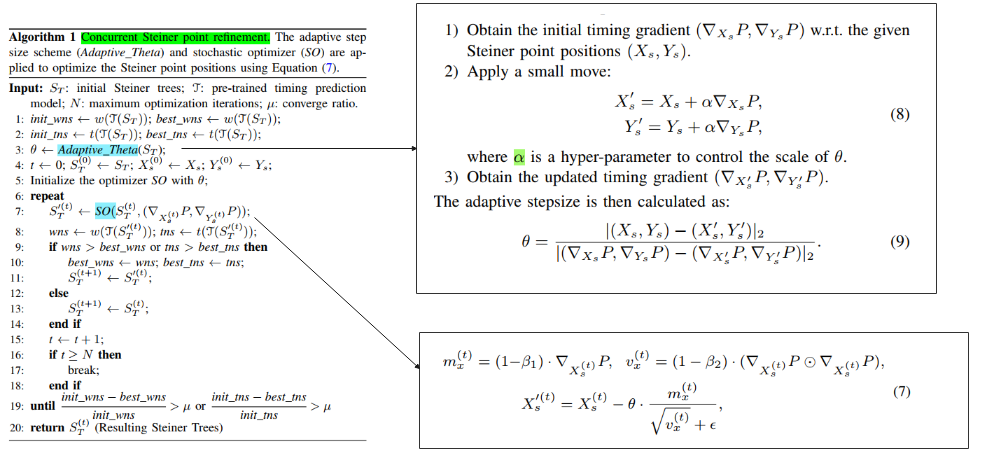
相比简单的梯度下降,只是减小了对不同benchmark的手动学习率微调
数据
实验
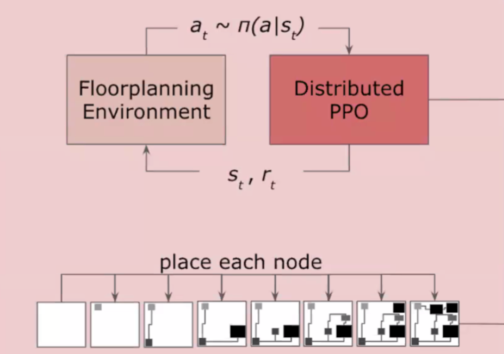
Marco Placement #
-marco placement-nature-2021-RL+GNN-google

Placement #
-Pin Accessibility+DRV prediction-DAC-2019-CNN-NTU #
background:
Standard cells on the lower metal layers severely suffer from low routability due to high pin density, low pin accessibility, and limited routing resources.
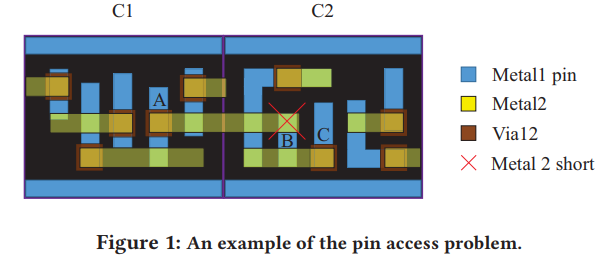
It can be observed that the access points of pin B are blocked by the metal 2 (M2) routing segments routed from Pin A and Pin C, so an M2 short design rule violation (DRV) will be induced when dropping a via12 on Pin B. pin accessibility is not only determined by cell layout design but also strongly affected by adjacent cells
对于传统方法,两个缺点:
- Cell libraries provided by foundries should not be considerably redesigned because the optimized cell performance and manufacturability may be highly sensitive to cell layouts
- Deterministic approaches based on human knowledge have been shown to be less effective in advanced nodes for optimization problems such as DRV prediction and minimization because of the extremely high complexity through the overall design flow

It can be observed that most of the congested regions in the layout do not have DRVs, while some regions with DRVs are not so congested. 但是我感觉还是有相关性的。他是想说明congestion出现的地方不一定有DRV,但是没congestion的地方可能因为poor pin accessibility导致DRV
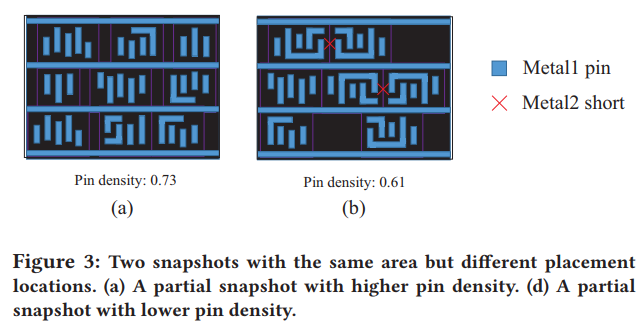
- 也是说明:congestion出现的地方不一定有DRV,但是没congestion的地方可能因为poor pin accessibility导致DRV
- the two M2 shorts occur at the locations having the same pin pattern in the top cell-row and mid cell-row
task:
DRV prediction, 二分类

pin accessibility optimization, 给一个合法化后的布局结构,通过算法进行减少bad pin accessibility的detailed placement

其实也是一个预测模型,一个优化模型
contribution:
- first work to apply pin pattern as the input features of
DRV prediction models.
flow:

model:
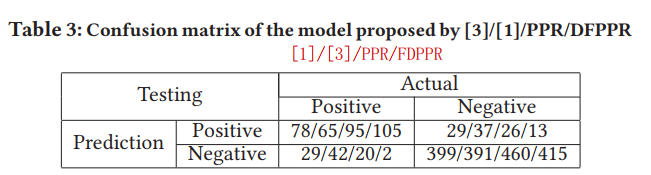
PPR&DFPPR:
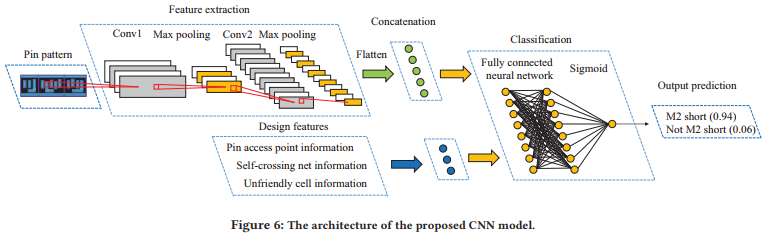
Model-guided Detailed Placement :
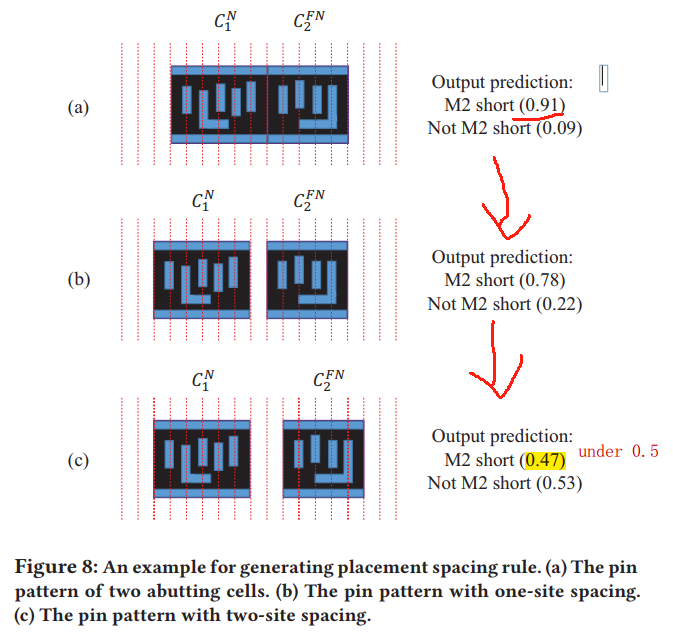
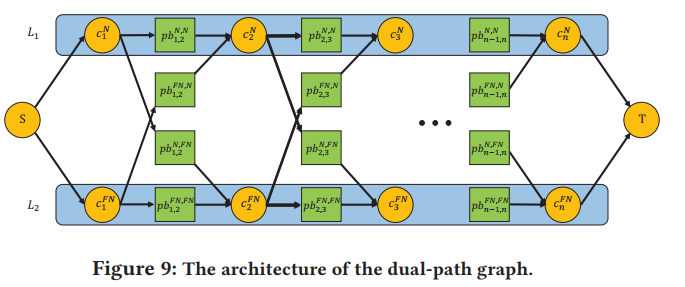
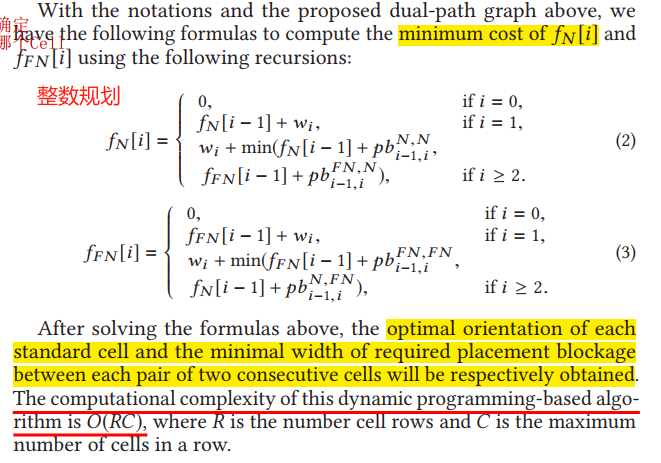
Dynamic Programming-based Placement Blockage Insertion
- 还会改方向?
Cell Displacement Refinement
data:
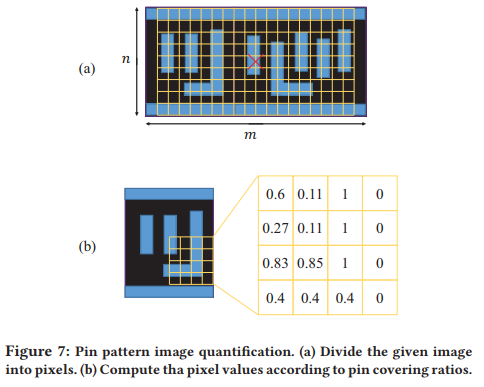
Both the width and height of each pixel are set as the minimum spacing of the M1 layer in order to prevent a pixel from being occupied by two different pins.
没看见关于benchmark的描述
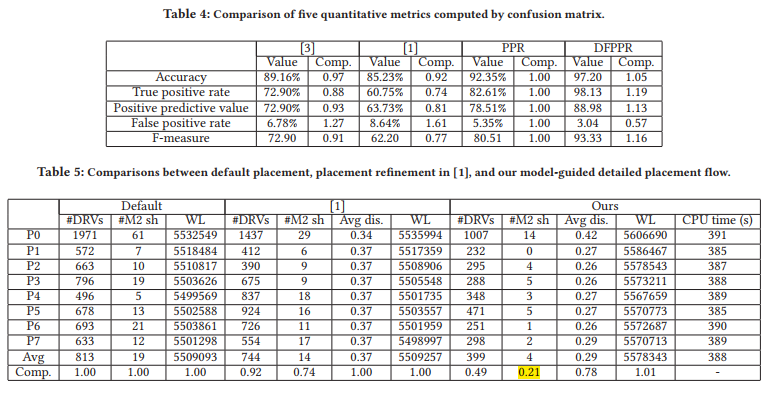
experiment:
shortcoming:
- flow need routed designs to train, time
- The trained model is not necessarily applicable to other designs using different cells or different reference cell libraries
- 对于VLSI,一行一行,一对一对进行,很慢?
-Pin Accessibility+activ-ISPD-2020- -NTU+Synopsys #
background:
With the development of advanced process nodes of semiconductor, the problem of
pin accesshas become one of the major factors to impact the occurrences of design rule violations (DRVs) due to complex design rules and limited routing resourcesupervised learningapproaches extract the labels of training data by generating a great number of routed designs in advance, giving rise to large effort on training data preparation. the pre-trained model could hardly predict unseen dataUnlike most of existing studies that aim at
design-specifictraining, we propose alibrary-basedmodel which can be applied to all designs referencing to the same standard cell library set.Due to the shrinking of modern process nodes of semiconductor, the pin access problem of standard cells has become more harder to be coped with, especially on the lower metal layers.
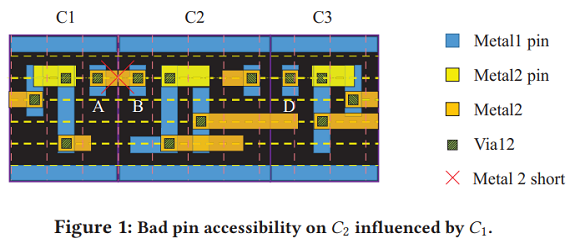
在这种placement下,Metal1 pin A/B由于各自左右两边在Metal2有pin,而且只能在黄色track下横向绕线,(Metal1不能绕线?),那么Pin A/B通过Via12后必定会短路
19年工作[5]的两个缺点
- flow need routed designs to train, time
- The trained model is not necessarily applicable to other designs using different cells or different reference cell libraries
contribution:
- first work of
cell library-basedpin accessibility prediction (PAP), which can be applied to predict other designs referencing to the same cell library set - applies active learning to train a PAP model
- the proposed cell library-based PAP model can be trained at the earlier stage in a process development flow: once the cell libraries are provided.
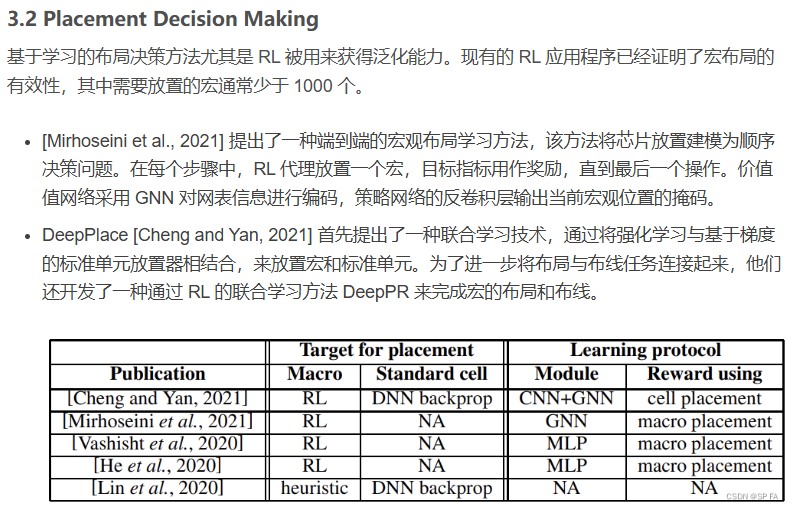
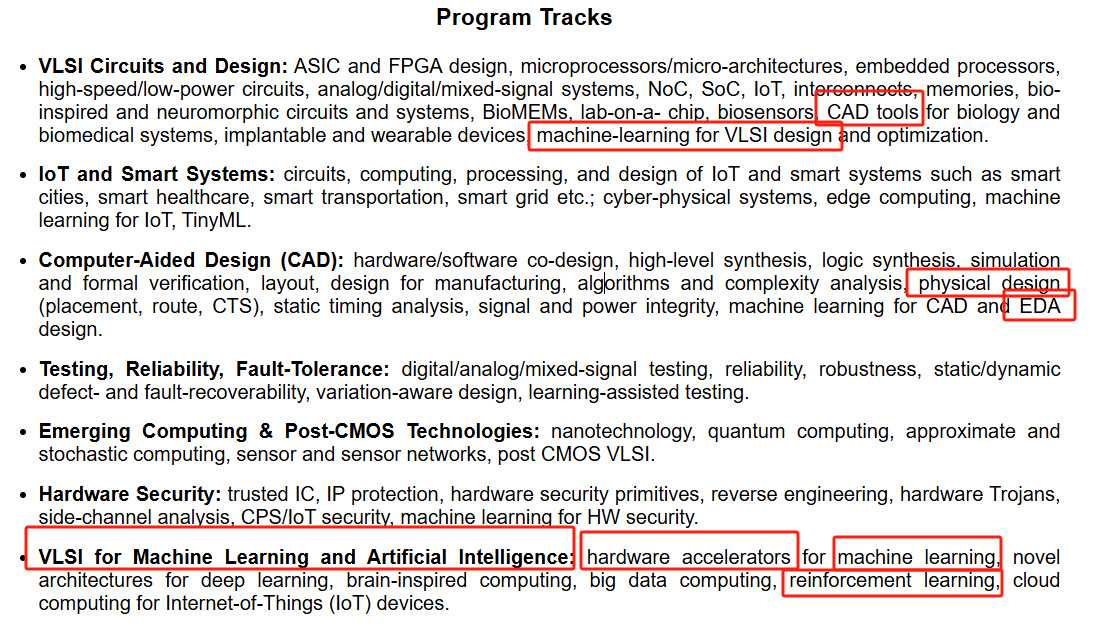
Placement Optimization with Deep Reinforcement Learning- -ISPD-2020-RL+GNN-Google #
PL GNN-Affinity Aware for ICC2- ISPD-2021-GNN-Atlanta #
background:
Placement is one of the most crucial problems, placement directly impacts the final quality of a full-chip design
multiple placement iterations to optimize key metrics(WL, timing), which is time-consuming and computationally inefficient, VLSI
the
logical affinityamong design instancesdominates the quality of the placement
logical affinity源于这篇文章?performing placement guidance requires in-depth design-specific knowledge,which is only achievable by experienced designers who knows the underlying data flows in Register-Transistor Level (RTL) well

K-means基础:
task:
- 基于网表数据,和floorplan结果(marco已经放好)
placement guidance(grouping information) for commercial placersICC2, by generating cell clusters based on logical affinity and manually defined attributes of design instances- our framework will determine the
cell clustersin an unsupervised manner which serve as placement guidance in order to guide commercial placers to optimize the key metrics such as wirelength, power, and timing by placing cells with a common cluster together
flow:
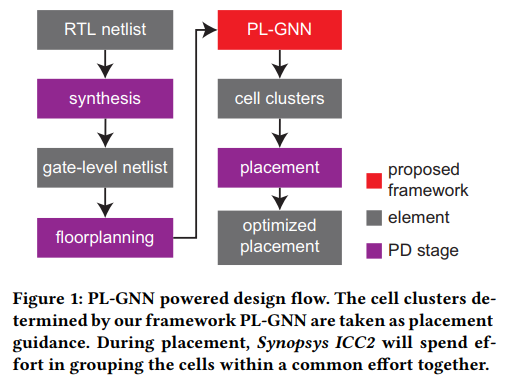
Two stages:
GNN do unsupervised node representation learning, (it is generalizable to any design)
weighted K-means clustering algorithm [3]to group instances into different clusters。To find the optimal number of groups for clustering, we introduce theSilhouette score [19]and perform sweeping experiments to find the sweet spotK-means算法的基本思想是:通过迭代的方式,将数据划分为K个不同的簇,并使得每个数据点与其所属簇的质心(或称为中心点、均值点)之间的距离之和最小。
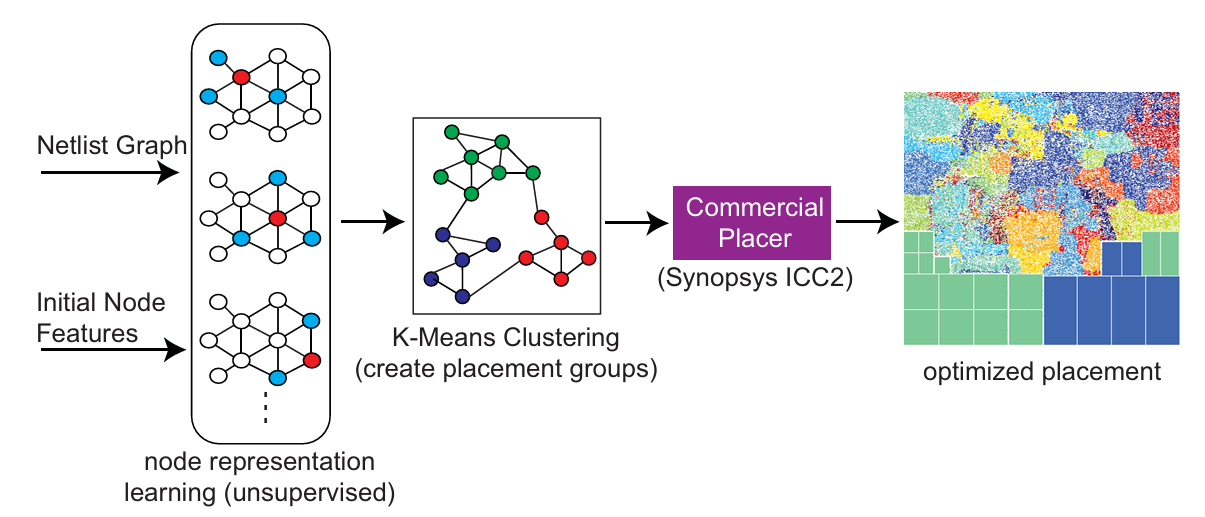
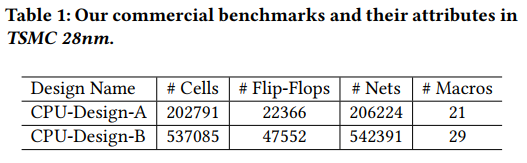
data
two multi-core CPU designs:
nf
design hierarchy : 根据网表层级. top/inst1/sky130_INV/A. (同时zero-padding)

logical affinity of memory macros :logical levels to memory macros 𝑀 as features. because the logic to memory paths are often the critical timing paths
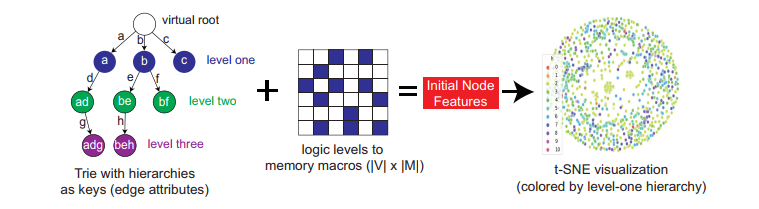
ef:
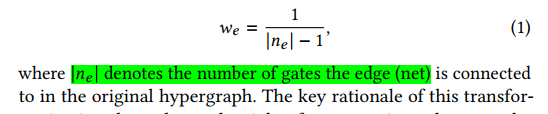
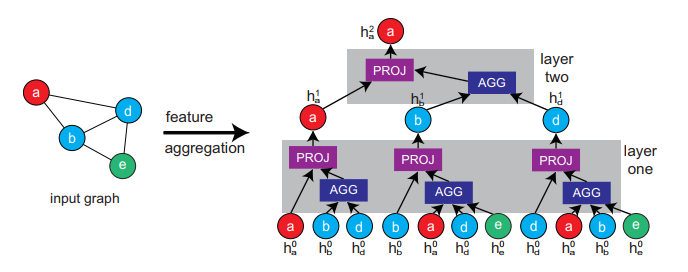
model
GraphSAGE-based, two layers
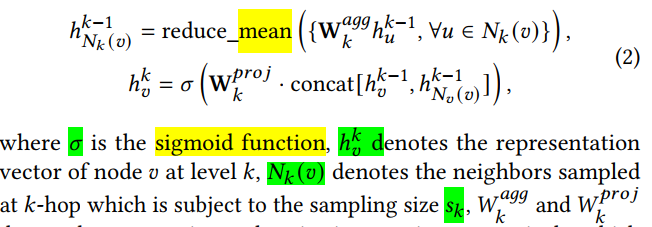
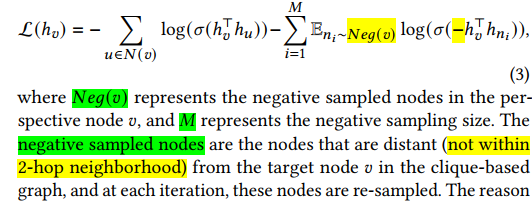
Loss Function:

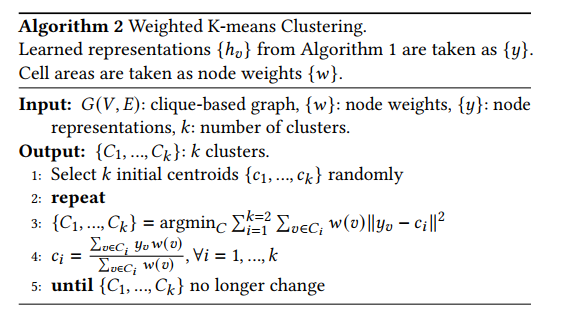
Silhouette score
用于评估分类结果,扫描分类数目,选择最高的分的
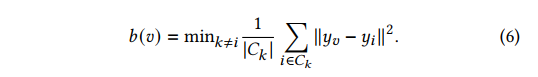
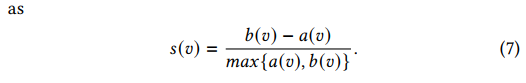

experiment:
env:
- 2.40𝐺𝐻𝑍 CPU
- NVIDIA RTX 2070
- 16𝐺𝐵 memory.
- PyTorch Geometric
setting:
- the placement of memory macros is achieved manually based on design manuals provided by the design-house
- Adam
result
Louvain:比较实验对比模型
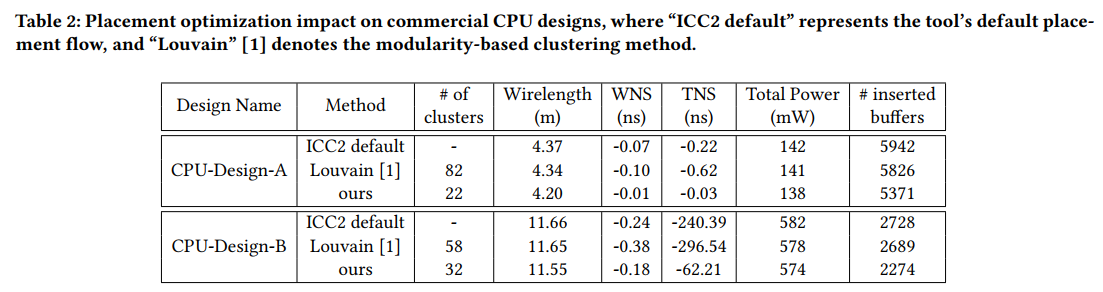
Question:
benchmark少
扫描到的就适用所有?
开环?
-Innovus PPA placement optimize-Neurips-2021-RL #
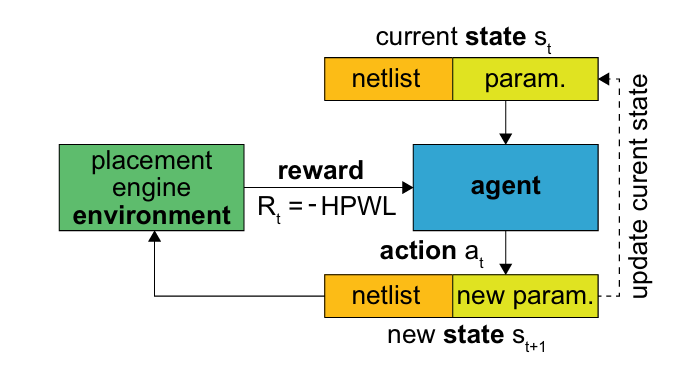
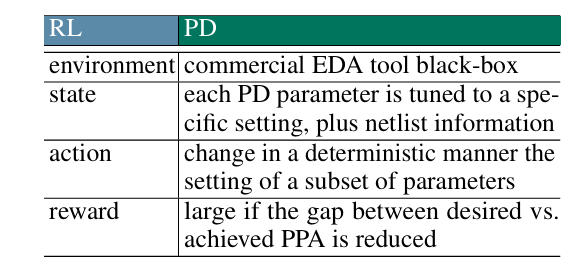
contribution:

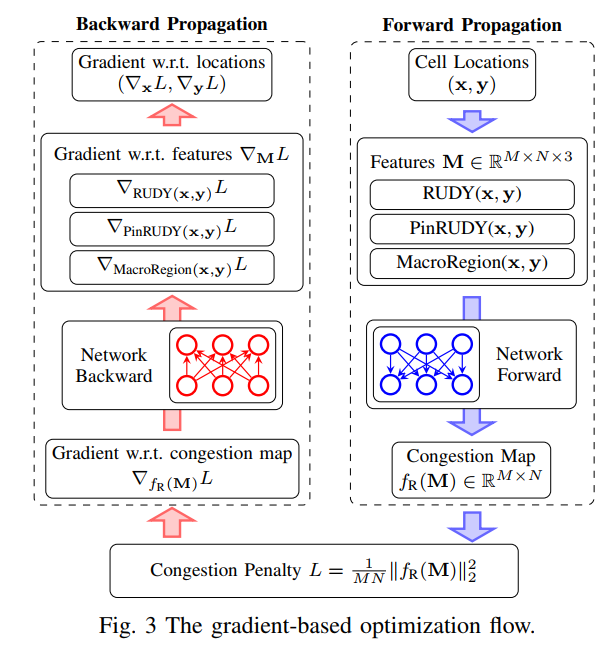
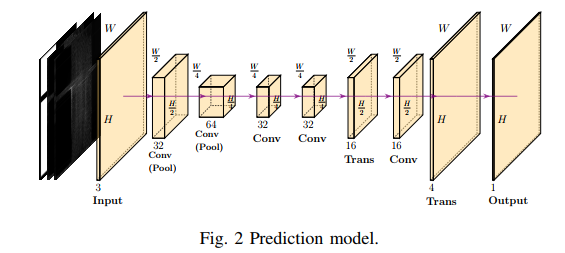
-GP Routability Opt-DAC-2021-FCN-CUHK(SitingLiu BeiYu)+Yibo Lin #
background
flow
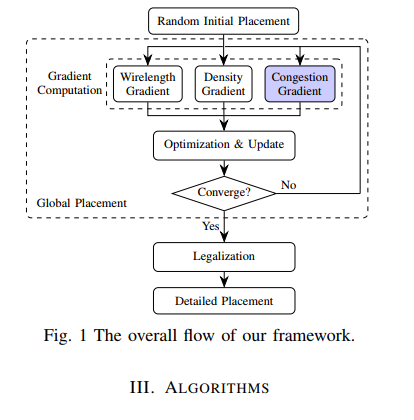
- three input features are extracted from the cell placement solution
- Through the inference of the pre-trained routability prediction model, we get the predicted congestion map.
- take
mean squared Frobenius normof this congestion map as the congestion penalty
data
model
Routing #
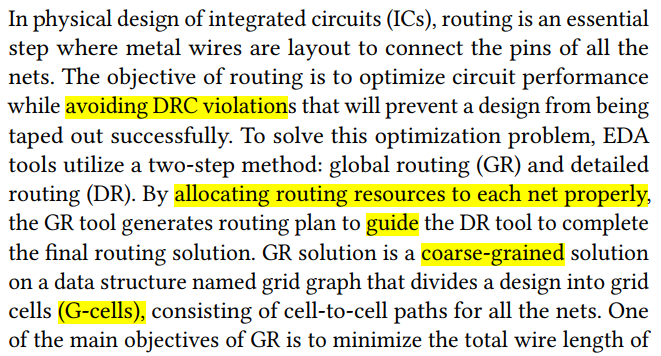
global routing #
backeground #
gr

drc


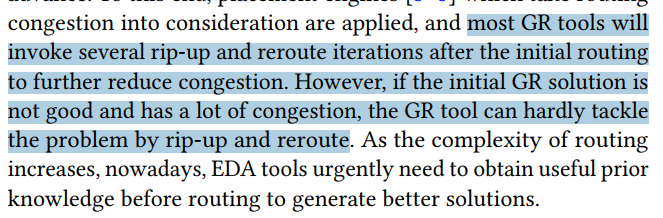
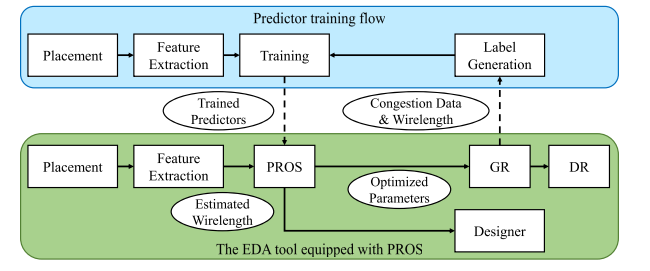
PROS-Routability Optimization-ICCAD-2020-FCN-CNHK+Cadence #
background

task
- congestion predictor and parameter optimizer
- only the data from the placement
- it can optimize the cost parameters before the first routing iteration of GR and thus can give a better GR solution with less congestion.
contribution
- with negligible runtime overhead
- plug-in
- can be embedded into the state-of-the-art commercial EDA tool (Cadence Innovus v20.1)
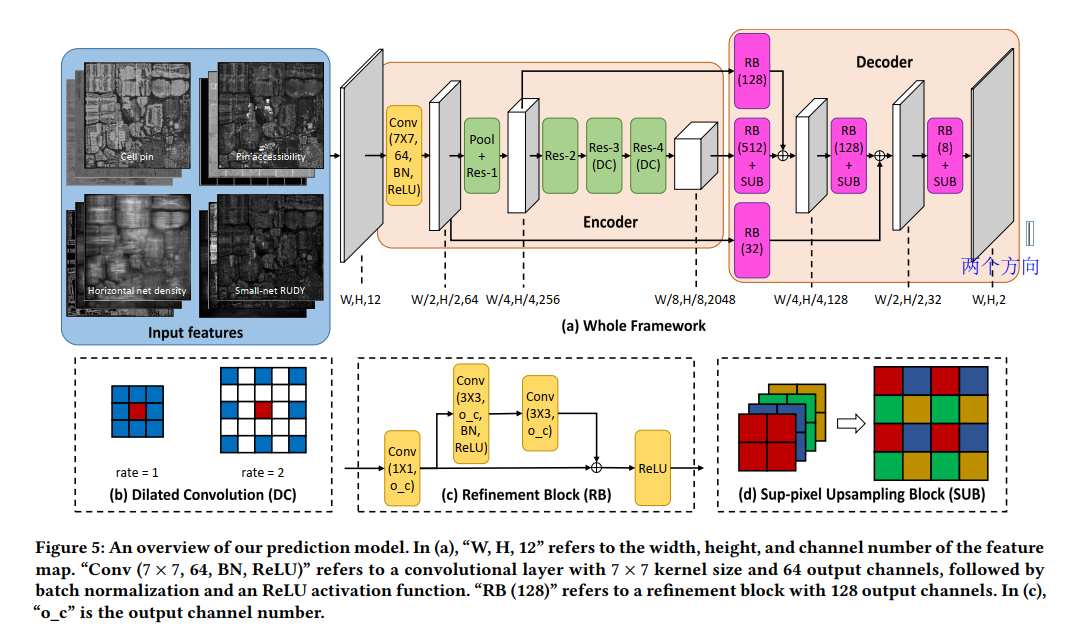
model
data
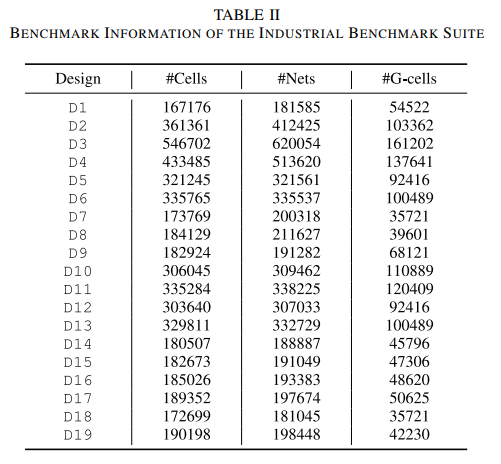
19 different industrial designs
通过不同的placement参数和旋转(CNN原理),一共有1664 design cases in total.
Feature Extraction
Horizontal/Vertical track capacity map
Cell density map
Flip-flop cell density map
Fixed cell density map
Cell pin density map
Pin accessibility map
Horizontal/Vertical net density map
Small/Large-net RUDY map
Pin RUDY map
a combination of cell pin density map and large-net RUDY map
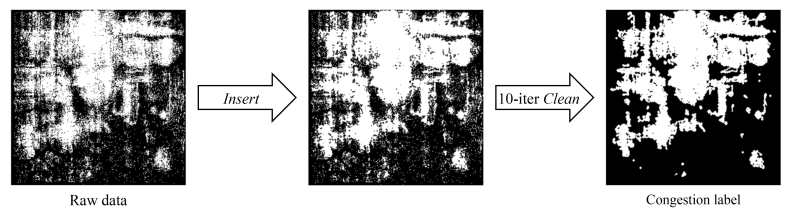
Label Generation
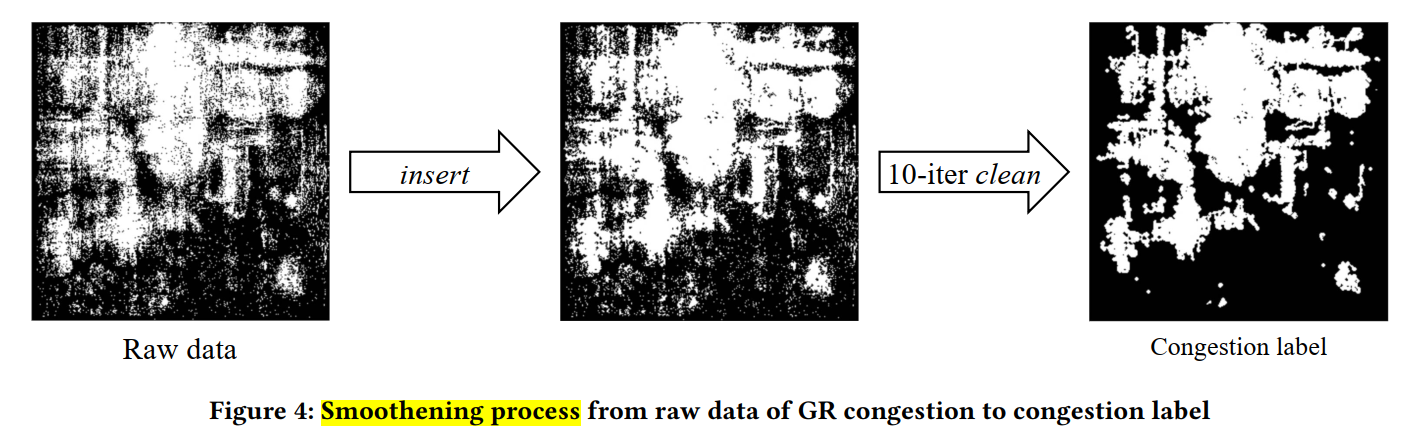 PROS does not need very detailed congestion map
PROS does not need very detailed congestion map
two-step smoothening process to convert raw data to desirable congestion labels
help to make the prediction task easier
if there are at least six congested G-cells out of the eight in the surrounding of a center G-cell д, д will be labeled as congested

优化原理
这两个值在cadence怎么改的? cadence企业内部自己弄的(这是cadence的文章)?
model
experiment
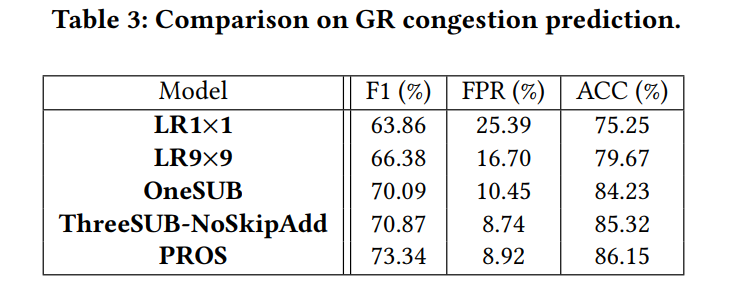
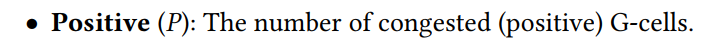
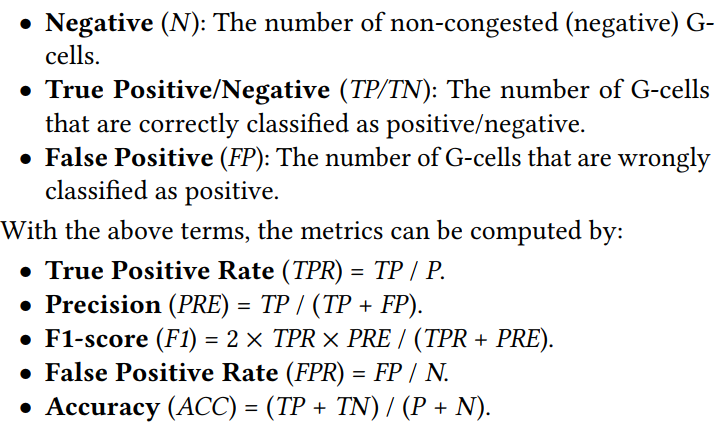
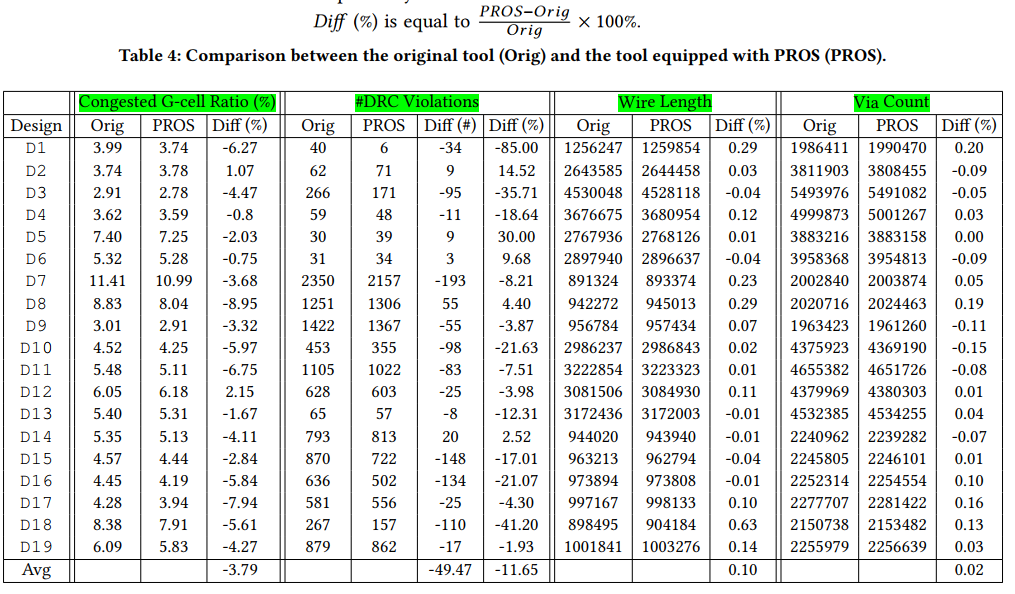
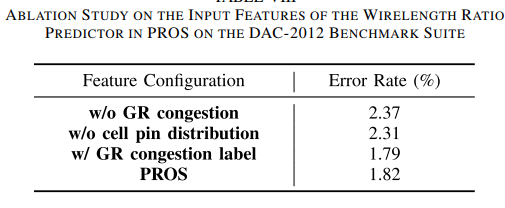
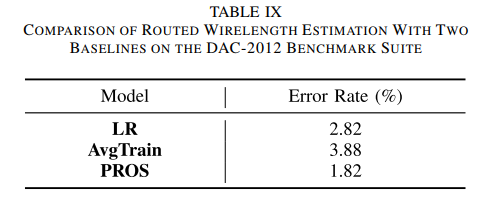
PROS 2.0 - Routability Opt+Route WL estimation-Trans-2023-CNN-CNHK+Cadence #
background
- the amount of routing resources on a design is limited.
- The quality of a GR solution has a great impact on that of the resulted DR routing solution
- Congestion in a GR solution is one of the major causes of DRC violations in the DR solution since most of DRC violations are due to overcrowded wires and vias [1], [2]
- a better GR solution with less congestion is needed to lower the probability of getting DRC violations in advance.
- if the initial GR solution is not good and has a lot of congestion, the GR tool can hardly tackle the problem by rip-up and reroute.
- placement engines [3]–[5] which take routing congestion into consideration are applied
- FCN:FCN常用于图像中的每像素分类问题。采用任意输入大小,并产生大小完全相同的输出。GR拥塞预测也可以被视为任意大小的芯片设计上的像素二进制分类问题(拥塞与否)。因此,基于FCN的预测器可以自然地应用于PROS。
task:
- stage: post-placement, pre-route
- FCN based GR congestion
predictor, use the predicted GR congestion to optimize the cost parameters of GR. - predictor based
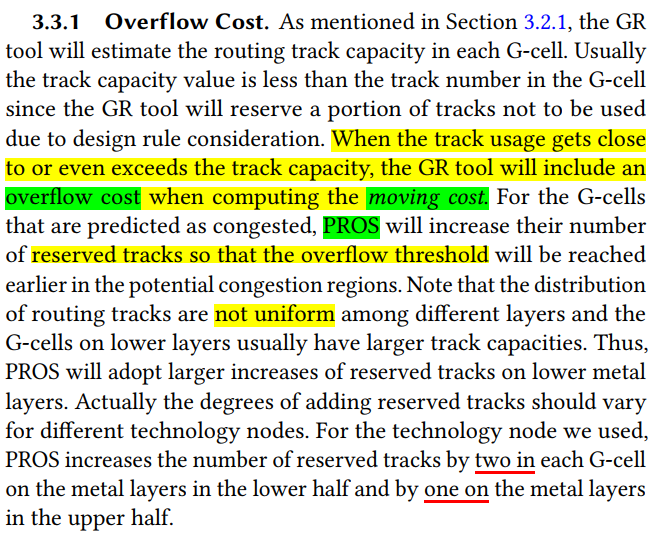
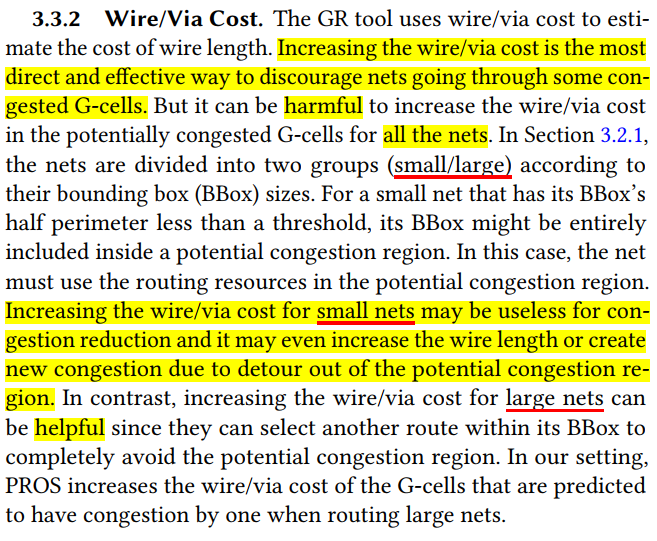
parameter optimizerto generate a better GR solution. GR tools are driven by the cost parameters stored in each G-cell. When arriving at a G-cell g, the tool will compute the cost, calledmoving cost, to move to each of its neighboring G-cells and push these costs into a heap. With optimized cost parameters in G-cells, the GR tool can find better paths and allocate the routing resources to each net more smartly. PROS optimizes two types of cost parameters based on the prediction result, includingoverflow costandwire/via cost. PROS will adjust the cost parameters in the projected congestion regions on all layers- overflow cost
- wire/via cost: divided into two groups (small/large) according to their BBox sizes.
- Increasing the wire/via cost for small nets may be useless for congestion reduction and it may even increase the wire length or create new congestion due to detours out of the potential congestion region.
- In contrast, increasing the wire/via cost for large nets can be helpful since they can select another route within its BBox to completely avoid the potential congestion region
- CNN based
wirelength estimator, By multiplying the predicted wirelength ratio and the precomputedFLUTEwirelength (训练一个系数). The lack of consideration of routing congestion in traditional methods is due to the dif ficulty of quickly obtaining accurate congestion estimation at the placement stage
contribution:
- plug-in for Innovus: it can avoid extra runtime overhead of feature preparation
- industrial design suite
- advanced technology node
- SOTA
- high accuracy
- first work that
- utilizes the information of GR congestion to estimate routed wirelength at the placement stage
- PROS does not change a lot for the original EDA steps
Overall Flow :
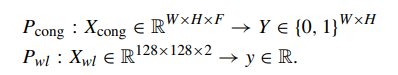
分类和回归

- F is the feature number.
- X
WLhas two features: These two features will be resized to 128 × 128 before prediction- the predicted congestion map
- the cell pin density map
data
feature F
Horizontal/Vertical Track Capacity Map
Cell Density Map
Flip-Flop Cell Density Map
Fixed Cell Density Map
Cell Pin Density Map
Pin Accessibility Map
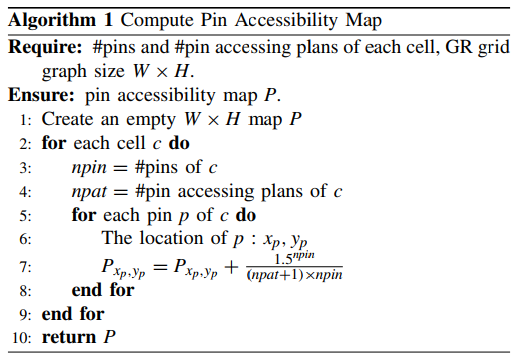
Horizontal/Vertical Net Density Map
Small/Large-Net RUDY Map

Pin RUDY Map ?
label
congestion label pre-process
PROS does not need a very detailed congestion map
最后还是为了优化服务的
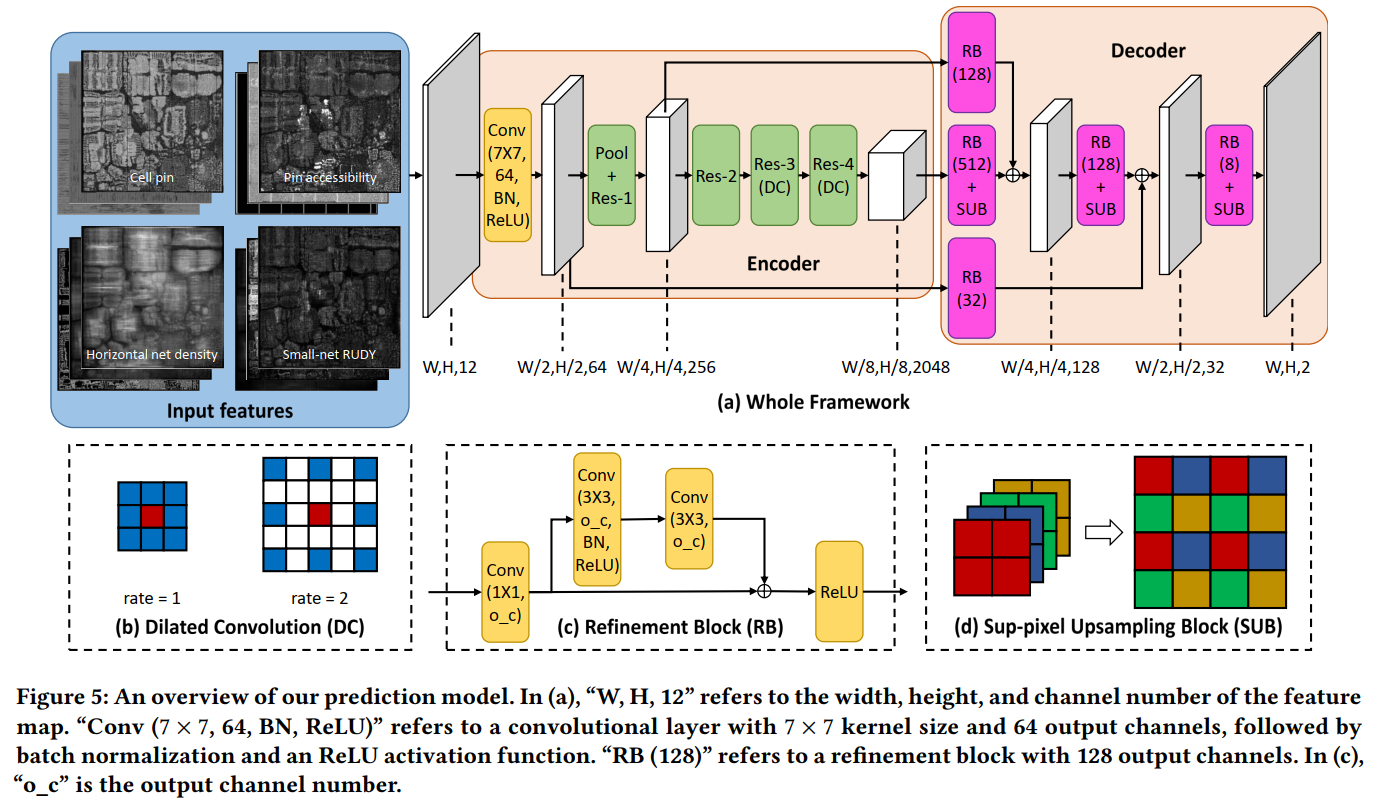
model
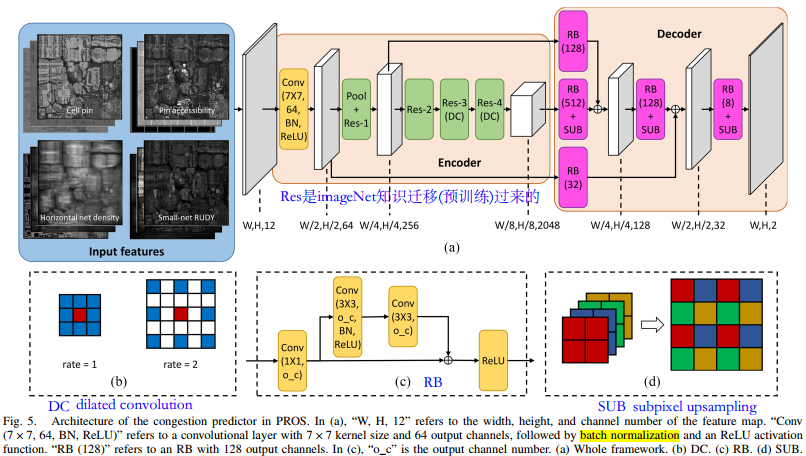
- DC: get more local information, but more GPU usage(acceptable)
- SUB: w*h*4c –>2w*2h*c.
- Compared with bilinear upsampling which is not trainable, subpixel upsampling can learn to recover the local information.
- Compared with deconvolution, subpixel upsampling is parameter free, so it will not significantly increase the training difficulty.
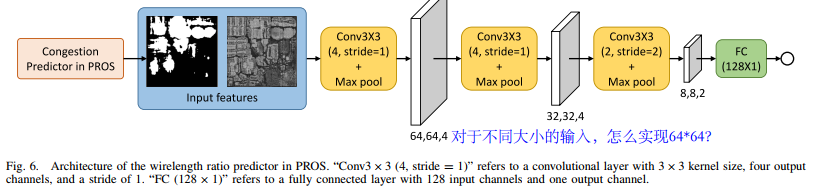
dataset
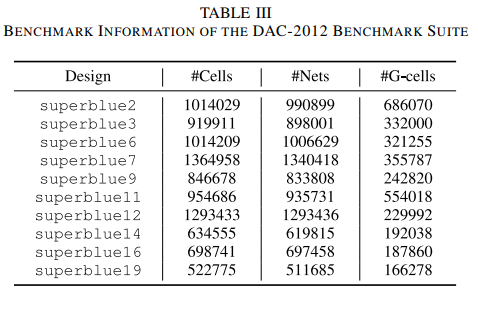
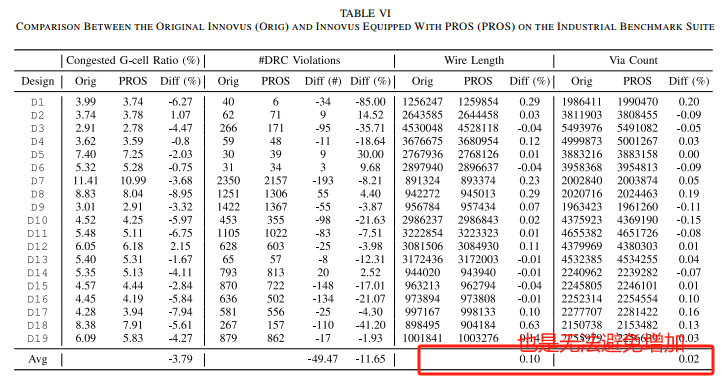
industrial benchmark suite and DAC-2012 benchmark suite(19个 benchmark)
industrial benchmark suite 通过11种不同布局参数,翻转和旋转,制造了一共有1664个(约等于19*11*8)benchmark
DAC-2012 20 different placements
(4, 4, 4, 4, 3) 5折交叉验证
experiment
env
- Tensorflow
- Intel Xeon CPUs at 2.2 GHz
- 256 GB memory
- NVIDIA TITAN V GPU
setting
Adam
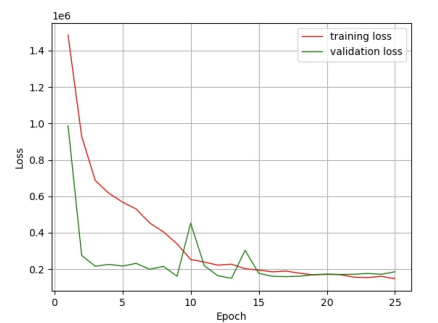
One entire training process of the congestion predictor has 25 training epochs! 这么少(收敛好快)
congestion classification prediction
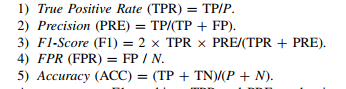
compare with PROBABILISTIC METHODS
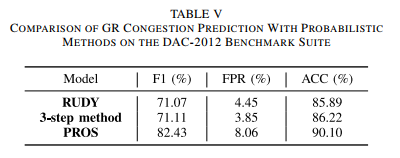
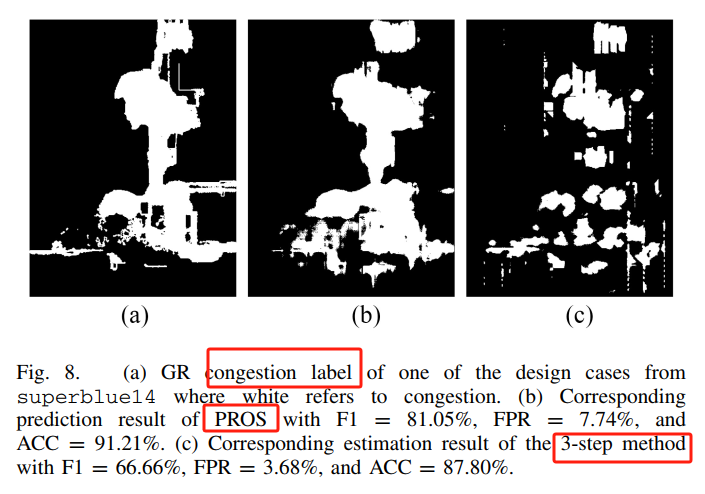

DR优化结果
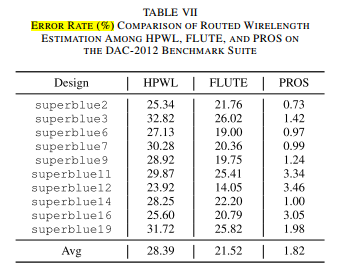
线长估计
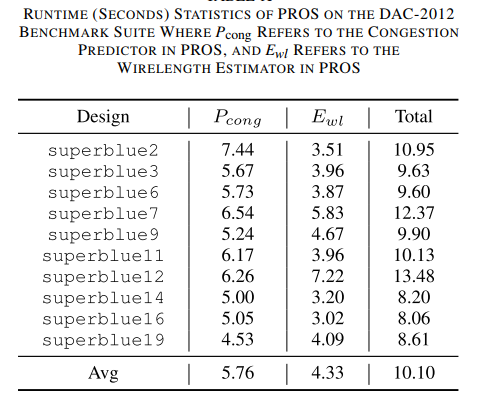
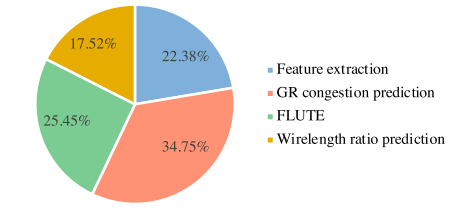
Runtime
detail routing #
background #

-Detailed Router-DATE-2021-RL #
[DPRouter-Detail Routing(package design) Opt+net order decision-ASPADC-2023-RL(MARL)-diagonally route](“D:\MyNotes\EDA\Routing\DPRouter-Detail Routing(package design) Opt+net order decision-ASPADC-2023-RL(MARL)-diagonally route.pdf”) #
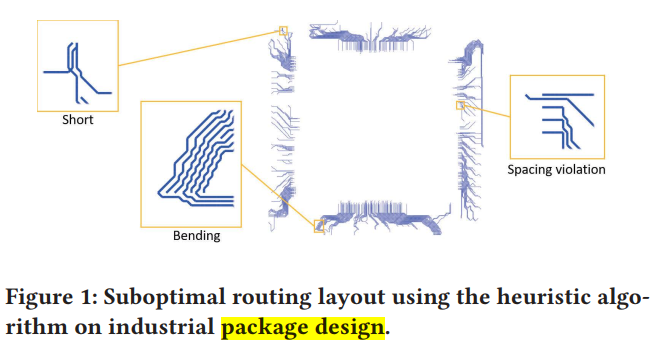
BackGround
- most time-consuming stages in the package design flow
- package designs have fewer layers; thus, we need to prevent net crashing cautiously
contrbution:
- redefine the routing area and shrink the routing problem by dividing the entire design into non-overlapping boxes
- use DRL, not heuristic
- prove the number of design rule violations (DRVs), wirelength and layout pattern.
task
- 2-pin nets

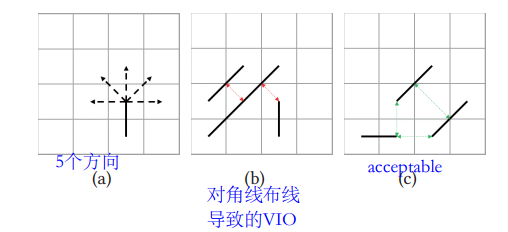
Initial routing: ignores the number of bends and allows design rule violations

Model
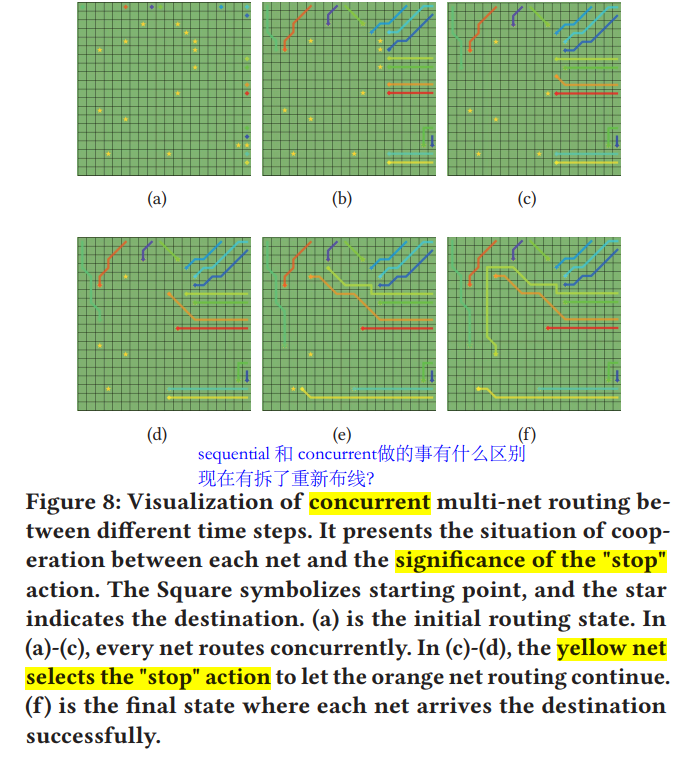
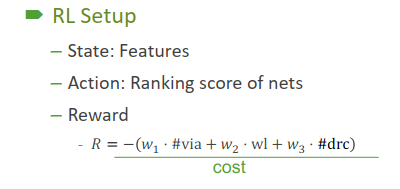
multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MARL) task [15] for asynchronous routing planning between nets. We regard each net as an agent, which needs to consider the actions of other agents while making pathing decisions to avoid routing conflict
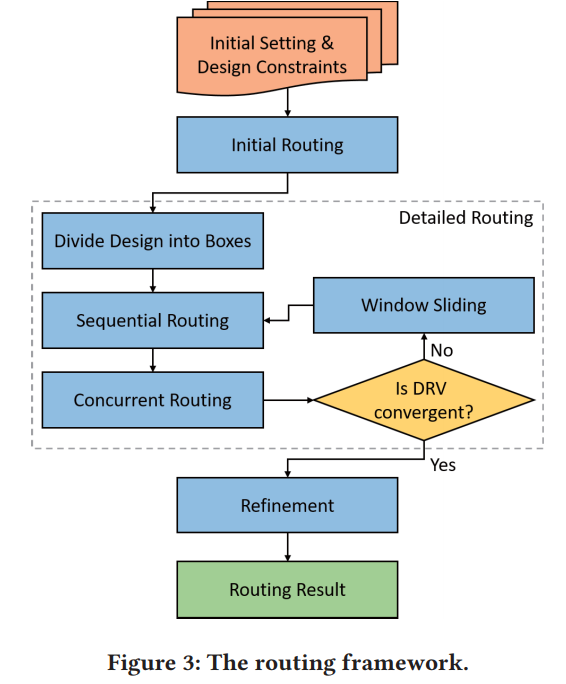
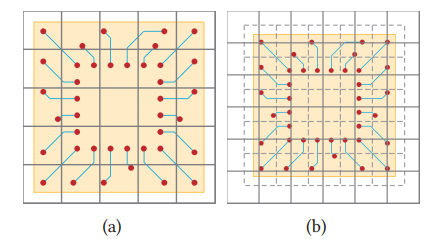
route and slide the window repeatedly. advantage of box:process every box independently
sequential routing
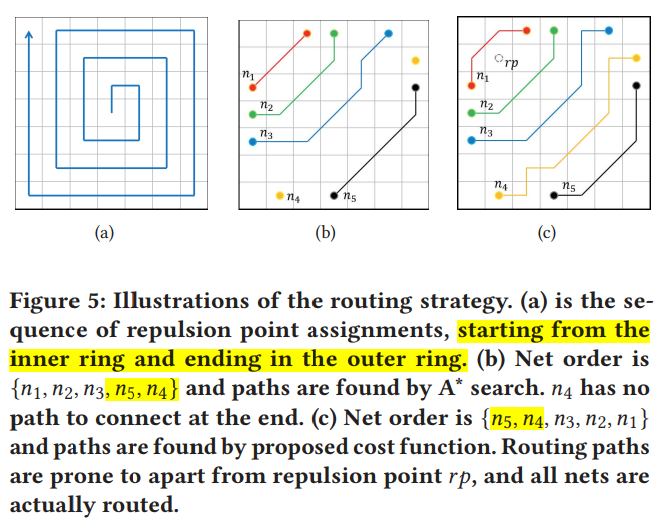

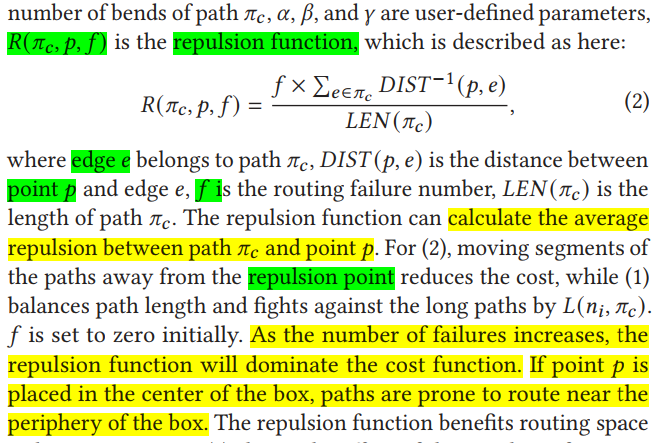
the repulsion point will be moved from the inner ring to the outer one until the box is successfully routed.
具体算法:

sequential routing
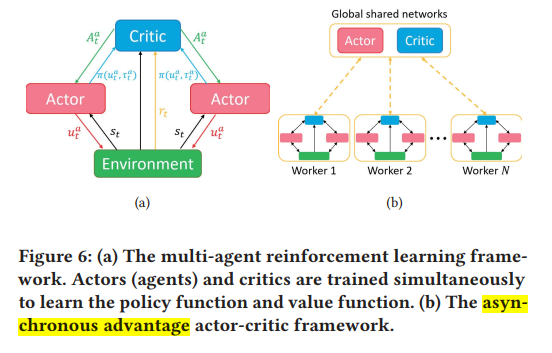
Refinement
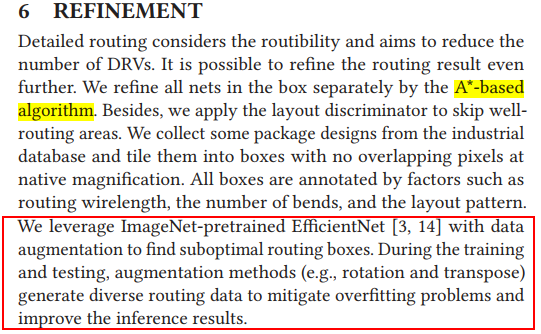
-Detail routing+match+Opt-ISPD-2023-RL+GNN-FinFET #
background:
cutom circuits: a custom detailed router cannot adopt specialized layout strategies for specific circuit classes like human layout experts


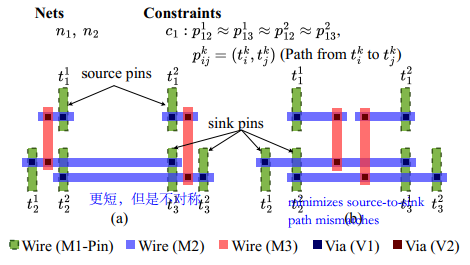
一直在强调match的问题:

contribution
- opt roouting, FinFET, sign-off solution
- 异构图
- A rip-up and re-routing scheme
- can easily adapt to future design constraints
three categories of routing methodologies
- Template-based methods
- manual design
- suffers from scalability issues
- Simulation-based techniques
- provide accurate performance feedback and can be generalized to consider various performance metrics (e.g., phase margin, power dissipation) across circuit classes
- long execution time and resource-hungry computations
- Constraint-based approaches
- widely adopted in existing custom routing studies
PR Tools #
Placement and routing (PnR) is the most time-consuming part of the physical design flow
Placer #
Chip Placement with Deep Reinforcement Learning-marcro-arXiv-2020-RL #
Differentiable-Timing-Driven Global Placement-global placement-DAC-2022-GNN- #
Polar 2.0 #
An effective routability-driven placer
cells that are estimated to have high congestion are spread out and inflated to distribute routing demand more evenly.
NTUPlace3 #
DeepPlace #
flow
RePlAce–TCAD-2018- #
DREAMPlace-GP-DAC+TCAD+ICCAD+DATE-2019~2023 #
introduction
Over 30X speedup over the CPU implementation (
RePlAce) is achieved in global placement and legalization on ISPD 2005 contest benchmarks
DREAMPlace runs on both CPU and GPU. If it is installed on a machine without GPU, only CPU support will be enabled with multi-threading.
DREAMPlace also integrates a GPU-accelerated detailed placer, ABCDPlace, which can achieve around 16X speedup on million-size benchmarks over the widely-adopted sequential placer
NTUPlace3 on CPU.
Publications
- Yibo Lin, Shounak Dhar, Wuxi Li, Haoxing Ren, Brucek Khailany and David Z. Pan, “DREAMPlace: Deep Learning Toolkit-Enabled GPU Acceleration for Modern VLSI Placement”, ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), Las Vegas, NV, Jun 2-6, 2019 ( preprint) ( slides)
- Yibo Lin, Zixuan Jiang, Jiaqi Gu, Wuxi Li, Shounak Dhar, Haoxing Ren, Brucek Khailany and David Z. Pan, “DREAMPlace: Deep Learning Toolkit-Enabled GPU Acceleration for Modern VLSI Placement”, IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (TCAD), 2020
- Yibo Lin, Wuxi Li, Jiaqi Gu, Haoxing Ren, Brucek Khailany and David Z. Pan, “ABCDPlace: Accelerated Batch-based Concurrent Detailed Placement on Multi-threaded CPUs and GPUs”, IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (TCAD), 2020 ( preprint)
- Yibo Lin, David Z. Pan, Haoxing Ren and Brucek Khailany, “DREAMPlace 2.0: Open-Source GPU-Accelerated Global and Detailed Placement for Large-Scale VLSI Designs”, China Semiconductor Technology International Conference (CSTIC), Shanghai, China, Jun, 2020 ( preprint)(Invited Paper)
- Jiaqi Gu, Zixuan Jiang, Yibo Lin and David Z. Pan, “DREAMPlace 3.0: Multi-Electrostatics Based Robust VLSI Placement with Region Constraints”, IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Nov 2-5, 2020 ( preprint)
- Peiyu Liao, Siting Liu, Zhitang Chen, Wenlong Lv, Yibo Lin and Bei Yu, “DREAMPlace 4.0: Timing-driven Global Placement with Momentum-based Net Weighting”, IEEE/ACM Proceedings Design, Automation and Test in Eurpoe (DATE), Antwerp, Belgium, Mar 14-23, 2022 ( preprint)
- Yifan Chen, Zaiwen Wen, Yun Liang, Yibo Lin, “Stronger Mixed-Size Placement Backbone Considering Second-Order Information”, IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Francisco, CA, Oct, 2023 ( preprint)
Architecture
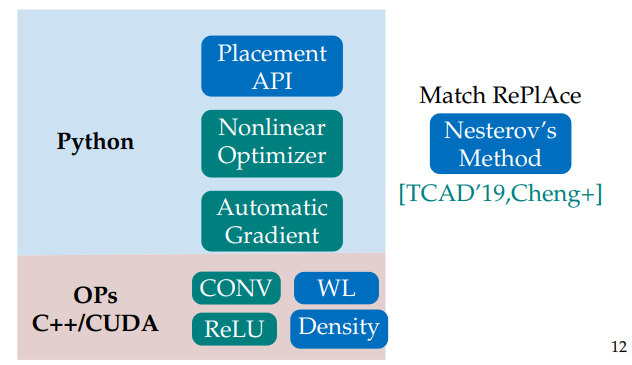
flow
Router #
background #

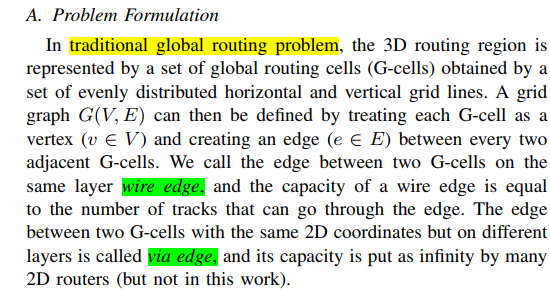
Global routing plays a crucial role in electronic design automation (EDA), serving not only as a means of optimizing routing but also as a tool for estimating routability in earlier stages such as logic synthesis and physical planning.
Optimal(最优) global routing is a NP-complete problem.

DRL:


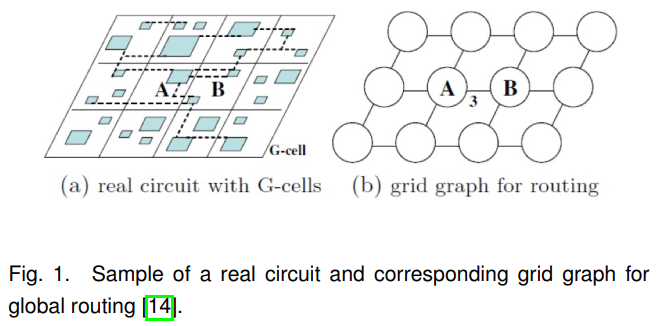
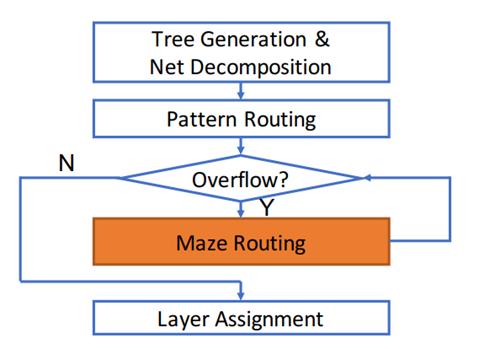
传统2dGR flow
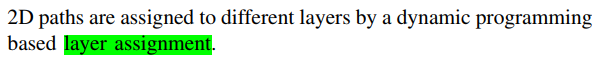
3dGR flow
GR_outdated #
FLUTE #
FLUTE is an RSMT construction algorithm adopting a look-up table approach, which is both fast and optimal for low-degree nets. However, FLUTE is unaware of routing congestion.

下面是一系列FLUTE和基于FLUTE的改进
FastRoute1.0—2006 #
- roposed a simple way to construct congestion driven Steiner tree and an edge shifting technique to further refine it
fastroute 2.0-Monotonic–2007 #
- monotonic routing to explore all shortest routing paths for two-pin connections.
task

flow
fastroute 3.0-virtual capacity-ICCAD-2008- #
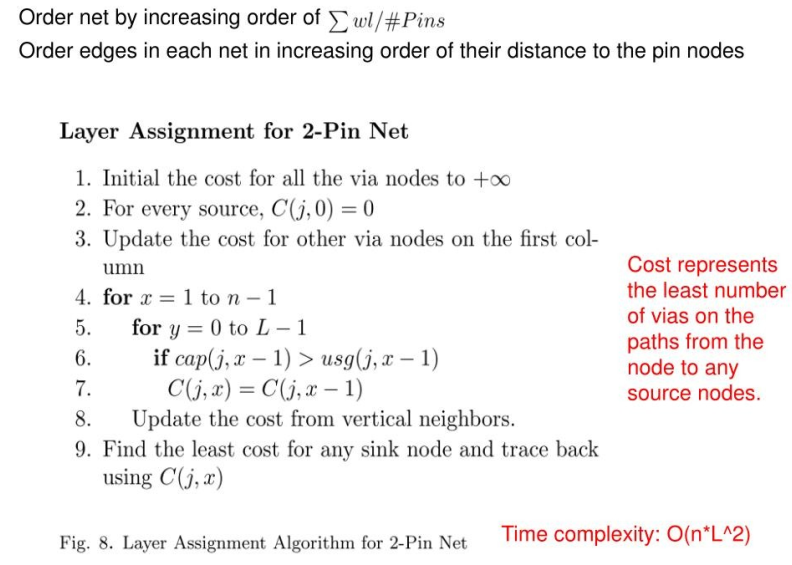
fastroute 4.0-via min tree+3 bending-ASPDAC-2009- #

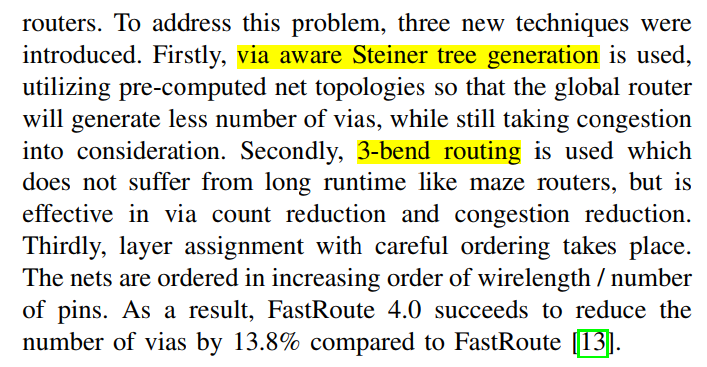
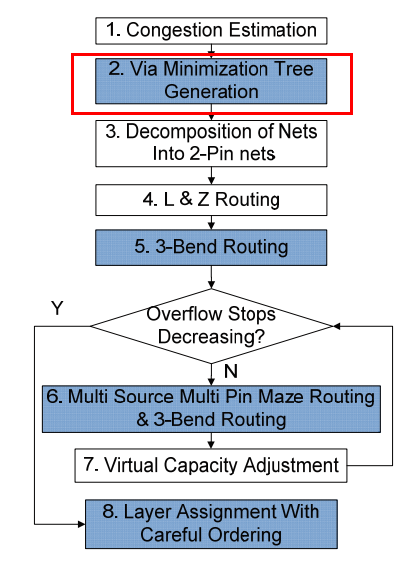


层分配

?
MaizeRouter- #
- 2nd place of ISPD 2007 contest 2D GR
- 1st place of ISPD 2007 contest 3D GR
BoxRouter 1.0 #
- 3rd place of ISPD 2007 contest 2D GR
- 2nd place of ISPD 2007 contest 3D GR
- integer linear programming (ILP) based
FGR-3d-TCAD-2008- #
- 1st place of ISPD 2007 contest 2D GR
- 3rd place of ISPD 2007 contest 3D GR
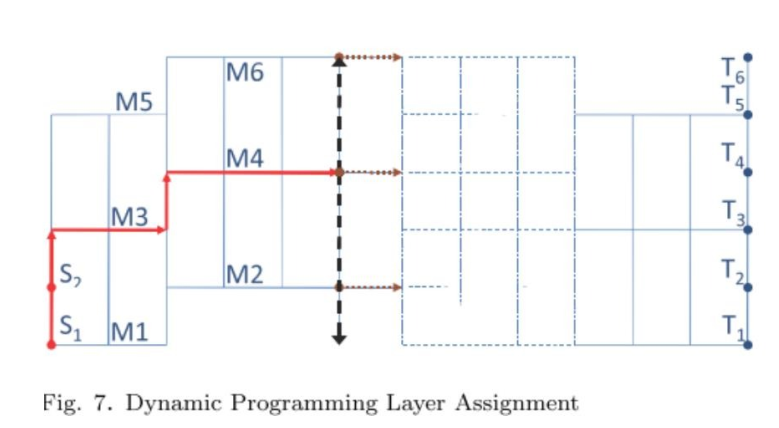
-Layer assignment+Via minization-Trans-2008-DP-NTHU #
- Congestion-Constrained Layer Assignment for Via Minimization in Global Routing
- CUGR’s rely work
- ISPD07 contest后的一个跟进工作
- 也没提到maze routing
- 没定义wire cost, 在每一对GCell之间layer assignment, 慢?
- 第一次用DP?
background:
there are two main approaches
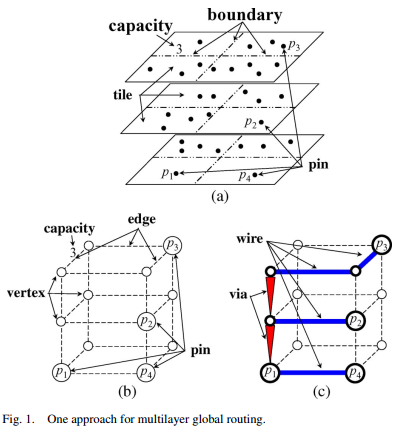
3D: route all nets directly on the multilayer solution space. Because this approach directly generates a multilayer global routing result, it can take the via cost into account during construction. However, this method may cost too much CPU time with a large problem size. (现在都用GPU做并行了,这种方法就变多了)such as

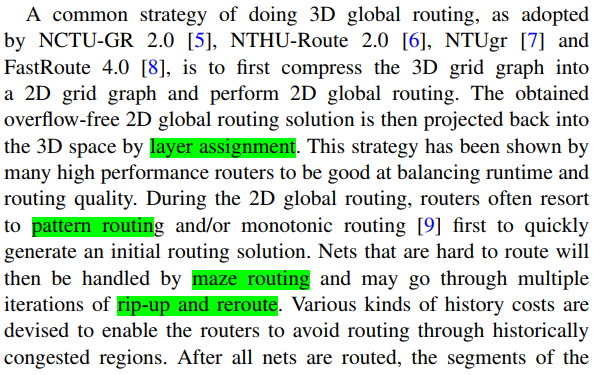
2D + layer assigment: The other approach is to first compress a multilayer grid graph into a one-layer grid graph, then use a one-layer router to solve the one-layer global routing problem, and finally perform layer assignment to assign each wire in the multilayer grid graph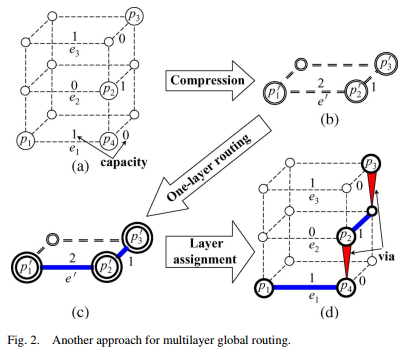
The edges corresponding to vias disappear in the one-layer grid graph. The capacity of each edge in the one-layer grid graph is obtained by accumulating the corresponding edge capacities in the three-layer grid graph
This approach can take advantage of many current full-fledged one-layer routers, e.g., [2]–[4], and use an affordable run time to generate an initial one-layer routing result. 本文主要针对layer assignment. 注意layer assignment 是对二维的所有边进行层分配。
vias not only degrade the reliability and the performance of a design but also increase the manufacturing cost.
previous work’s layer assignment use greedy heuristics [8] or time-consuming integer linear programming methods [9] to minimize the via cost.
像这种串行的还是要考虑net order, 越早布线的net越不会拥塞,net order很重要
task and contribution:
- 这篇没有考虑优先方向(To simplify the presentation of our algorithm, we do not make any assumption about the preferred routing direction for each layer in the layer assignment problem.)不过也说明了这个工作能够很简单引用到考虑优先方向的情况
- follow ISPD07 contest, 假设via的capacity是无限的(CUGR中明确了不进行这种假设)
- based on a one-layer routing result
- minimize
via cost,WLandcongestion overflow - propose a polynomial-time algorithm: first generate
net order, then solves the layer assignment problem - can improve 3 winner of ISPD07 contest
model
COngestion-constrained Layer Assignment (COLA)’s submodule
Net order generation
The net order has a direct influence on the utilization of routing resources, so it is one of the key parts of COLA.
对net进行打分决定order
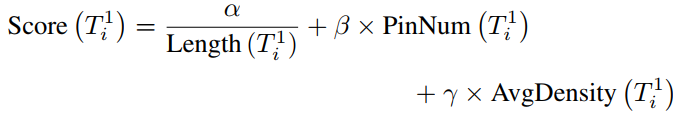
注意,线长越短,分数越高,net越应该先布线。解释:
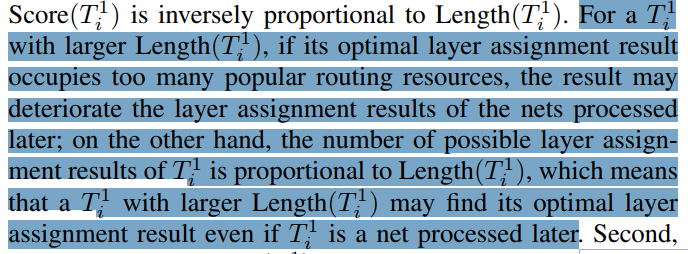
Eemove Cycles
Arbitrarily remove.
(为什么映射到第一层会有cycles?初始是怎么连起来的?没说?FLUTE算法是08年才出来,可能当时还没用上)
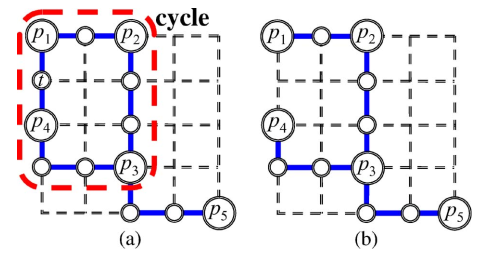
Single-net layer assignment (SOLA+APEC)
SOLA(Singlenet Optimal Layer Assignment)
determines an optimal layer assignment result without considering congestion constraints for a given net
dynamic programming technique
不考虑拥塞,这个方法能得到最好质量
step:
01: for tree in layer 1, random select a pin as root, then use DFS or DFS to get a queue, so get the edge order. It become a DAG
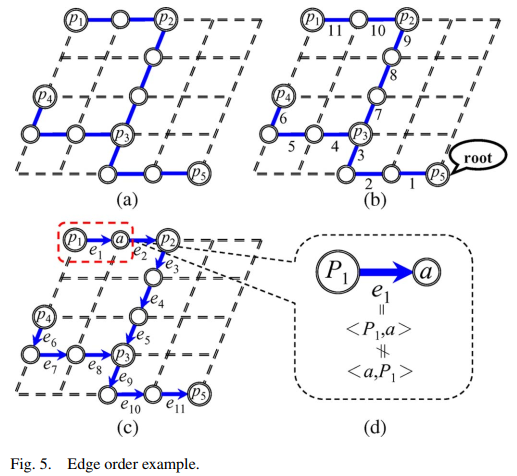
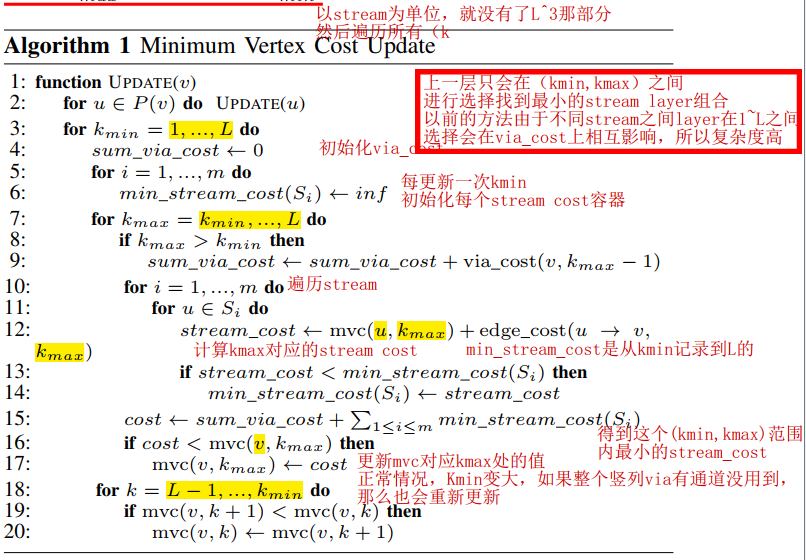
02: 定义图5(c)中, a的父节点是p2,定义mvc(v, r)(minimum via cost)
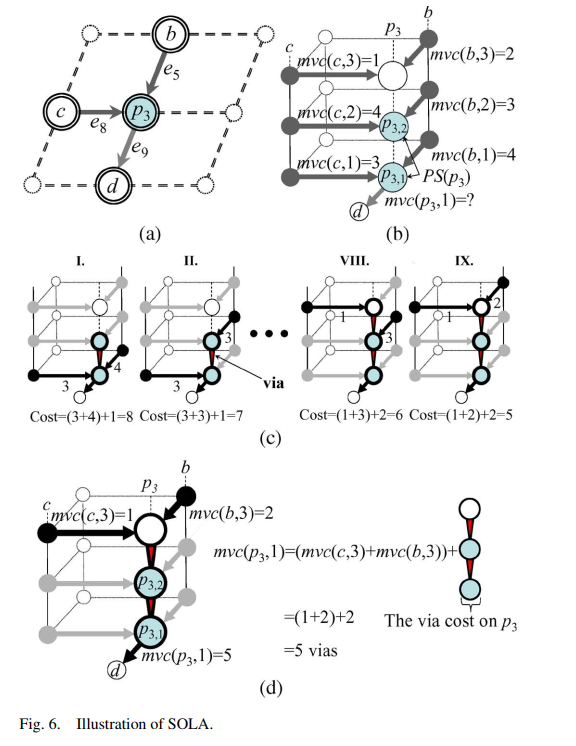
03:
for pins who have not child, mvc:
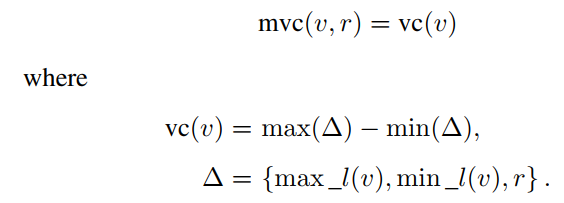
for pins who have child and not root:
这个公式其实就是为了确定下每个点下一步的layer在哪里。比如算出最小是mvc(v, 1), 那么e_(v, ch(e))就在第r层
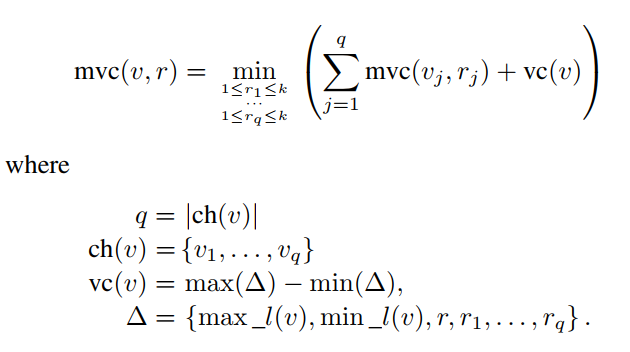
for root:
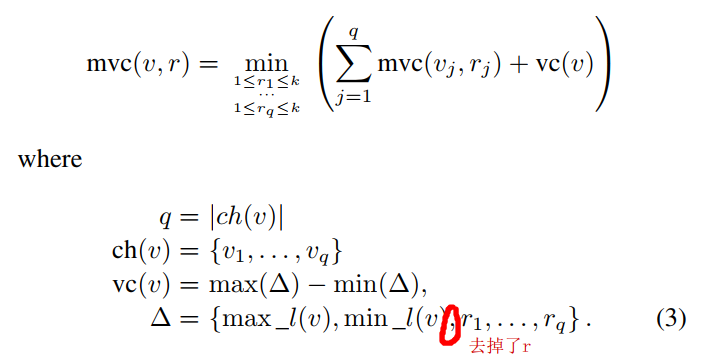
the difference is excluding r in ∆
because mvc(v, r) does not depend on the value of r when v
is the root, we have mvc (v, 1) = mvc(v, 2) = · · · = mvc(v, k)
APEC(Accurate and Predictable Examination for Congestion constraints)
can detect and prevent any congestion constraint violation in advance
prevention condition:
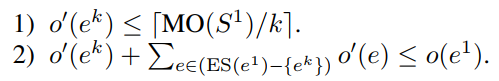
如果存在一个在layer1上压缩的边不满足这两个condition,那么这条边的layer assignment(SOLA)结果就不可能满足congesion
SOLA+APEC always finds a layer assignment result satisfying both prevention conditions for each net
COLA
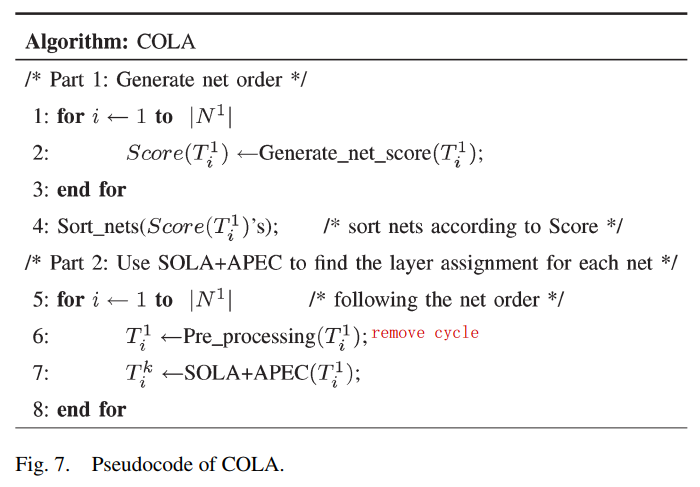
data:
six-layer benchmarks from ISPD’07
GRIP-3d+IP-DAC-2009 #
基于整数规划
3d: solve the 3D problem directly on the 3D routing grids,
slow: Although theoretically the direct 3D technique should produce better solutions, in practice it is less successful in both solution quality and runtime than 2D routing with layer assignment –cite–> [Fastroute4.1]
slow: Although we see solutions with shorter wirelength generated by full-3D concurrent approach like GRIP [21], that solution quality is achieved by impractically long runtime –cite–> [Fastroute4.1]
multi-level (coarsened and fine-gained)
FastRoute4.1-an efficient and high-quality global router-2012 #
https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1155/2012/608362
background
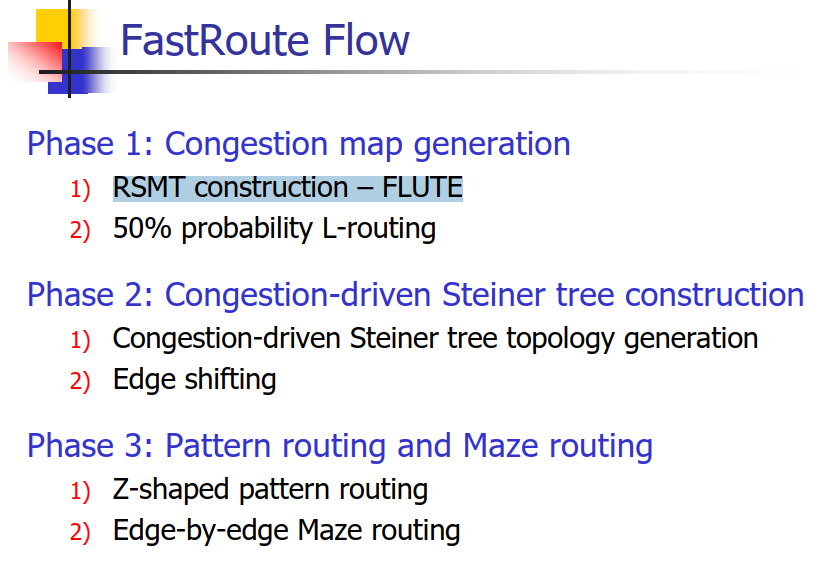
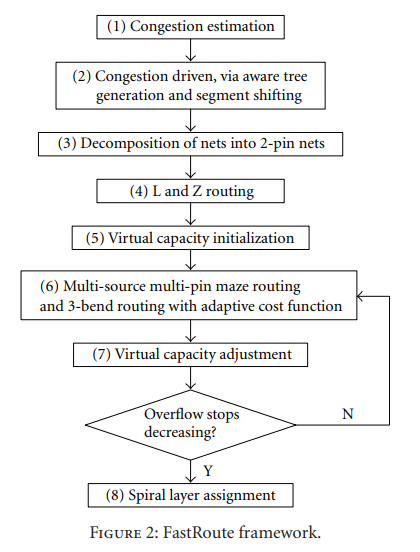
FastRoute is a global routing tool for VLSI back-end design. It is based on sequential rip-up and re-route (RRR) and a lot of novel techniques. FastRoute 1.0 first uses FLUTE to construct congestion-driven Steiner trees, which will later undergo the edge shifting process to optimize tree structure to reduce congestion. It then uses pattern routing and maze routing with logistic function based cost function to solve the congestion problem. FastRoute 2.0 proposed monotonic routing and multi-source multi-sink maze routing techniques to enhance the capability to reduce congestion. FastRoute 3.0 introduced the virtual capacity technique to adaptively change the capacity associated with each global edge to divert wire usage from highly congested regions to less congested regions. FastRoute 4.0 proposed via-aware Steiner tree, 3-bend routing and a delicate layer assignment algorithm to effectively reduce via count while maintaining outstanding congestion reduction capability. FastRoute 4.1 simplifies the way the virtual capacities are updated and applies a single set of tuning parameters to all benchmark circuits.
model
flow
NTHU Route 1.0- -TVLSI-2010- #
NTHU Route 2.0- -TCAD-2013 #
2D
NCTU GR 1.0-3D-congestion relaxed layer assignment- 2011- #
- it improved the scheme to estimate the realtime congestion more accurately by using a history term that will gradually wear off as the number of iterations increases if the overflow disappears.
NCTU GR 2.0-Multithreaded Collision Aware- CAD-2013- #
people.cs.nycu.edu.tw/~whliu/NCTU-GR.htm
PengjuY/NCTU-GR2: This is a binary file of NCTUgr2, which is a global router
- net-level parallel method
- 2D
BoxRouter 2.0 #
background
task
是一个2d的
整数规划
OGRE- new cost function- -2019- - #
- Open source!
- LEF/DEF-based
- 3D
- 用的是老方法,不过解释的挺清楚的
- components by a group of undergraduate students as a course project.
GR_Adv #
-DRL method-2019-DRL- #
task
- DRL(DQN) for global route
- have not use real world design
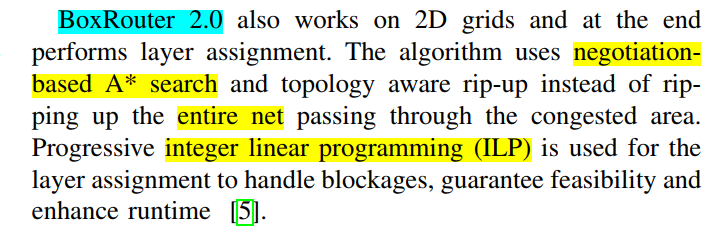
example:
from A to B
read means over flow
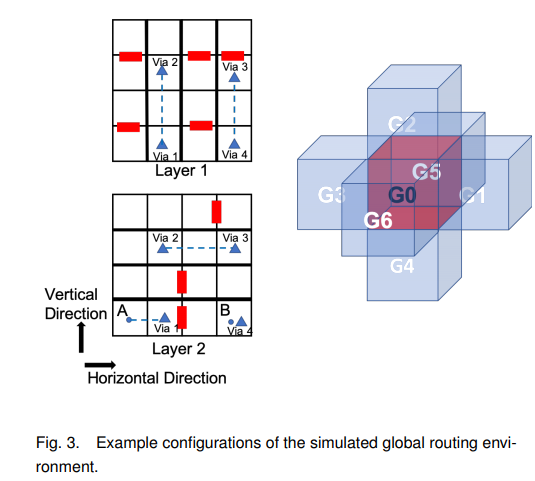

pipeline
model
state:
- (pos_x/y/z, distance_x/y/z, 周围的capacity, )这种编码方案可以被视为当前状态、导航和本地容量信息的混合
action: 上下左右前后
reward:
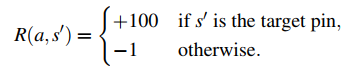

contribution
first deep learning model for global routing
-only CNN-DAC-2020-CNN(VAE)- #
- no experiment!
- 只用CNN分类结果不会好吧
- 不知道是什么类型的文章,只用了两页
background
is approach treats the global routing problem as an image processing problem and solves it with a deep learning system
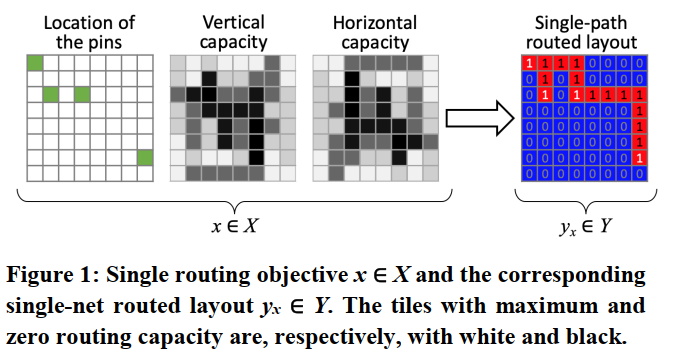
dataset
ISPD’98 ibm01 64x64 circuit
model
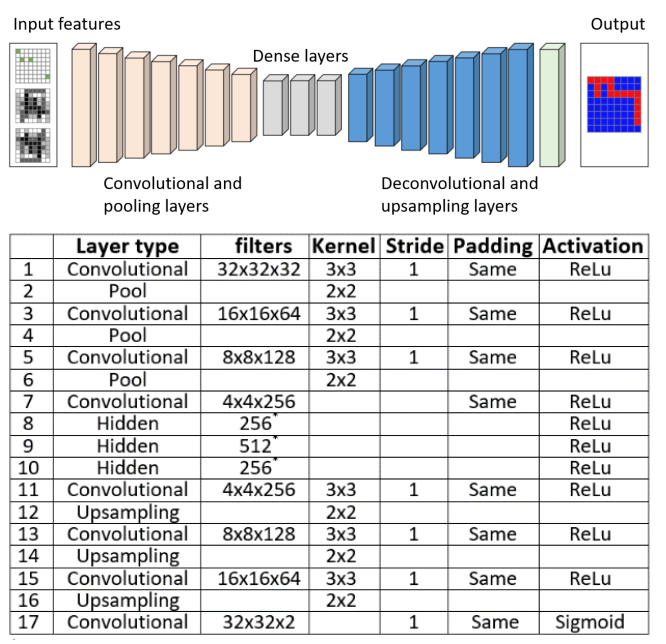
-DRL-arxiv-2021-JP #
[SPRoute 1.0: A Scalable Parallel Negotiation-based Global Router-ICCAD-2019]( IEEE Xplore Full-Text PDF:) #
task
基于net-level多线程的并行加速迷宫算法
negotiation-based rip-up and reroute two-phase maze routing
resolves livelock issue
open source
- introduced a concept called
soft capacityto reserve routing space for detailed routing and exploredseveral parallelization strategiesto speed up global routing.
background
总体
In many global routers, maze routing is the most time-consuming stage.

challenge

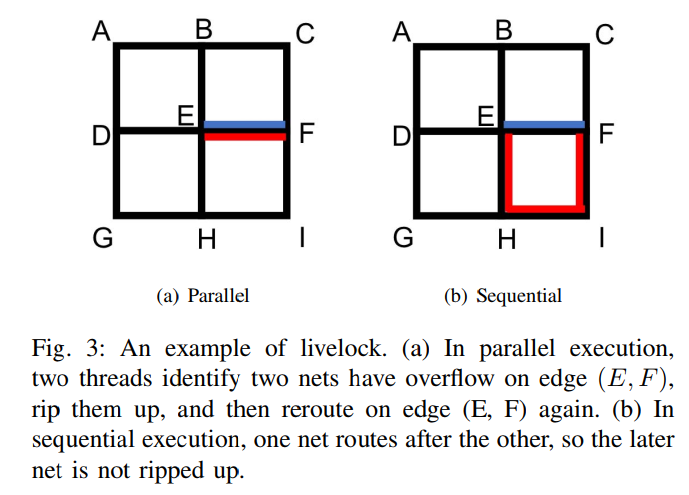
因为这个现象,多线程反而慢了
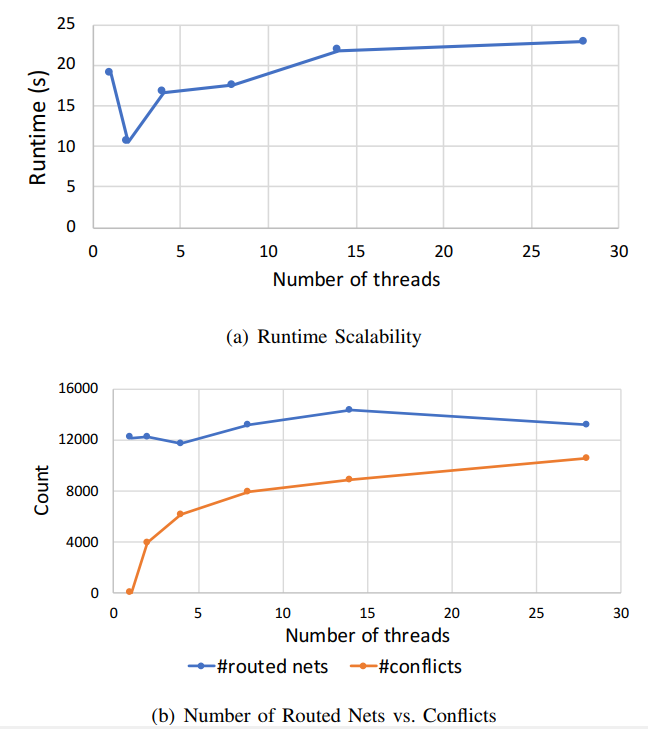
原理
Galois system
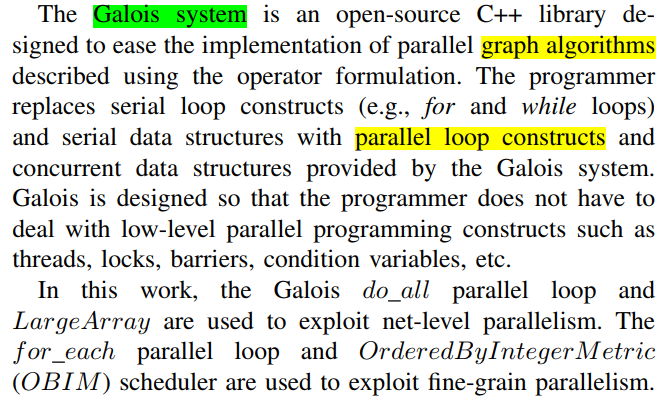
Net-level Parallelism
Fine-grain Parallelism
data
ISPD 2008 contest
SPRoute 2.0- detailed routability driven-ASP DAC-2019- #
特点
基于多线程的并行加速
2D
开源: asyncvlsi/SPRoute: A parallel global router using the Galois framework
CUGR-3D pattern+Multi level maze routing+patching-DAC-2020-CUHK #
ICCAD 2019 Contest First Place
3d+多线程+
这个文章没有讨论prefer direction
多线程体现在哪里?
注意:这种格式的GR输出可以适配Innovus
time-complexity of 3D pattern routing is $\mathcal{O}(L^4|V|)$
compare with [Trans-2008](# -Layer assignment+Via minization-Trans-2008-DP-NTHU), CUGR reduces the complexity to $\mathcal{O}(L^4|V|)$ by selecting the root carefully so that each vertex will have at most three preceding vertices instead of four.
注意,这里说 相比[Trans-2008](# -Layer assignment+Via minization-Trans-2008-DP-NTHU)的$\mathcal{O}(L^5|V|)$ ,它的复杂度是$\mathcal{O}(L^4|V|)$ ,感觉是放在了[Trans-2008](# -Layer assignment+Via minization-Trans-2008-DP-NTHU)进行不转弯的DP-based layer assignment方法上了,实际上按照本文说的方法,理论上是$L * L^{23}|V|$,因为CUGR每次是对一个L pattern为单位计算.确实是$L^4$, CUGR对一个L pattern分了两部分计算mvc,时间复杂度是$2L*L$mvc没一部分时间复杂度是$L*2$
background
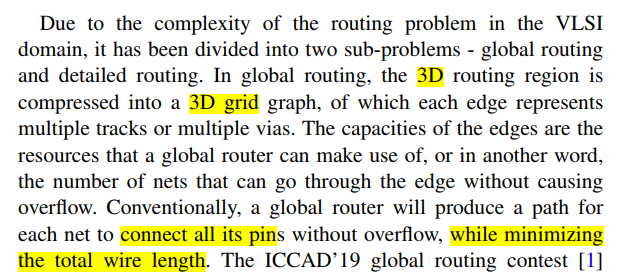
- A common strategy of doing 3D global routing, as adopted by NCTU-GR 2.0 [5], NTHU-Route 2.0 [6], NTUgr [7] and FastRoute 4.0 [8], is to first compress the 3D grid graph into a 2D grid graph and perform 2D global routing.
- directly route the nets in a 3D grid graph:FGR [10] , GRIP [11] , MGR [12]
- Traditional pattern routing generates 2D topologies only, while our proposed 3D pattern routing directly generates 3D topologies without the need of an extra layer assignment stage
- 使用DR结果进行多角度metrics 评估:

task
- detailed-routability-driven directly-3d multi thread GR
contibution
- probability-based cost scheme
- minimizing the possibility of overflow after detailed routing
3D pattern routingtechnique (2D pattern routing + layer assignment)(前面又说directly in the 3D space?)- without overflow even only L shape patten routing
- pre-work[15] 是先在2d上进行pattern routing, 然后进行layer assignment, 这里是直接在3d进行pattern routing. 3d pattern routing can avoid loss of accuracy caused by compressing 3D grid graph to 2D
multi-level maze routing:- coarsened level –> searches for a region with the best routability. first narrows the search space to a smaller region
- fine-grained level –> searches for a lowest cost solution within the region
- patching mechanism
- further improve the detailed routability
flow
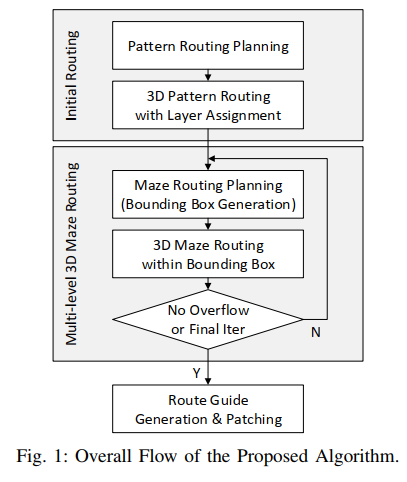
In 3D pattern routing (inital routing), the nets are broken down into two-pin nets, and a dynamic programming based algorithm will route the two pin nets sequentially using Lshape patterns and stacking vias at the turns.
In the multi-level 3D maze routing phase, the grid graph is coarsened to shrink the routing space, and maze routing is first performed in the coarsened space with an objective to find a routing region with the highest routability. A fine-grained maze routing will then search for a lowest cost path within the region. use its patching mechanism here.
model
Gcell之间的容量等于track,一般GR表征via的容量是无限的,但是在本文中不是
three base definition:
- resource = capacity - demand
- 这三个变量在GCell和wire_edge上都有特征,也就是说有6个值
- resource 能够直接表示拥程度
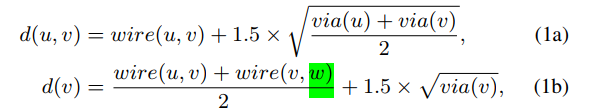
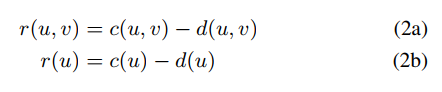
cost scheme
主要分成wire和via两部分:
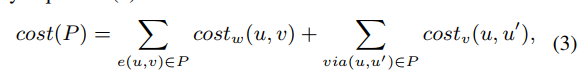
wire cost:
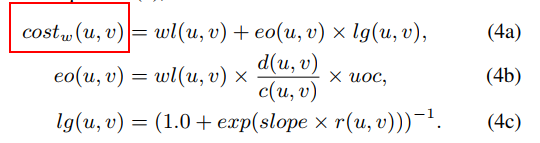
*
wl*is wire lenght costeois expected overflow cost, whereuocis hyper parameter, The largerd(u, v)is, the more likely it is to be congested. is accurate if the DR adopts the simplest strategy of picking a track randomly to route. However, most well designed detailed routers will do much better than random selection.lg(u,v)is a variable to refined(u, v). “+1” 是为了值域在(0,1)表示概率。slopeis hyper parameter. When the resources are abundant, there is almost no congestion cost, but the cost will increase rapidly as the resources are being used up and will keep increasing almost linearly after all the resources are used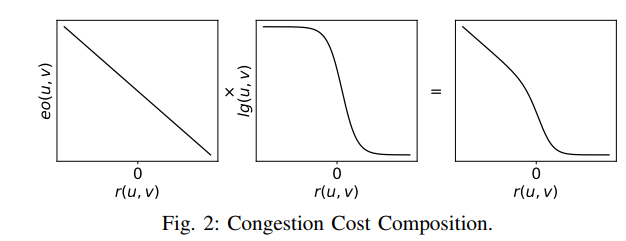
via cost:
- thanks to our 3D pattern routing strategy, a via cost scheme can be embedded to reflect the impact.
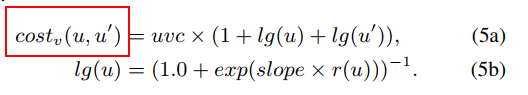
uvcis hyper parameter.- 公式(5a)为什么要“+1”
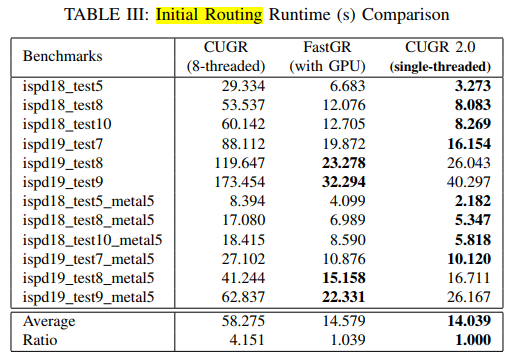
Initial Routing / 3D Pattern Routing
use
FLUTEfirst (not congestion awared)use
edge shifting(described in FastRoute) to alleviate congestion.randomly choose one node in net, use DFS to get a queue and then get a DAG
类似[15],动态规划选择cost最小的3d L pattern,每个L pattern有(2 * L * L)种可能
最后在root处得到最终的结果
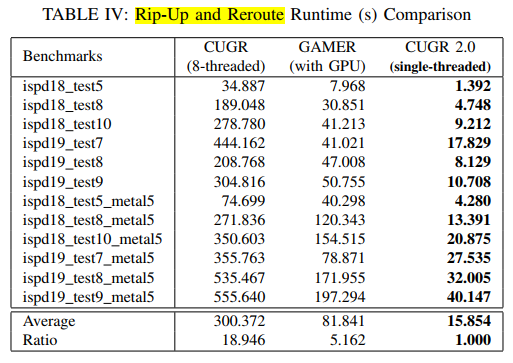
Multi-level 3D Maze Routing
maze route planing
aims at finding a smaller but highly routable search space
compress a block of G-cells (5x5 in our implementation), use avg to descripe
capacity, demand, resourcecost function:
得到灰色粗网格:

之后会在这几个BBox中分别进行计算
cost scheme,得到上图黑色实线
fine-grained maze routing within guides
Postprocessing / Guide Patching
we can add new guides to improve detailed routability. adding new stand-alone guides to alleviate routing hot spots.
three kind of patching:
Pin Region Patching
most effective
the ideal way of improving pin accessibility is to identify those hard-to-access pins and assign more resources to them
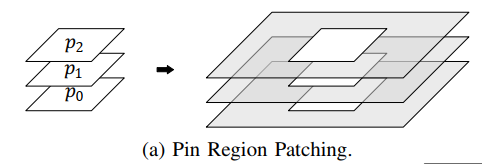
Our global router will check the upper (or lower) two layers of a pin, which are vital for accessing the pin. use 3 × 3 patching guides.
没写判断
hard-to-access pins的具体的方法
Long Segment Patching:
- a longer routing segment often means more wrong way wires and causing more congestion.
- If a guide is longer than a specified length I, we’ll consider long segment patching.
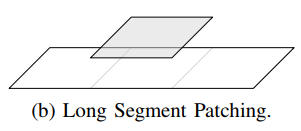
- if a G-cell with resource below a threshold T is encountered, a single G-cell route guide will be patched above or below it, depending on which of them has sufficient resource
Violation Patching:
For G-cell with inevitable violations, patching will be used again to enable the detailed router to search with more flexibility.
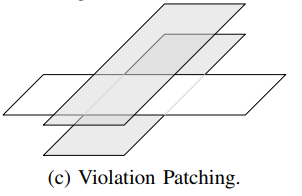
data
iccad 2019 dataset
experiment
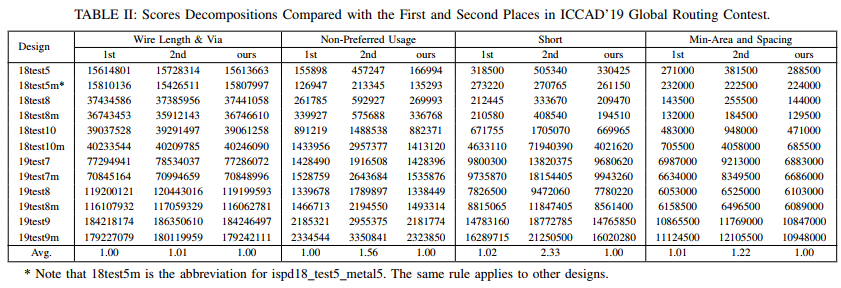
他自己又比赛后改进了
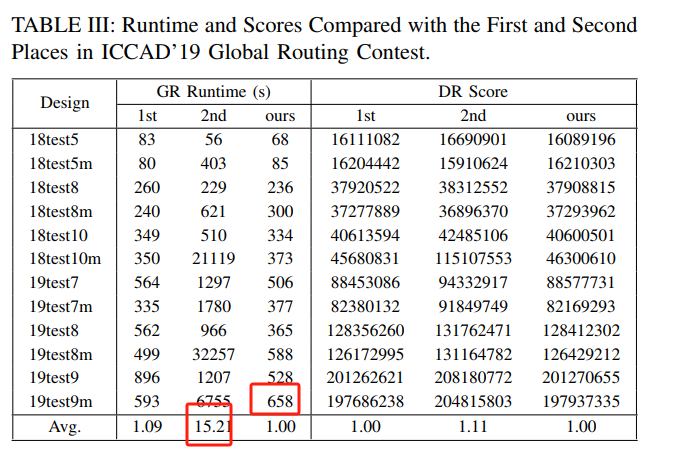
our algorithm’s peak memory is close to the first place and is 1.83 times of that of the second place on average (ours is 8.22 GB on average and is 19.8 GB for
the biggest design)
FastGR-GPU pattern routing+ multi thread maze–DATE-2022-PKU+CUHK+HNAL #
- GPU-accelerated
- accelerated the 3D pattern routing algorithm of [CUGR](#
CUGR-3D pattern+Multi level maze routing+patching-DAC-2020-CUHK) for initial routing by both
net-levelandpath-levelparallelization on GPU
Gamer- -Trans-2022- - #
- GPU-accelerated
- accelerated the two-level maze routing of [CUGR](# CUGR-3D pattern+Multi level maze routing+patching-DAC-2020-CUHK) for rip-up and reroute by updating vertical and horizontal routing costs alternatively on GPU
GGR-super fast gpu accelerate-ICCAD-2022- #
open source! Xplace/cpp_to_py/gpugr at main · cuhk-eda/Xplace
background

Performance depends on the detail route
Modern global routing problem, which was introduced at the 2019 CAD contest at ICCAD, targets at closing the gap between global routing and detailed routing. The LEF/DEF files for detailed routing are directly used as the input for global routing.
The global routing quality is evaluated using an academic detailed router Dr. CU[8]
2019 ICCAD contest on global routing did not directly evaluate global routing results based on overflows and total wirelength. The new evaluation uses the global routing results as route guides for a detailed router, and the metrics are all detailed routing related
2D & 3D
NCTU-GR 2.0[13], SPRoute[7] and FastRoute 4.0[14] are 2D GR
However, compressed 2D grid graphs are less accurate than 3D grid graphs in terms of routing resources, which could limit the global routing quality.
CUGR[11]. It has both 3D pattern routing and 3D maze routing
multi-thread vs GPU
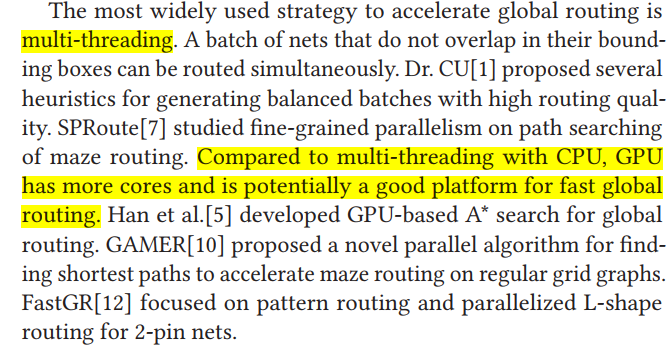
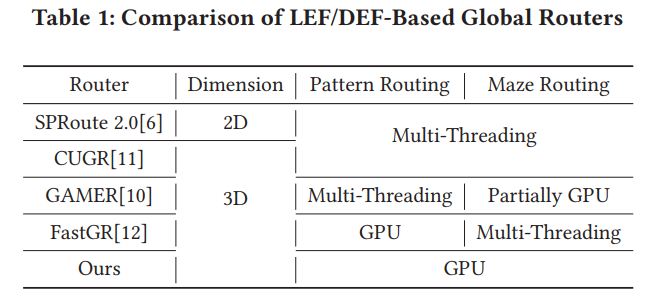
LEF/DEF based academic global routers SPRoute 2.0[6] is the only 2D GR
GAMER[10] is a novel parallel maze routing algorithm integrated in CUGR.
FastGR[12] introduced GPU parallelization of L-shape pattern routing
contribution

flow
data
model
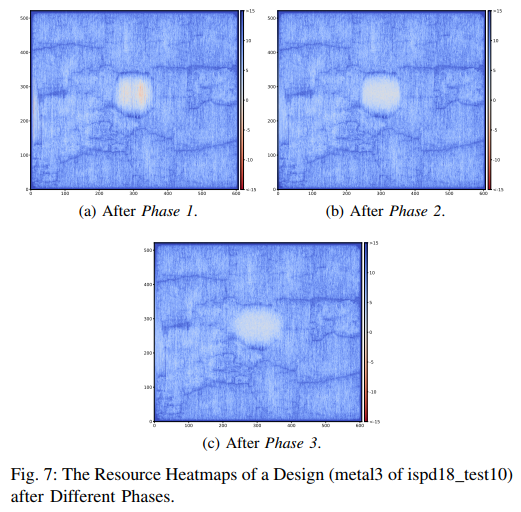
CUGR 2.0-DAG-based-DAC-2023- -CUHK #
background
- many of the aforementioned global routers is that most of them rely heavily on time-consuming path search algorithms like maze routing to resolve overflows. These approaches are not efficient enough even with parallilization and may cause lots of unnecessary detours
contribution:
a DAG-based generalized pattern routing algorithm
a new
dynamic programming-basedalgorithm to calculate the routing costtime complexity from $\mathcal{O}(L^4|V|)$ to $\mathcal{O}(L^2|V|)$
a DAG
augmentation algorithmthat enables the creation of alternative paths in a routing DAG. can even shift or create Steiner points. over 99% nets can be successfully routed without the need of maze routinga new sparse graph maze routing algorithm
creation of alternative paths in a
routing DAG
flow
RSMT
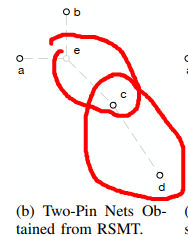
DFS and
Routing DAGwith L pattern注意多了节点g,f,i,h, 现在每条都是直线
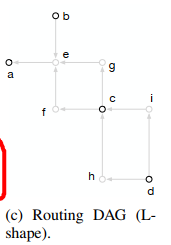
Routing DAGwith other patterns,但是在这里没用做初始布线,初始只用了L-shape。文章也就这里提了一下,后面都和这个无关,得去源码仔细看看。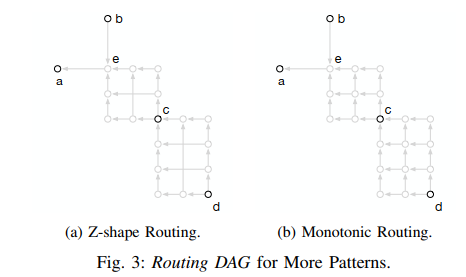
Dynamic Programming-based DAG routing(L-shape + Layer assignment)
没说怎么舍弃的?
DAG-based pattern routing with augmentation
sparse graph maze routing algorithm
model
cost
Dynamic Programming-based
DAG Augmentation for Congestion

create alternative paths
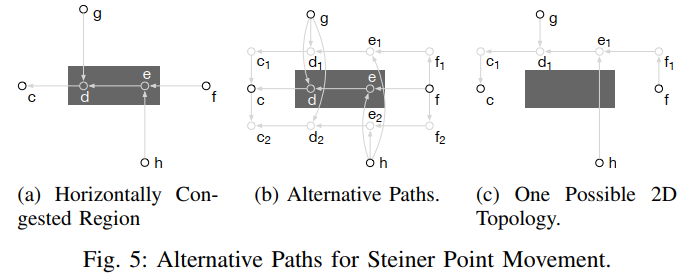
Steiner point movement
具体怎么移动的文章也没说
experiment:
compare with CUGR [12] and SPRoute 2.0 [13]
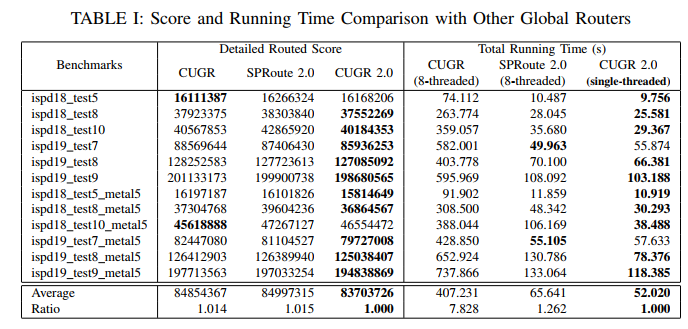
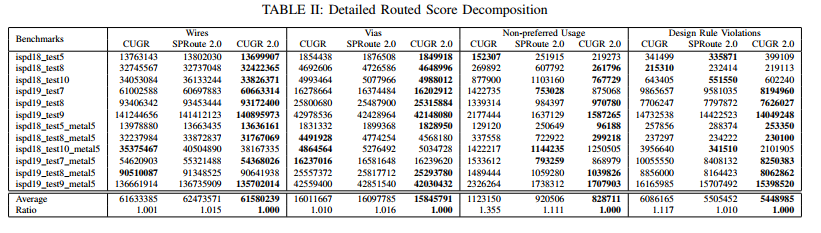
only one thread for run time
Effectiveness of steiner point augmentation

run time compare with GPU-accelerated GR
compare with FastGR [14] and GAMER [15]
GPU的好坏也有关系吧。本实验用的RTX 3090
slightly faster than FastGR for initial routing
around 5.2× as fast as GAMER
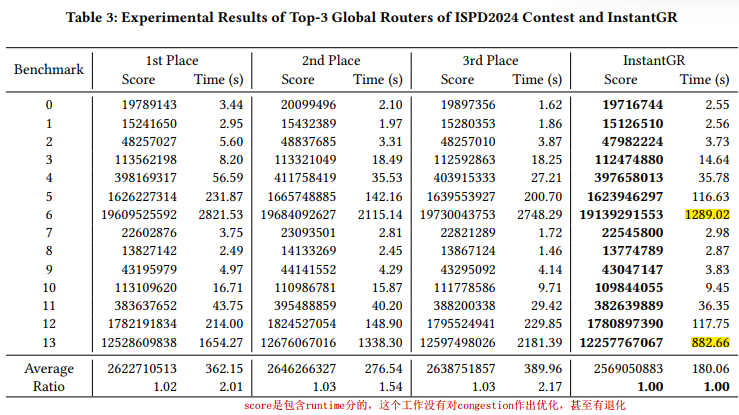
InstantGR-Scalable GPU Parallelization-ICCAD-2024-CUHK #
- open source!
- second place of ISPD25 contest
- GPU Parallelization
- parallel algorithm is mainly based on the DAG-based global routing algorithm in [CUGR2](# CUGR2.0 EDGE- -DAC-2023-). 应该是3D pattern routing DP的部分和maze routing的部分
- parallel while do initial routing and RRR
- 提高了并行度,但是还是有串行的部分
- 也用了FLUTE
- 一定要以net为单元吗?是为了用DP
background
- GPU memory is limited
- This requires memory-efficient solutions that can minimize CPU-GPU communication while maximizing GPU utilization
- large designs have more nets with bigger routing graphs, providing many new parallelization opportunities that are not yet explored
- nets in a batch can be routed in parallel
task:
- parallelism for large-scale
- partitioned design
contribution
- a new method for
net-level batch generation. based on 3D fine-grained overlap checking and explores more parallelism by increasing the number of nets per batch node-levelparallel routing approach. achieves much higher parallelism compared to traditional net-level parallel routing.
flow
- In initial routing, we construct a basic
routing DAGto perform L-shape pattern routing.
key points
specific explanation show in routing2
NET-LEVEL PARALLELISM
simultaneous routing of a
batchof nets that do not “overlap”[2, 3, 14, 19, 20, 22, 26] 19年开始的,cugr2和fastgr都用了
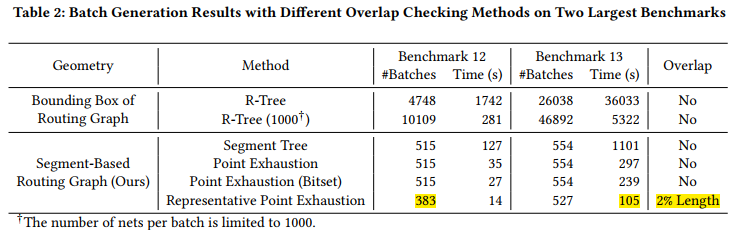
Typical Batch Generation Algorithm
used in [2, 3, 14, 19, 20]
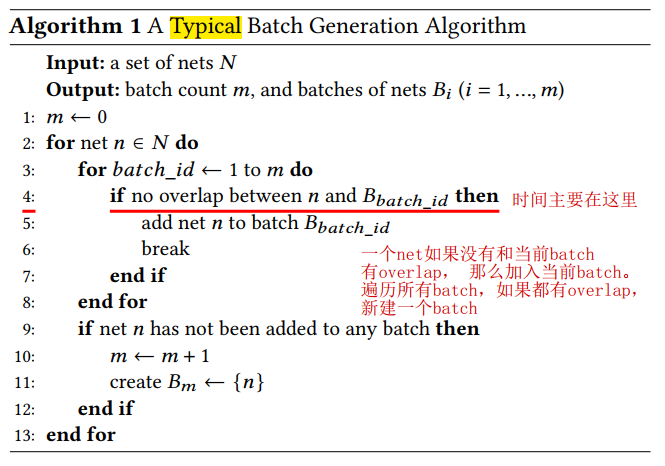
R-trees是实现line 4的常用做法pessimistically approximatessignificantly lowers the degree of parallelismdefine and graph model
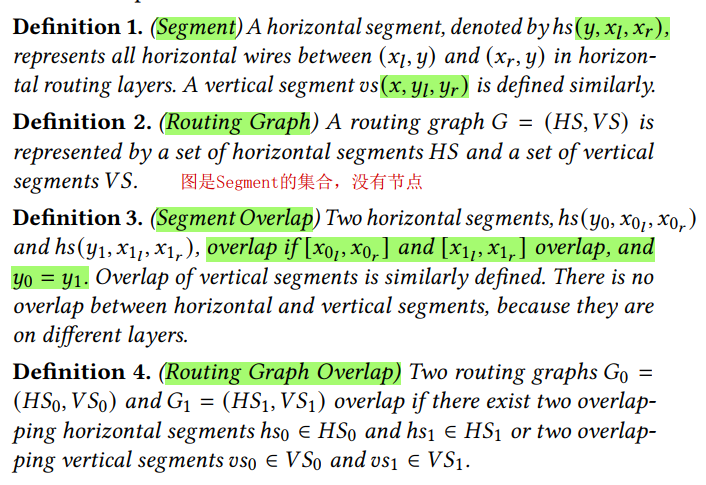
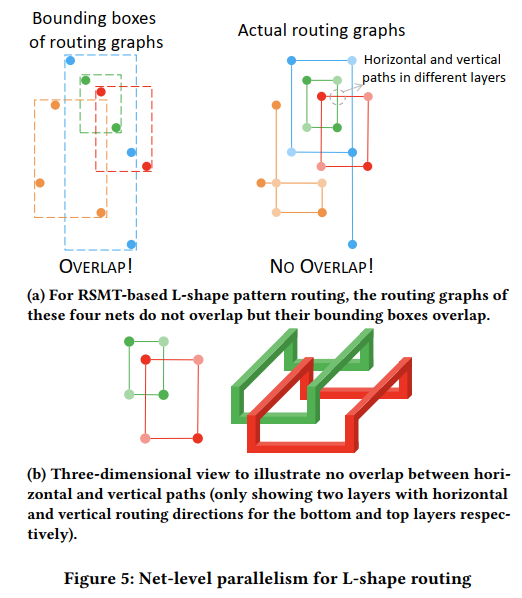
以
segment为单位,同时分开了水平和垂直两个部分,假设全部为L-shape,同时对于不在一条线上的两个节点,有两个LThese four nets will be divided into just
one batchbased on our exact representation of routing graphs for overlap checking, while intofour batchesby the traditional bounding box-based pessimistic approximationvia model:
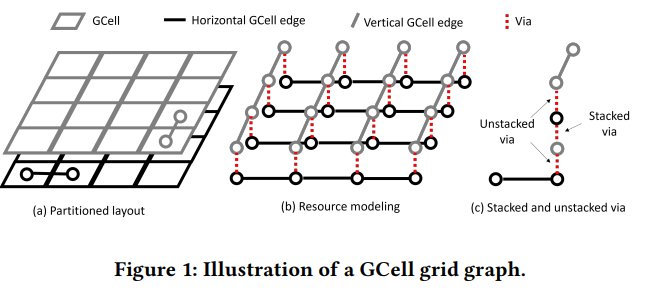
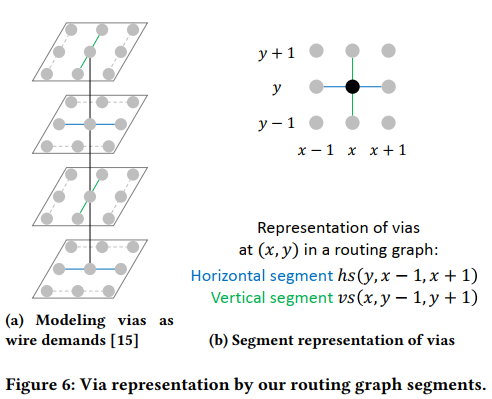
via用一个十字表示
Overlap Checking Algorithms
以水平子图进行展示,垂直同理
以水平segment为单位进行checking
首先判断是不是y坐标相等:group the segments with the same 𝑦
tradictional algorithm:
This is a classical computational geometry problem that can be efficiently solved by
segment trees[1] in 𝑂(log𝑛) time for both operations,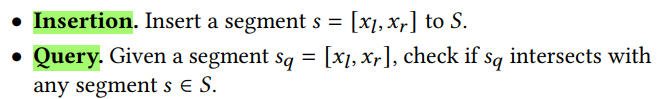
new algorithm motivation:

segments are very short
new algorithm:
Point Exhaustionsimply use a Boolean array to record whether each point in [1, 𝑛] is covered by some segment 𝑠 ∈ 𝑆. We mark every point 𝑥 ∈ [𝑙, 𝑟] when a segment [𝑙, 𝑟] is inserted, and check every point 𝑥 ∈ [𝑙𝑞, 𝑟𝑞] for overlap query of a segment [𝑙𝑞, 𝑟𝑞].
further improve the efficiency of this point exhaustion by using bit arrays
another improvement:
representative point exhaustion- allowing a little bit of overlap.
- it only checks the two end points of a query segment. ??什么意思
- covering most overlap scenarios in practice.
- The only scenario that this algorithm fails to find the overlap of two overlapping segments is when the query segment [𝑙𝑞,𝑟𝑞] contains the overlapping segment [𝑙,𝑟], [𝑙,𝑟] ⊂ [𝑙𝑞,𝑟𝑞]
NODE-LEVEL PARALLELISM
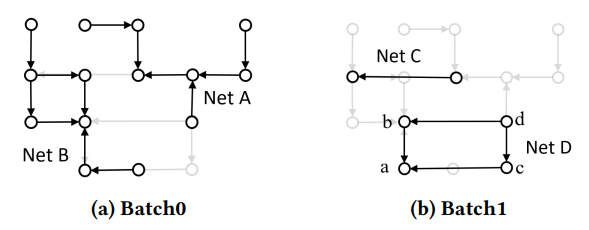
还是以net为单位分到不同的batch?
routing nodes of the same depth in parallel
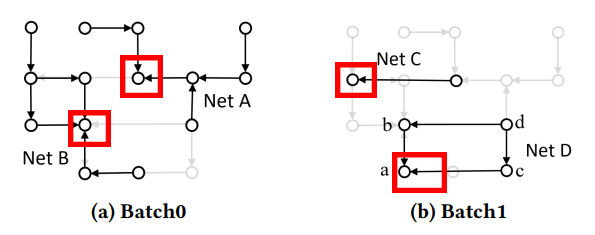
Suppose we have 4 nets, Net A, B, C and D in our grid graph. Since nets with overlap cannot be routed together, Net A and B are distributed to batch 0, as shown in Figure 7a, and nets C and D are distributed to batch 1.
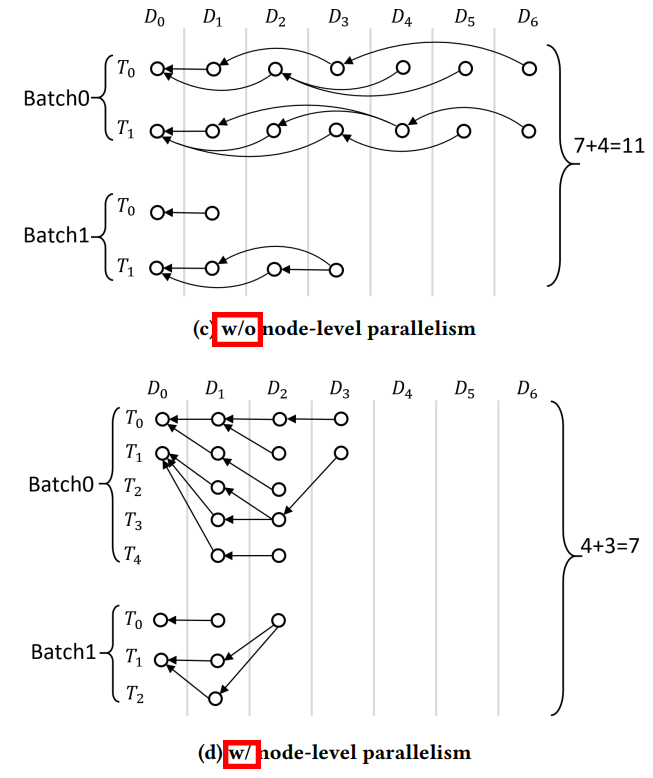
experiment:
4 NVIDIA A800 GPUs and 8 CPU threads.
compare different overlap checking methods
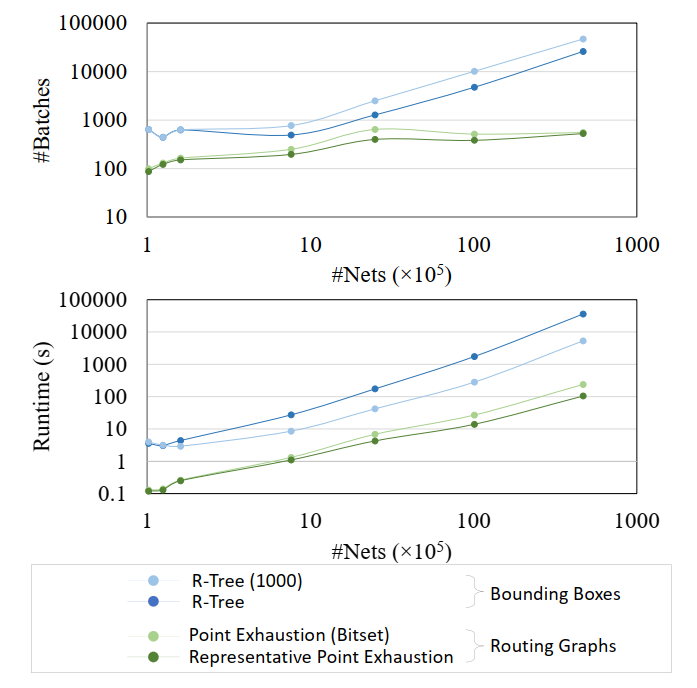
The number of nets per batch is limited to 1000
compare 2 largest benchmark
compare with Top-3 Global Routers of ISPD2024 Contest
Runtime (s) of DAG-Based Augmented Routing with and without Node-Level Parallelism
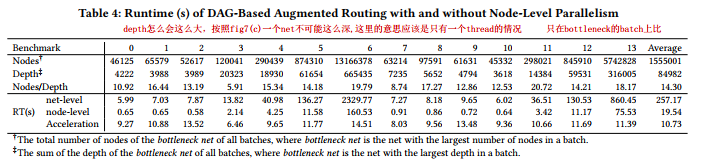
acceleration 那一行好像是加速倍率才对
HeLEM-GR-Heterogeneous+Linearized Exponential Multiplier Method-ICCAD-2024- -PEK #
- first place of ISPD25 contest
- not open source 2025/2/6
- 2D routing algorithm
background
PRNet- -NeurIPS-2022- -SJTU+Noah’s Ark #
- PRNet can generate each route in
one-shotbut cannot guarantee connectivity which requires considerablepost-processingfor failed routes - HubRouter 是两阶段框架,PRNet 是端到端框架。
HubRouter-generative model-NeurIPS-2023-GAN+RL-SJTU #
- open source!
- a chinese interpretation
- a global routing solver that includes a two-phase learning framework
- HubRouter 是两阶段框架,PRNet 是端到端框架。
- 对比 PRNet 生成模型,PRNet 在 CGAN 中使用双向映射将连接约束注入训练目标,将准确率提高了 10%,但在复杂情况下几乎无效。
background
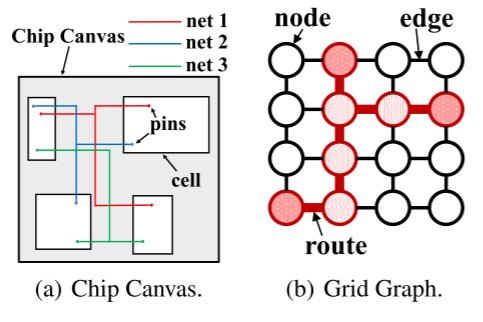
全局布线(Global Routing - GR)是 VLSI 设计中最复杂且最耗时的组合问题之一。GR 目标是总线长最小,同时避免拥塞(Congestion),是个 NP 问题。
传统采用启发式算法,多样性和规模问题对传统算法有了挑战,机器学习(ML)已经用于全局布线,在芯片设计中从逻辑合成到布局
深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning - DRL )和生成式模型(Generative model)已经被用来解决全局布线。问题在于,DRL很受状态空间(State Space)影响,随着网格空间增大,需要花费大量时间生成。However, DRL methods suffer from large state space and often need to spend enormous time on generating routes as the scale of grids increases on the test instance, i.e., the netlist, which is practically intimidating for real-world global routing
相反,生成式模型有一次性生成能力,在计算上更容易处理。
生成式方法在训练时候考虑连通性限制,确保布线满足电路连通性要求。但是问题在于,如果初始生成路径不满足连通性要求时候,后处理阶段会变成一种穷举搜索过程。
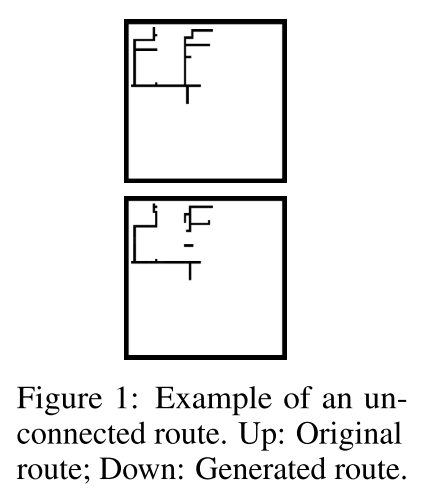
图一这里上图表示原始布线,下图表示算法生成的布线,生成布线没有正确连接所有应该连接的点(pin),对于这样的情况,平均连通率很低,低于20%,意味着超过80%的生成布线需要经过耗时的后处理才能达到要求。显著的缺点。其实就和[CNN-based](# -only CNN-DAC-2020-CNN(VAE)-)这篇一样
contribution:
为了解决上述问题,定义了一个新的概念,叫
hub。将pin - pin问题 –> hub - pin问题 。提出了一种新的两阶段全局布线方法 –> HubRouter
generation phase(生成阶段)
hubs,routes, andstripe masksare together generated under a multi-task framework by generative models可以在多个框架下生成,比如 GAN (Generative Adversarial Nets) , VAE (Variational Auto-Encoder) , DPM (Diffusion Probabilistic Models) 。虽然hub是生成阶段的主要输出,但为了提升生成质量和准确性,发现生成附加信息是非常有用的。比如感知和掩码(
local perceptionandstripe masks),能够去除噪声点。引入多任务学习,布线和掩码一起生成,提高 hub 生成质量pin-hub-connection phase(hub和pin连接阶段)
将连接视为
最小斯坦纳树(RSMT)问题,使用actor-critic模型网络策略。is hub generate correcttly, reconstruction time complexity can be reduced to O(n log n)
SOTA generative global routing models
model:
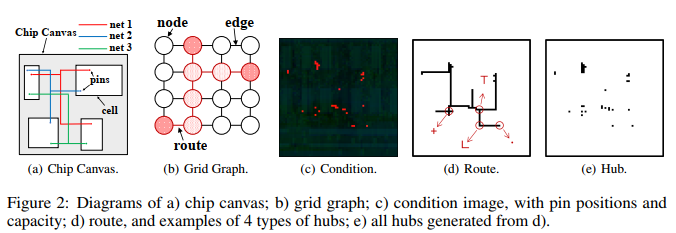
Hub

- (virtual) key point in the route
- transferring the pin-pin connection problem to the hub-pin connection problem
- 斯坦纳点(Rectilinear Steiner Point –> RSP)是搜索全局最小总距离,但是 hub 是来确定路径。RSPs are special cases of hubs
- RSP是Hub的特例,Hub可以随意生成不同形状的路径(不仅是最短的)
- 这里的
c和x分别代表条件图像和输入图像。条件图像可能包括引脚位置、已经提取的中心点以及条带掩模(stripe mask)。条带掩模是用来指示布线区域的一种方式,它可以帮助模型更好地理解哪些区域可以用于布线
flow
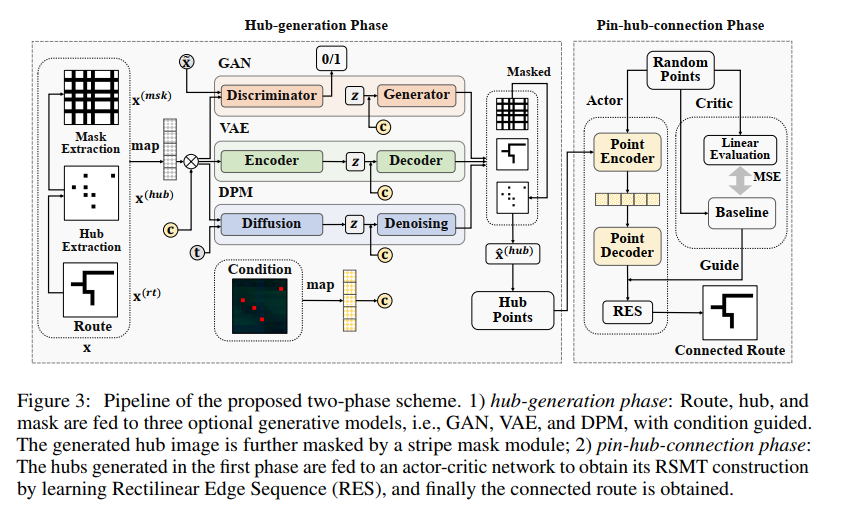
hub生成阶段
Hub 生成可以表示为图像到图像的
multi-task learning framework任务, address the impact of sensitive noise points with stripemask learning附录 B介绍了将 GAN,VAE,EAN 纳入到生成框架在这个阶段,模型旨在逼近条件分布
pθ(x|z, c)使其接近先验分布p(x|c)。给定条件c和从先验分布pz(z)中采样得到的潜在变量z(通常假设为高斯分布),模型会生成一些“中心点(hubs)”. 这里的c和x分别代表条件图像和输入图像。z is a latent variable from a prior distributionThe main objective of hub generation is to minimize the difference between probability distributions
p(x|c)andpθ(x|z, c)a noise hub, especially the outermost one, can largely harm the wirelength of routing. Use
stripe maskto focus on bad cases for hub generation
hub和pin连接阶段
- 模型连接第一阶段生成的中心点,以获得最终的布线路由。这个过程可以被视为构建矩形稳定最小生成树(Rectilinear Steiner Minimum Tree,RSMT)的一部分。为了完成布线,模型遵循了一个基于强化学习(Reinforcement Learning,RL)的算法
REST。 - 在两阶段的过程中,作者还提出了一个
多任务学习框架来提高生成中心点的质量。特别是,提出了一种新颖的条带掩模学习方法,旨在减轻噪声点案例可能造成的负面影响。算法的具体细节在附录 B中给出。
- 模型连接第一阶段生成的中心点,以获得最终的布线路由。这个过程可以被视为构建矩形稳定最小生成树(Rectilinear Steiner Minimum Tree,RSMT)的一部分。为了完成布线,模型遵循了一个基于强化学习(Reinforcement Learning,RL)的算法
detail router #
academic detailed
综述 #
ML4PR #
Towards Machine Learning for Placement and Routing in Chip Design: a Methodological Overview
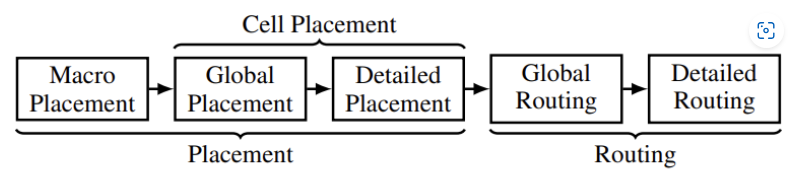
放置和布线是两个不可或缺且具有挑战性的 NP-hard 问题
机器学习凭借其数据驱动的性质显示出了广阔的前景,它可以减少对知识和先验的依赖,并且通过其先进的计算范式具有更大的可扩展性 (例如 GPU 加速的深度网络)
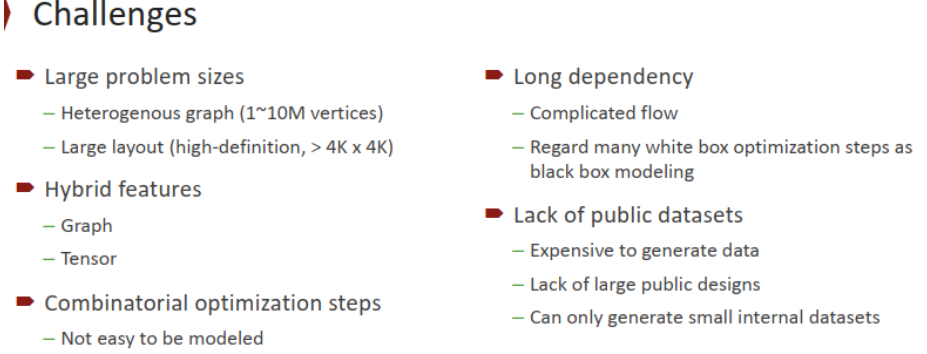
挑战:
placement:
- 在路由完成之前,无法评估诸如可达性之类的放置目标;因此,在优化循环中可能需要花费数小时才能获得反馈,这对于进行数千次查询来说是负担不起的
- 现代的放置器需要在几个小时内处理数万个宏和数百万个标准单元。这种可扩展性的要求仍然超出了现有 ML 方法的能力
routing:
- 在公平的比较下,现有技术很难在效率和求解质量上系统地优于经典布线算法
- 大多数基于学习的技术在具有数千个网络的小型电路上工作得很好,而实际的布线引擎需要在超大型 3D 网格图 ( > 1000 × 1000 × 10 ) (> 1000 × 1000 × 10)(>1000×1000×10) 上有效地处理数百万个网络并产生高质量的解决方案
相关工作
placement
Routing
超大规模集成电路布线算法综述 #
background



布线相关详细看routing2.md, 详细布线、面向可制造性设计的布线算法 还没记录
EDA+GNN #
详细看 A Comprehensive Survey on Electronic Design Automation and Graph Neural Networks
参考 #
- [AI技术带给EDA的机遇和挑战](AI技术带给EDA的机遇和挑战-Yibo Lin.pdf)
- [Towards Machine Learning for Placement and Routing in Chip Design: a Methodological Overview]([ 读论文] Towards Machine Learning for Placement and Routing in Chip Design: a Methodological Overview_toward machine learning….lake-CSDN博客)
- 【阅读】A Comprehensive Survey on Electronic Design Automation and Graph Neural Networks——EDA+GNN综述翻译_ppaml-CSDN博客
bak #
CongestionNet-Congestion Prediction-IFIP-2019-GNN
-placement Congestion prediction-arXiv-2021-GNN
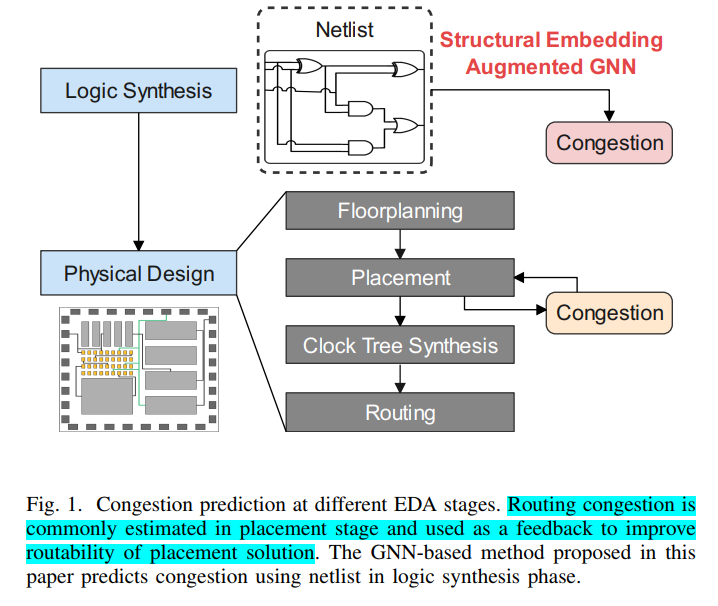
输入:网表
输出:congestion at placement stage
EDA-ML: Graph Representation LearningFramework for Digital IC Design Automation
德雷塞尔大学电气与计算机工程系 Pratik Shrestha和Ioannis Savidis
background
VLSI : traditional methodologies -> ML,Graph representation learning ability to capture complex relationships in graph-structured data
GNN:

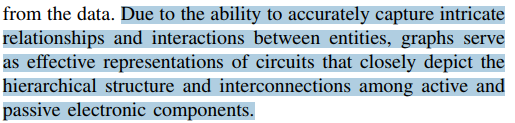
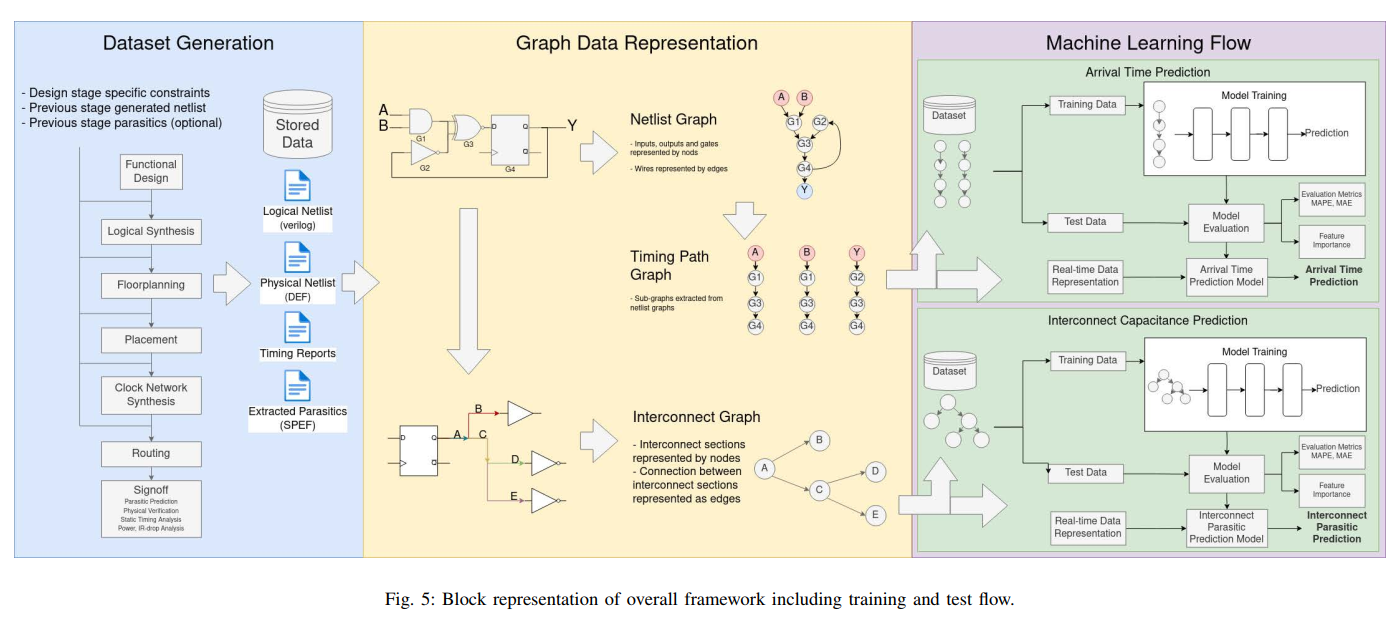
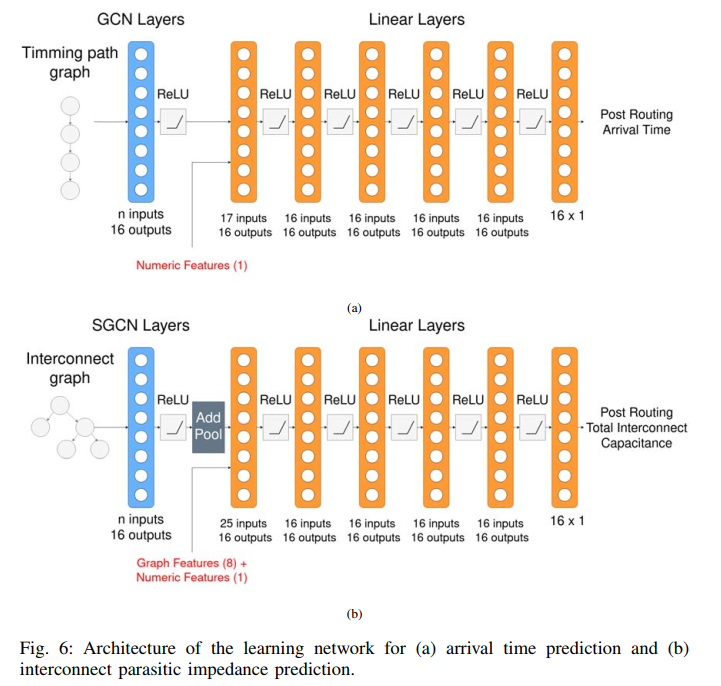
task

flow
data
模型
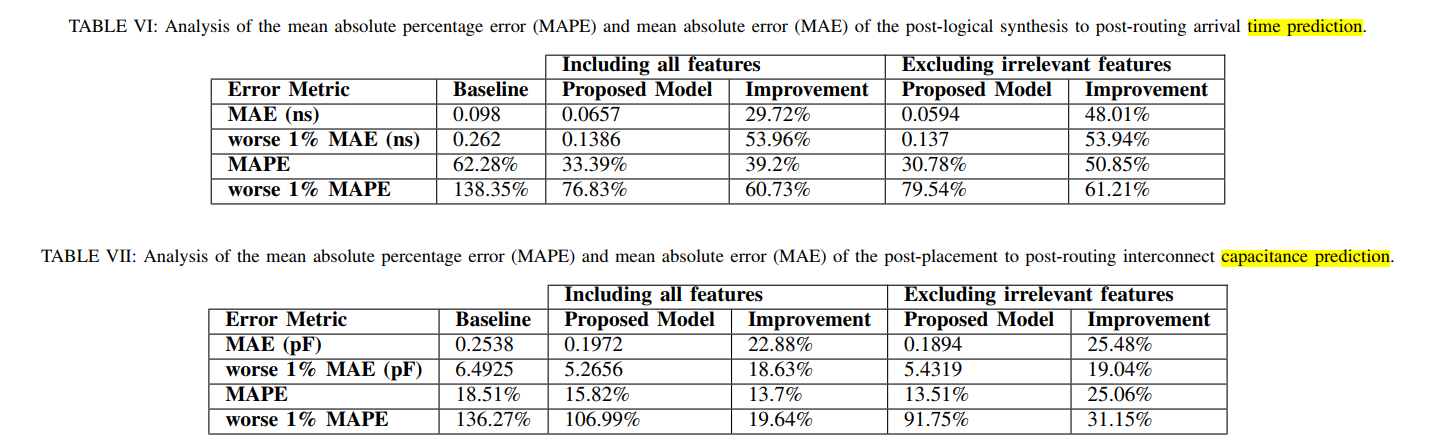
实验
相关数据集 #
only rtl #
Home :: OpenCores #
IWLS 2005 Benchmarks #

openlane-examples: Examples from the Openlane repository #

Global route #
ISPD-2007 #
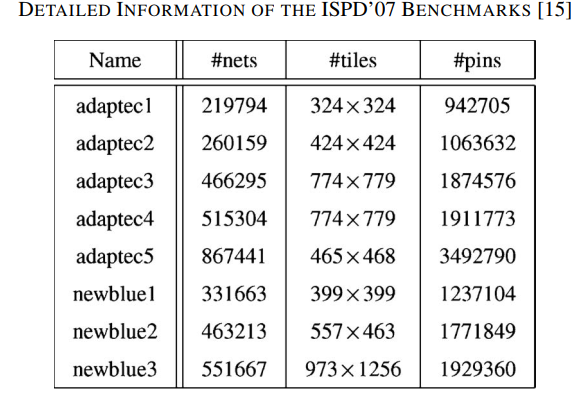
- the first published multilayer global routing benchmarks and the sizes of these benchmarks are large enough as compared to real industry cases
- has a two-layer and a six-layer version.
ISPD-2008 #
ICCAD-2019 #
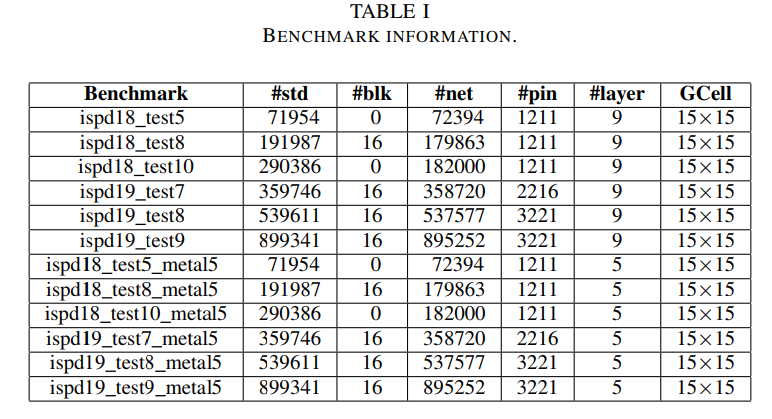
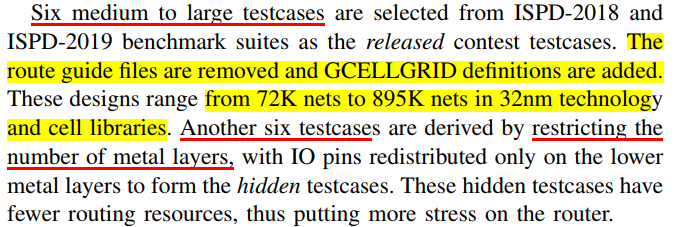

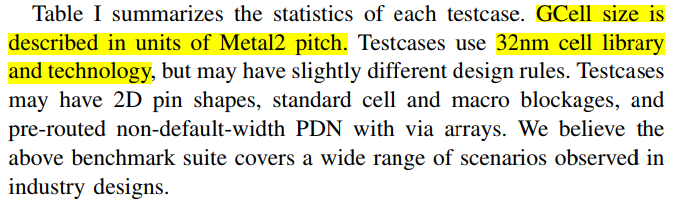
ISPD-2024 #
Dockerfile无法创建镜像了,401,Github也找不到benchmarks
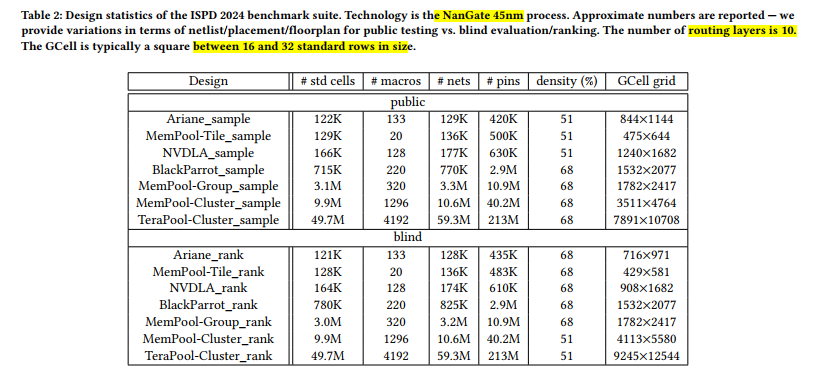
ISPD-2025 #
Detail Route #
ISPD-2018/2019 #
Initial Detailed Routing Contest at ISPD 2018
Initial Detailed Routing Contest at ISPD 2019
一个别人写的parse脚本:Handling-the-ISPD19-benchmark-dataset
https://ispd.cc/contests/19/ispd19eval.tgz:一个结果验证工具
还可以看看被人的结果
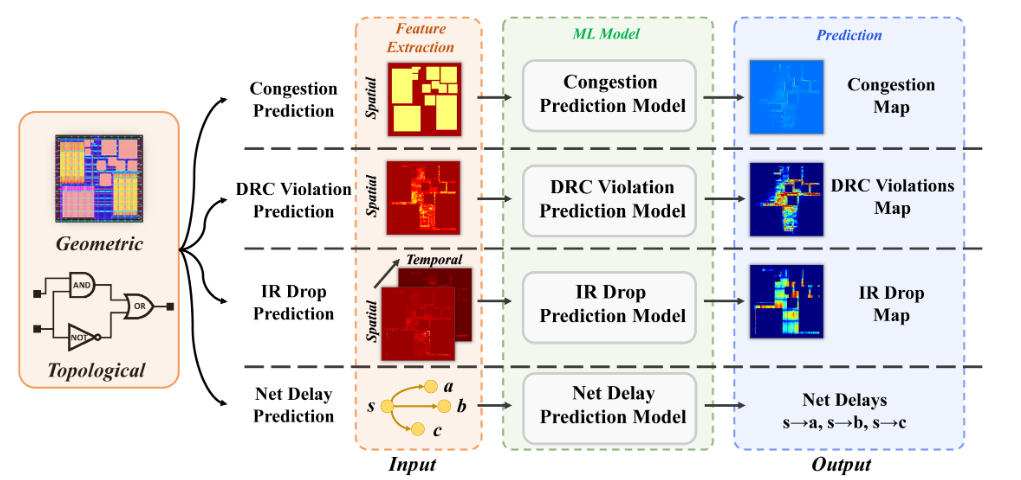
congestion/DRC/IR drop/timing #
背景:
- f.daixianiu.cn/csdn/14209355328255857.html在研究过程中,我们发现AI+EDA的研究常常受限于公开数据集,不像计算机视觉领域有ImageNet这样的大数据集可以很方便地验证算法。针对这一问题,我们近期跟黄如院士、王润声教授等合作,发布了首个致力于芯片设计AI for EDA应用的开源数据集——CircuitNet,包含1万以上的数据样本,涵盖从实际制造工艺PDK下数字设计流程不同阶段中提取到的各类特征。
相关会议/期刊 #
会议 #
DAC:
- 每年举办一次学术论坛和工业贸易展览
- 一般11月截止
- International Conference on Computer-Aided Design
- 由电气电子工程师学会(IEEE)和美国计算机学会(ACM)共同举办的国际计算机辅助设计会议(ICCAD)被公认为EDA领域最重要的会议之一,享有很高的国际学术地位和广泛的影响力。该会议是探索EDA研究领域新挑战、展示前沿创新解决方案和识别新兴技术的重要论坛,涵盖了从器件和电路级到系统级的所有设计与自动化主题、以及后CMOS设计等新型方向。着重于学术研究,论文涉及专门的算法的研究进展。
- 一般4月截止
- Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference
- 欧洲设计自动化和测试会议
- 一般9月截止
- 亚洲、南太平洋设计自动化会议
- 一般7月截止
ISPD:
International Symposium on Physical Design
国际物理设计会议。是专注集成电路物理设计的国际研讨会,主题涵盖从ASIC和FPGA的传统物理设计到新兴半导体技术的物理设计自动化方法。
CCF-C. 9月份左右
每年ISPD会议同步举办国际物理设计竞赛,通常由国际知名芯片企业命题和组织,竞赛历时3个多月,结果在ISPD会议上揭晓。
- CCF-C
- 大湖区超大规模集成电路设计国际会议
- 一般2月截止
- 25年为第35届
VLSI:
- 有个DTCO?
- 一般1月

- 由IEEE和ACM主办,EDA²和CIE EDA委员会联合主办的ISEDA (EDA国际研讨会)是一个致力于VLSI设计自动化的年度顶级论坛。研讨会旨在探索新的挑战,展示前沿技术,并为EDA社区提供预测EDA研究领域未来发展方向的机会。ISEDA涵盖了从器件和电路级到系统级的所有EDA主题,从模拟到数字设计以及制造。会议的形式旨在培养富有成效和新颖
- 二月
- 25年第三届


- NeurIPS
- ICML
期刊 #
- 由美国电器电子工程师学会(IEEE)出版(就是Trans?)
- 由美国计算机学会(ACM)出版的电子系统设计自动化汇刊
- It publishes innovative work documenting significant research and development advances on the specification, design, analysis, simulation, testing, and evaluation of electronic systems, emphasizing a computer science/engineering orientation. Design automation for machine learning/AI and machine learning/AI for design automation are very much welcomed. For topics of interest please see https://dl.acm.org/journal/todaes/about.
参考 #
相关科研实验室 #
清华 #
清华大学是国内较早从事EDA研究的高校,洪先龙教授和边计年教授做物理实现和逻辑综合,两位老先生的学生大部分去了三大EDA公司
北大-无锡EDA研究院 #

北京大学集成电路学院成立了国内唯一聚焦EDA技术的“设计自动化与计算系统系”,打造先进的教学与人才培养体系,并与国内外领先的企业深入合作,部分成果已经成功得到转化应用,相关技术是业内目前唯一的解决方案;近期依托院系新成立了无锡北京大学EDA研究院,加上此前与EDA及设计方向头部企业共建的多个联合实验室,形成了教育、科技和人才三位一体的布局。
研究方向包括布局布线、FPGA设计自动化的可重构算法
林亦波 Yibo Lin:yibolin@pku.edu.cn
Contest@ISPD 2024第一名指导的本科生赵春源提出的高效GPU异构并行布线算法CADathlon@ICCAD 2024第一名指导郭资政(毕设开源项目作者)、麦景。在9小时内,运用自己的编码和分析技巧来解决6道集成电路与系统中电子设计自动化问题CAD Contest@ICCAD第一名指导杜宇凡、郭资政。C赛题《Scalable Logic Gate Sizing Using ML Techniques and GPU Acceleration》DreamPlace,Limbo开源项目作者
一个现象:


复旦 #
集成芯片与系统国家重点实验室
研究方向包括物理实现、参数提取、逻辑综合、可制造性设计等方向
陈建利教授
- 指导蔡志杰、魏民、邹鹏,ISPD 2024 contest 第三名
北航 #

港中文-EDA Center #
CAD Contest@ICCAD 2012第二名获得者

- Jinwei Liu
- 方向:VLSI CAD and deep learning accelerators for edge devices
- chentinghuan@cuhk.edu.cn
CHEN, Tinghuan #
福大 #
福州大学早期EDA研究始于范更华教授和朱文兴教授,当前的研究方向主要是物理实现。福州大学团队曾连续三年在CAD Contest@ICCAD夺冠。
福州大学团队在CAD Contest@ICCAD大赛中提出的6T&6T PPNN单元布局方法已转让给华大九天
林智锋教授
- 指导陈忆鹭、吴昭怡, ISPD 2024 contest 第三名
上海交大 #
东南大学-国家ASIC工程中心 #
研究方向是亚阈值和近阈值相关的时序分析
CAD Contest@ICCAD 2017第一名获奖者福州大学的朱自然(Ziran Zhu)毕业后任教于东南大学ASIC中心
2020年和国微集团成立EDA联合实验室,瞄准EDA共性技术研发
时龙兴:
- 老所长
闫浩:
- yanhao@seu.edu.cn
- 领域:智能EDA,面向先进工艺、高能效电路设计中存在的问题,应用人工智能算法辅助电路设计;先进制程/低电压下的时序分析与优化
华中科技大学 #
西安电子科技大学 #
在国内较早开始从事成品率分析算法的研究,并且一直在宽禁带半导体的器件建模、可靠性分析等领域有深入的研究和突出的成果
在2019年和囯微集团建立EDA研究院之后,开始进入布局布线和原型验证领域
广东工业大学 #
电子设计自动化(EDA)科研团队依托广东工业大学集成电路学院成立。面向人工智能辅助集成电路设计EDA工具开发、应用等国家重大战略与行业重大需求,以人工智能辅助EDA为研究核心,聚焦于数字集成电路设计后端工具、FPGA设计工具优化等领域的前沿基础理论和关键技术研究。团队主要开展“数据驱动机器学习的集成电路智能设计”、“人工智能方法实现集成电路的敏捷设计”、“基于传统的分析和优化技术的集成电路辅助设计”等研究
- 数据驱动机器学习的集成电路智能设计
- 人工智能方法实现集成电路的敏捷设计
- 基于传统的分析和优化技术的集成电路辅助设计

国立清华大学 #
University of California #
相关企业/机构 #
华为诺亚方舟 & 海思 #
Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab AI4EDA
CAD Contest@ICCAD 2018第一名获奖者香港中文大学的陈劲松(Jingsong Chen,2021年博士毕业)毕业后加入华为
EDA国创中心 #
与东南大学 有关联
中心介绍—国家集成电路设计自动化技术创新中心,EDA国创中心【官方网站】


芯行纪 #

AmazeSys #
应用于数字芯片物理设计领域的布局布线工具
包含宏单元布局规划、电源规划、布局、时钟树综合、布线、优化、寄生参数提取以及时序功耗分析等全功能模块,支持先进工艺制程下的超大规模设计,可完成数字芯片从Netlist到GDS的完整设计流程,快速达成性能、功耗、面积优化等设计目标
基于强大的机器学习引擎内核,AmazeSys具备自适应超高质量优化能力。该引擎智能提取设计本身特点进行样本训练,综合性能、功耗、面积和布线拥塞等多项关键指标,快速获取量身定制的最佳优化方案,可有效帮助用户降低调整大量工具设置的时间成本。
AmazeFP #
智能布局规划工具AmazeFP将机器学习技术与布局规划引警结合,在兼顾性能、功耗和面积(PPA)的同时,提供了高度智能的拥塞感知、便捷的数据流分析和宏单元自动整理对齐功能,有效解决当前数字芯片在后端设计阶段的布局规划节点面临的经验值需求高、手工耗时长、数据流结构分析不够深入、设计目标收敛性差等难题,助力用户在后端设计初期快速有效地获取高质量布局规划方案,减少迭代次数,从而节约大规模设计的研发成本,提速产品上市时间。
AmazeFP-ME #
作为一款EDA机器学习的工具,AmazeFP-ME在AmazeFP的基础上,能够快速探索数百倍甚至更多的庞大解空间,无需用户手动调参,同时配备优异且精准的数据、图形分析功能,可为用户提供高效便捷的设计体验
AmazeFP-ME作为AmazeFP的AI配套工具,将机器学习技术引入到AmazeFP的解空间探索中,不仅进一步显著地提升了PPA,还为用户创造全新的自动化使用体验。
AmazeDRCLite #
云 #
华大九天 #
东南大学-华大九天-NiiCEDA联合实验室
PyAether #
Aether就是全定制电路(例如模拟、存储、射频、平板等)设计平台,包括原理图,版图,仿真环境,以及数据版本管理工具和Python接口等。
Python拥有众多针对****数据科学和人工智能的强大的开源库,例如NumPy和Pandas用于数据处理,Matplotlib用于数据可视化,Scikit-Learn提供了大量的预处理方法和机器学习算法,TensorFlow和PyTorch则是深度学习领域的重要工具。这些库大大降低了开发难度,使得Python在AI领域的地位无可替代。所以无论是数据清洗和预处理,还是模型建立,例如决策树,神经网络,贝叶斯优化等,以及模型训练和测试,对模型结果的解读等,都会天然的使用Python。
所以Python的开放性生态、天然的数据挖掘、包括机器学习的人工智能(AI)以及各类算法优化包,友好的web开发,使用户可以在更开放、更强大的生态体系里开展设计。可以用它来构建电路与版图的自动化任务,快速进行数据处理和分析。例如,PyAether可以赋能IC CAD,更好得响应IC 设计和版图各种要求。

import pyAether
class InvLe:
def __init__(self, lib, cell, tech_lib, view="layout", mode="a"):
r"""InvLe init function, receive the specified layout information.
Parameters
----------
lib : str
Library name.
cell : str
Cell name.
tech_lib : str
Attach tech library name.
view : str
View name, the default value is 'layout'.
mode : str
Mode for open design, the default value is 'a'.
"""
pyAether.emyInitDb()
pyAether.emyInitLog()
self.pnt_x = 0
self.pnt_y = 0
self.namespace = pyAether.emyUnixNS()
self.design = self.open_design(lib, cell, view, mode=mode)
self.block = self.design.getTopBlock()
if self.block is None:
self.block = pyAether.emyBlock.create(self.design)
self.uu2dbu = self.block.getDBUPerUU()
oplib = self.design.getLib()
tech_scl = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, tech_lib)
tech = pyAether.emyTech.open(tech_scl)
tech.attach(oplib, tech_scl)
def open_design(self, lib, cell, view, view_type="maskLayout", mode="r"):
r"""This function is used to open design and return an emyDesign object.
Parameters
----------
lib : str
Library name.
cell : str
Cell name.
view : str
View name.
view_type : str
Type of view, the default value is 'layout'.
mode : str
Mode for open design, the default value is 'r'.
Returns
-------
design : emyDesign
An emyDesign object opened by given parameters.
"""
lib_scl = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, lib)
cell_scl = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, cell)
view_scl = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, view)
reserved_view = pyAether.emyReservedViewType(view_type)
view_type = pyAether.emyViewType.get(reserved_view)
design = pyAether.emyDesign.open(lib_scl, cell_scl, view_scl,
view_type, mode)
return design
def create_inst(self, master_lib, master_cell, master_view, inst_name,
point, params, **kwargs):
r"""This function creates an emyScalarInst object on specified block.
Parameters
----------
master_lib : str
Library name of instance.
master_cell : str
Cell name of instance.
master_view : str
View name of instance.
inst_name : str
Text string of instance.
point : tuple
Point to create an emyTransform object, such as (0, 0).
params: emyParamArray
emyParamArray
kwargs
Other keyword arguments,
here specifies view_type, mode, view, status.
"""
view_type = kwargs.get("view_type", "maskLayout")
mode = kwargs.get("mode", "r")
view = kwargs.get("view", pyAether.emcInheritFromTopBlock)
status = kwargs.get("status", pyAether.emcNonePlacementStatus)
master = self.open_design(master_lib, master_cell, master_view,
view_type, mode)
inst_scl_name = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, inst_name)
pnt_x0, pnt_y0 = point
point_1 = pyAether.emyPoint(int(pnt_x0 * self.uu2dbu),
int(pnt_y0 * self.uu2dbu))
trans = pyAether.emyTransform(point_1)
pyAether.emyScalarInst.create(self.block, master, inst_scl_name, trans,
params, view, status)
def create_net(self, net_name, path, **kwargs):
r"""This function creates an emyScalarNet object on specified block.
Parameters
----------
net_name : str
It specifies the net name string.
path : list
It specifies path list.
kwargs
Other keyword arguments,
here specifies sigType, isGlobal, view.
Returns
-------
scl_net : emyScalarNet
An emyScalarNet object created by given parameters.
"""
sig_type = kwargs.get("sigType",
pyAether.emySigType(pyAether.emcSignalSigType))
is_global = kwargs.get("isGlobal", False)
view = kwargs.get(
"view",
pyAether.emyBlockDomainVisibility(pyAether.emcInheritFromTopBlock))
net = pyAether.emyScalarName(self.namespace, net_name)
scl_net = pyAether.emyScalarNet.create(self.block, net, sig_type,
is_global, view)
path.addToNet(scl_net)
return scl_net
def create_path(self, layer, purpose, width, start_point, end_point):
r"""This function creates an emyScalarNet object on specified block.
Parameters
----------
layer : str
It specifies the layer name string.
purpose : str
It specifies the purpose name string.
width : float
Define the width of the path.
start_point : tuple
Path start point, such as (0, 0).
end_point : tuple
Path end point, such as (1, 1).
Returns
-------
path : emyPath
A path object created by given parameters.
"""
(sta_x0, sta_y0), (end_x0, end_y0) = start_point, end_point
sta_pnt = pyAether.emyPoint(
int(self.pnt_x * self.uu2dbu) + int(sta_x0 * self.uu2dbu),
int(self.pnt_y * self.uu2dbu) + int(sta_y0 * self.uu2dbu))
end_pnt = pyAether.emyPoint(
int(self.pnt_x * self.uu2dbu) + int(end_x0 * self.uu2dbu),
int(self.pnt_y * self.uu2dbu) + int(end_y0 * self.uu2dbu))
points = [sta_pnt, end_pnt]
layernum = pyAether.emyGetLayerNumByName(self.design, layer)
purposenum = pyAether.emyGetPurposeNumByName(self.design, purpose)
wid = int(width * self.uu2dbu)
path = pyAether.emyPath.create(self.block, layernum, purposenum, wid,
points)
return path
def create_gr(self, centerLine, templateName, **kwargs):
r"""This function creates an emyScalarNet object on specified block.
Parameters
----------
centerLine : emyPointArrayF
Set the drawing route of the guard ring.
templateName : str
Set the template name of the guard ring.
kwargs
Other keyword arguments,
here specifies type, justify, offset, topLayer, stackMode, maxContPattern,
isBodyMode, bodyWidth, contRow, contSpaceX, contSpaceY, contSizeX, contSizeY,
bIsChamfer, chamferAmount, metalSameBody, stackSameMetal, cornerContact.
Returns
-------
rect_nwgr : emyRect
Build nwGuardRings.
"""
type = kwargs.get("type", "Polygon")
justify = kwargs.get("justify", "Center")
offset = kwargs.get("offset", 0)
topLayer = kwargs.get("topLayer", None)
stackMode = kwargs.get("stackMode", False)
maxContPattern = kwargs.get("maxContPattern", False)
isBodyMode = kwargs.get("isBodyMode", True)
bodyWidth = kwargs.get("bodyWidth", 0.5)
contRow = kwargs.get("contRow", 0)
contSpaceX = kwargs.get("contSpaceX", 0)
contSpaceY = kwargs.get("contSpaceY", 0)
contSizeX = kwargs.get("contSizeX", 0)
contSizeY = kwargs.get("contSizeY", 0)
bIsChamfer = kwargs.get("bIsChamfer", False)
chamferAmount = kwargs.get("chamferAmount ", 0)
metalSameBody = kwargs.get("metalSameBody", False)
stackSameMetal = kwargs.get("stackSameMetal", False)
cornerContact = kwargs.get("cornerContact", True)
pyAether.aeCrtGuardring(self.design,
centerLine,
templateName,
type=type,
justify=justify,
offset=offset,
stackMode=stackMode,
maxContPattern=maxContPattern,
isBodyMode=isBodyMode,
contRow=contRow,
contSpaceX=contSpaceX,
topLayer=topLayer,
contSpaceY=contSpaceY,
contSizeX=contSizeX,
contSizeY=contSizeY,
bIsChamfer=bIsChamfer,
chamferAmount=chamferAmount,
metalSameBody=metalSameBody,
stackSameMetal=stackSameMetal,
cornerContact=cornerContact,
bodyWidth=bodyWidth)
def close(self):
r"""This function save and close the emyDesign object which is opened.
"""
self.design.save()
self.design.close()
def create(self, x_0, y_0):
r"""This function creates an inverter.
"""
self.pnt_x = x_0
self.pnt_y = y_0
# Create scalar instances
params_p18 = pyAether.emyParamArray()
params_p18.append(pyAether.emyParam('Single_Width', '1u'))
self.create_inst("reference_pdk", "p18", "layout", "M0", (0.43, 3.15),
params_p18)
# pyAether.emyArray()
params_n18 = pyAether.emyParamArray()
params_n18.append(pyAether.emyParam('Single_Width', '600n'))
params_n18.append(pyAether.emyParam('SD_Metal_Width', '370n'))
self.create_inst("reference_pdk", "n18", "layout", "M1", (0.29, 1.17),
params_n18)
# Create path
path1 = self.create_path("GT", "drawing", 0.18, (1.0, 3.15),
(1.0, 1.77))
path2 = self.create_path("M1", "drawing", 0.23, (1.36, 3.47),
(1.36, 1.21))
path3 = self.create_path("M1", "drawing", 0.23, (0.64, 1.21),
(0.64, 0.18))
path4 = self.create_path("M1", "drawing", 0.23, (0.64, 4.11),
(0.64, 5.14))
# Create net
self.create_net("Y", path1)
self.create_net("A", path2)
self.create_net("vss", path3)
self.create_net("vdd", path4)
# create GR
self.create_gr([(0.53, 4.89), (1.47, 4.89)], "NWGR", bodyWidth=0.4)
# create PGR
self.create_gr([(0.52, 0.41), (1.48, 0.41)], "PGR", bodyWidth=0.4)
if __name__ == '__main__':
example = InvLe("lib01", "test", "reference_pdk", "layout", mode="w")
example.create(0, 0)
example.close()
概伦电子 #
收购了Entasys

鸿芯微纳 #


华芯巨数 #
浙江


嘉立创 #
PCB
相关竞赛 #
CADathlon@ICCAD #
CADathlon@ICCAD 2024 | ICCAD 2024
- EDA领域的**“奥林匹克运动会”,始于2002年**
- in-person event, all-day programming competition, 9 hours, two-person teams, information about the problems and relevant research papers will be released online one week before the competition.
- 一般在10月份举办
- six problems
- Circuit Design & Analysis
- Physical Design & Design for Manufacturability
- Logic & High-Level Synthesis
- System Design & Analysis
- Functional Verification & Testing
- Future technologies (Bio-EDA, Security, AI, etc.)
Contest@ISPD #
International Symposium on Physical Design (ISPD)
- 于2005年首次举办
- Contest@ISPD作为ISPD研讨会的一部分,是全球三大顶尖国际物理设计学术竞赛之一,由全球研究计算机科学的权威学会ACM(Association for Computing Machinery)所举办
- 每年12月份由业界一流公司(IBM、Intel、Xilinx等)公布学术竞赛题目,3月份提交研发成果和软件系统,由业界公司负责提供测试电路,并测试参赛队伍所提交的软件系统,最后于3月底或4月初在年度ACM ISPD会议上公布竞赛结果。
| 题目 | First Place | |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Blockage-Aware Detailed Routing-Driven Placement Contest | NTUPlacerDR |
CAD Contest@ICCAD #
- 始于 2012年
- 覆盖了EDA前端(front-end)和后端(back-end)
- 由IEEE CEDA、ACM SIGDA和工业界Cadence、Synopsys等共同赞助
- Each year the organizing committee announce three challenging problems in different topic, can participate in one or more problems
Blockage-Aware Detailed Routing-Driven Placement Contest

历年相关赛题 #
| 题目 | Sponsor | |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-C | Scalable Logic Gate Sizing Using ML Techniques and GPU Acceleration | Nvidia |
| 2011 | Routability-driven Placement Contest and Benchmark Suite | |
侠客岛 #
EDA精英挑战赛 #
TAU Contest #
- 数字电路时序分析竞赛(TAU)
- 始于2011年,是由国际计算机协会ACM所举办的专业赛事
- 一般由IBM、Cadence、Synopsys、TMSC等国际顶尖公司参与命题
- 好像到21年就没了。。。
Programming Contest@IWLS #
- 始于2017年
- 是由IEEE/ACM International Workshop on Logic & Synthesis(IWLS)举办
- 由业界一流公司(Synopsys、Xilinx、Google等)公布竞赛题目
- 以逻辑综合(Logic Synthesis)和工具研发为竞赛主题
“全国大学生集成电路创新创业大赛”的华大九天赛道 #
第八届集创赛杯赛题目——华大九天杯 - 全国大学生集成电路创新创业大赛

LLM4HWDesign Contest #
2024年ICCAD新设立LLM for Hardware Design Contest
LLM4HW Design竞赛旨在为硬件代码生成构建大规模、高质量的Verilog代码生成数据集。在基于LLM的硬件代码生成中引发一场类似ImageNet的革命。为了实现这一目标,LLM4HWDesign竞赛鼓励参与者收集数据样本,并开发创新的数据清理和标记技术,以有效提高硬件代码生成数据集的规模和质量,为推进LLM辅助硬件设计工作流程建立关键基础设施。
DAC System Design Contest #
DAC 2012 Routability-Driven Placement Contest and Benchmark Suite